Description
- A turbocharger increases engine power by increasing the pressure in the intake manifold above atmospheric pressure.
- The turbocharger is driven by exhaust gases. The exhaust gases, passing through the turbocharger, accelerate the turbine to a high speed, which is located on the shaft, at the other end of which the compressor is installed. The compressor, rotating in its own casing, compresses the air on its way to the intake manifold.
- boost pressure (intake manifold pressure) limited by a damper that diverts exhaust gases away from the turbine wheel in response to a pressure-sensitive actuator.
- The turbine shaft is lubricated with engine oil supplied through a tube from the main engine oil passage.
Precautionary measures
- A turbocharger operates at extremely high speeds and temperatures, so certain precautions must be taken to avoid premature failure.
- Do not operate the turbocharger with any part or hose removed. Foreign particles falling on the rotating vanes can damage the turbocharger.
- Do not increase the engine speed immediately after starting, especially on a cold engine. Wait at least a few seconds to ensure proper oil circulation.
- Let the engine idle before turning off the engine. If you turn off the engine immediately after closing the throttle, the turbocharger turbine will rotate without lubrication.
- Allow the engine to idle for a few minutes before shutting down after running the engine at high RPM.
- Strictly follow the recommended oil change intervals and oil filter. Use only recommended quality oil to lubricate the engine. The use of low-grade engine oil can lead to the formation of deposits on the turbine shaft and failure of the turbocharger.
Removing
Note. To facilitate loosening of the nuts securing the turbocharger to the exhaust manifold, it is recommended to spray hot nuts immediately before removing the turbocharger.
- Remove the air inlet.
- Loosen the clamp and disconnect the air hose from the turbocharger (pic. 4.41).
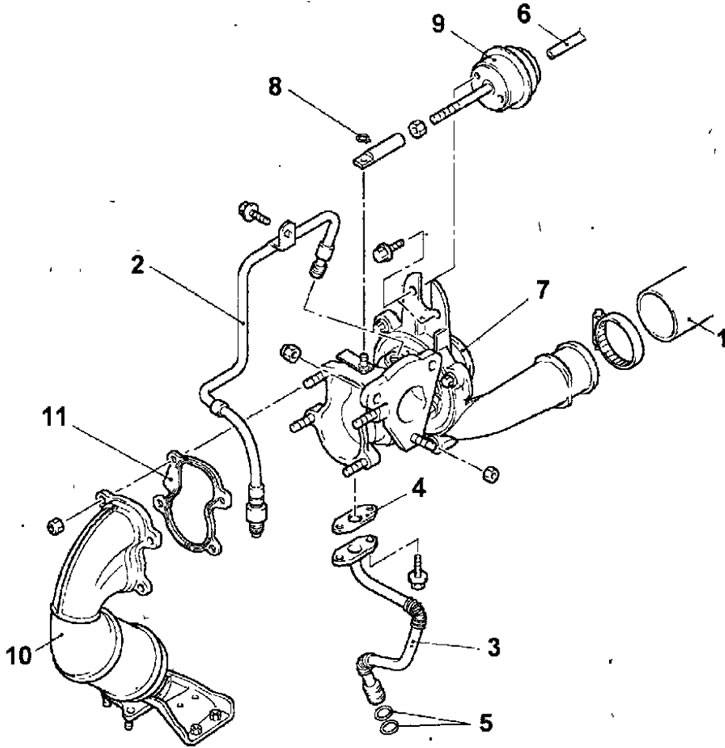
Pic. 4.41. Turbocharger: 1 - air hose; 2 - engine oil supply pipe; 3 - engine oil return pipe; 4 - gasket for the engine oil return pipe; 5 - sealing ring; 6- vacuum hose; 7 - turbocharger; 8 - retaining ring; 9 - damper control drive; 10 - outlet pipe; 11 - gasket
- Turn out a bolt of fastening of an oil supply pipe. Loosen the union nuts and remove the oil supply pipe.
- Remove the two bolts and remove the oil return pipe and gasket. Remove the O-rings from the bottom of the oil return tube.
- Disconnect the vacuum hose from the turbocharger flap actuator solenoid valve.
- Turn away nuts and remove a turbocharger together with an exhaust branch pipe.
- Remove the circlip and disconnect the turbocharger flap actuator solenoid valve stem from the turbocharger.
- Remove the two bolts and remove the turbocharger flap actuator solenoid valve from the turbocharger.
- Turn out bolts and remove a final branch pipe and a lining from a turbocharger
Examination
- Check that the inner surface, the bypass bolt and the mating surface of the oil supply tube are not clogged and clean if necessary.
- If carbon deposits have accumulated in the turbocharger oil passage, clean them and blow out the passage with compressed air. Keep foreign matter out of the turbocharger.
- Check the turbine wheel and turbocharger impeller for cracks or damage.
- Check ease of rotation (by hand) turbine and pump wheels.
- Check the turbocharger for oil leakage.
- Check the oil supply and return pipes for blockages, kinks, or other damage.
Installation
- Installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal, taking into account the following.
- Add fresh engine oil through the intake port in the turbocharger.
- Before starting the engine, disconnect the connector from the pressure regulator to the injection pump.
- Operate the starter for a few seconds until the oil pressure warning light goes out.
- Connect the regulator connector, turn on the preheat and start the engine.
- Let the engine idle and check for oil leaks from the turbocharger oil line fittings.
