- The location of the pipelines of the air conditioning system is shown in Figure 18.35.
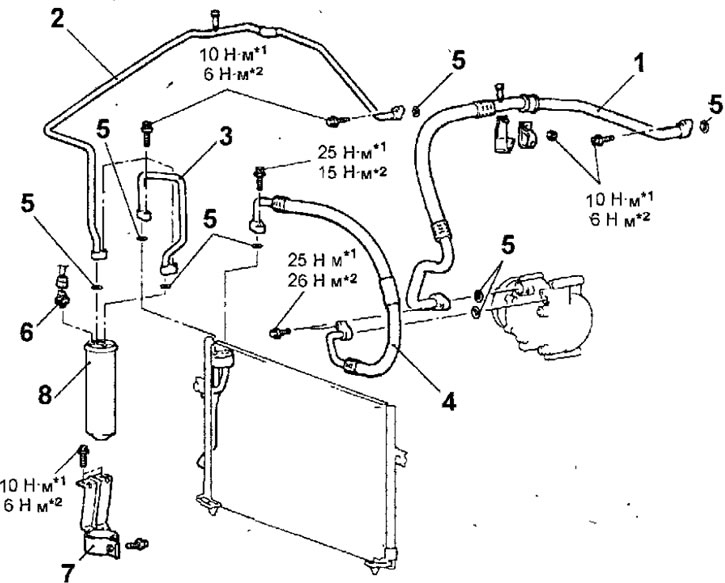
Pic. 18.35. Air conditioning pipes and hoses: 1 — suction hose; 2 - tube B for refrigerant; 3 - tube A for refrigerant; 4 - discharge hose; 5 - sealing ring; 6 - double pressure sensor; 7 - receiver-drier bracket; 8 - receiver-drier
Note. Figure 18.35*1 bolts and nuts with a flange are marked, and*2- bolts and nuts with washers.
- The effective operation and life of an air conditioning system depend on the chemical stability of the elements of the air conditioning system.
- When impurities such as dirt, air or moisture enter the air conditioning system, they change the cooling stability and degrade the properties of the compressor oil. They also affect the pressure and temperature in the system, reduce the efficiency of its functioning and lead to the appearance of internal corrosion and abnormal wear of moving parts.
- To maintain chemical stability in the air conditioning system, do the following:
- after disconnecting the system elements, close the open connections as soon as possible with plugs or adhesive tape, which will prevent dirt, air or oil from entering the system;
- do not keep the air conditioning circuit open for longer than is necessary to complete the job;
- when installing new components of the air conditioning system, remove them from the packaging immediately before installation;
- after opening the air conditioning circuit, evacuate the air and charge the system with refrigerant.
- All O-rings on standard air conditioning connections are non-reusable. Before installing new O-rings, lubricate them with compressor oil.
- When replacing any part of the air conditioning system with a significant refrigerant leak, add oil to the system to keep its volume at the original level.
