The ECM then sends a throttle valve opening angle setpoint signal to the throttle controller. The throttle servo, acting on the throttle, opens it to an angle predetermined by the electronic engine control unit.
The system maintains the idle speed at a certain level by varying the amount of air flowing through the throttle valve in accordance with the condition of the engine at idle and the load on the engine at idle.
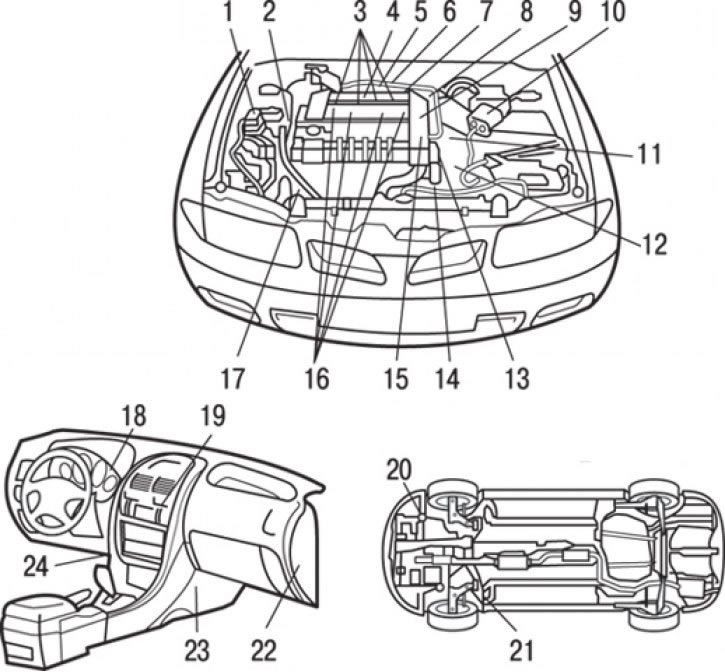
Pic. 8.1. Location of injection system elements (GDI): 1 - relay of the electromagnetic clutch of the air conditioner compressor; 2 - crankshaft position sensor; 3 - nozzles; 4 - knock sensor; 5 – shaper of injector control signals; 6 – relay of the injector control signal generator; 7 - solenoid valve for adsorber purge; 8 - throttle position sensor; 9 - throttle servo; 10 - air flow meter sensor (together with built-in atmospheric sensors (barometric) air pressure and temperature in the intake manifold); 11 - vehicle speed sensor; 12 - starter blocking switch (automatic transmission); 13 - fuel pressure sensor; 14 - coolant temperature sensor; 15 - camshaft position sensor; 16 - ignition coil; 17 - sensor-switch of fluid pressure in the hydraulic system of the power steering; 18 - control lamp GDI ECO; 19 - air conditioner switch; 20 - oil temperature sensor in a manual transmission (manual transmission); 21 - oxygen sensor; 22 - throttle controller; 23 - electronic engine control unit; 24 - accelerator pedal position sensor (1st and 2nd channels)
The electronic engine control unit acts on the throttle servo so that the idle speed remains constant within the specified value. This value is determined depending on the temperature of the coolant and the load from the air conditioner. Location of elements of the direct fuel injection system (GDI) shown in fig. 8.1.
