Principle of operation
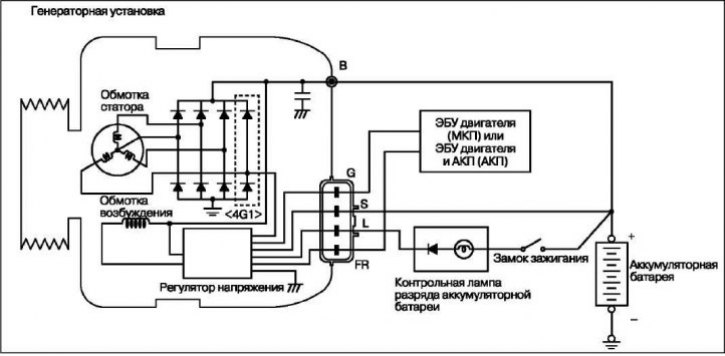
When the excitation coil rotates, through which an electric current is passed, an alternating voltage is induced in the stator windings.
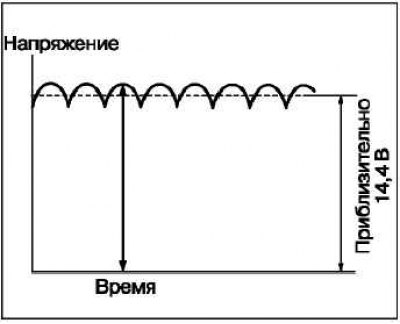
With the help of rectifier diodes, the alternating voltage of the generator is rectified. The rectified voltage graph is shown in the figure.
The average value of the rectified voltage varies slightly depending on the load.
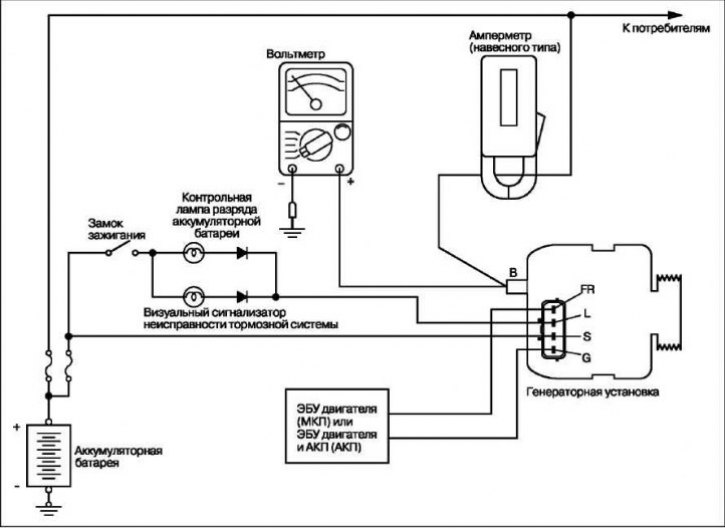
When the ignition is turned on, current from the battery is passed through the excitation winding, providing the initial excitation of the generator. After starting the engine, the excitation of the generator is provided by the voltage induced in the stator windings. The output voltage of the generator increases with an increase in the field winding current and decreases with a decrease in the field winding current. When the battery voltage (output voltage «S» generator) reaches a value of approximately 14.4 V, the field current will stop. As soon as the battery voltage drops below the regulated value, the voltage regulator closes the excitation winding circuit again. Thus, by regulating the current of the field winding, a constant voltage of the on-board network is maintained. If the field winding current remains constant, then with an increase in engine speed, the generator voltage increases.
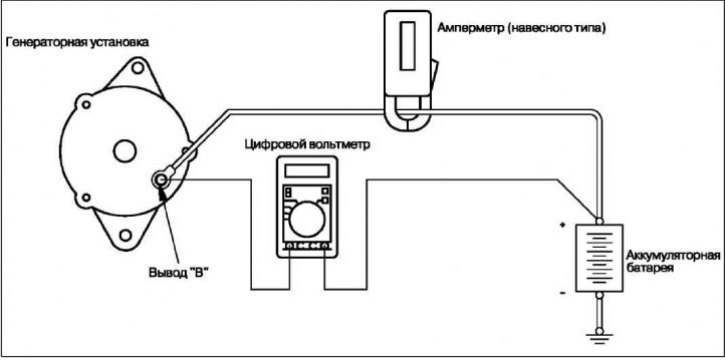
Data for control and regulation
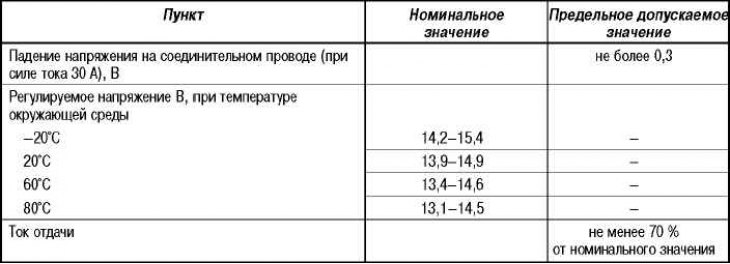
Genset performance