Road test (road test)
Before road testing, make sure that basic checks have been completed, including checking the level and condition of the automatic transmission fluid and adjusting the automatic transmission control cable.
1. Turn the ignition key from position "OFF" (OFF) into position "ON" (ON) and check the operation of the automatic transmission control relay (presence of voltage).
2. When the ignition key is in the "ON" (ON), the engine is not running and the automatic transmission selector is in position "R" do the following:
A) Move the automatic transmission selector to positions "R", "N", "D", "3", "2", "L" Check the operation of the start inhibit switch (correspondence of the position of the selector and the signal of the switch).
b) Check the throttle position sensor:
- When the accelerator pedal is released (535 - 735 mV).
- Pressing half way (smoothly increases from 535 mV).
- When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed (4500 - 5000 mV).
3. Move the automatic transmission selector to position "R" or "N". Set the ignition key to position "START" (START) (engine not running) and make sure the engine start (crankshaft cranking by starter) only possible in the specified selector positions.
4. Drive the vehicle for 15 minutes or more and check the transmission fluid temperature sensor (the temperature of the automatic transmission fluid gradually increases to 70 - 80°C).
5. When the engine is idling and the automatic transmission selector is in position "N" perform the following checks:
A) When the air conditioner switch is in the position "ON" (ON) or "OFF" (OFF) check the function of the double refrigerant pressure switch.

Table. Checking the voltage at the terminals of the electronic control unit for the engine and automatic transmission.
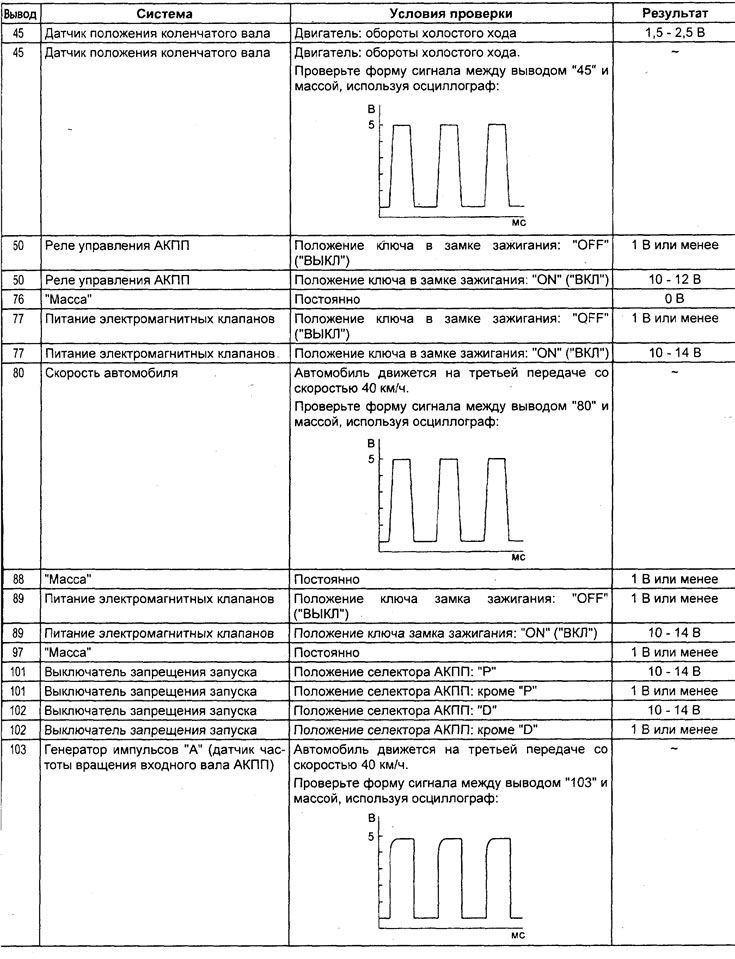
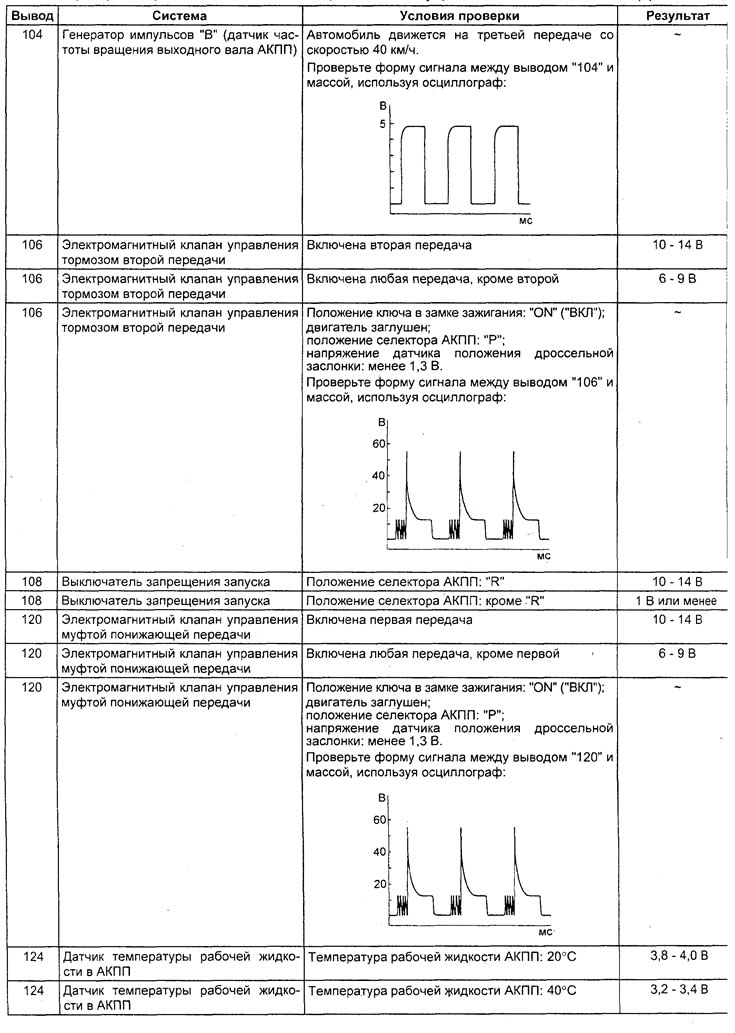
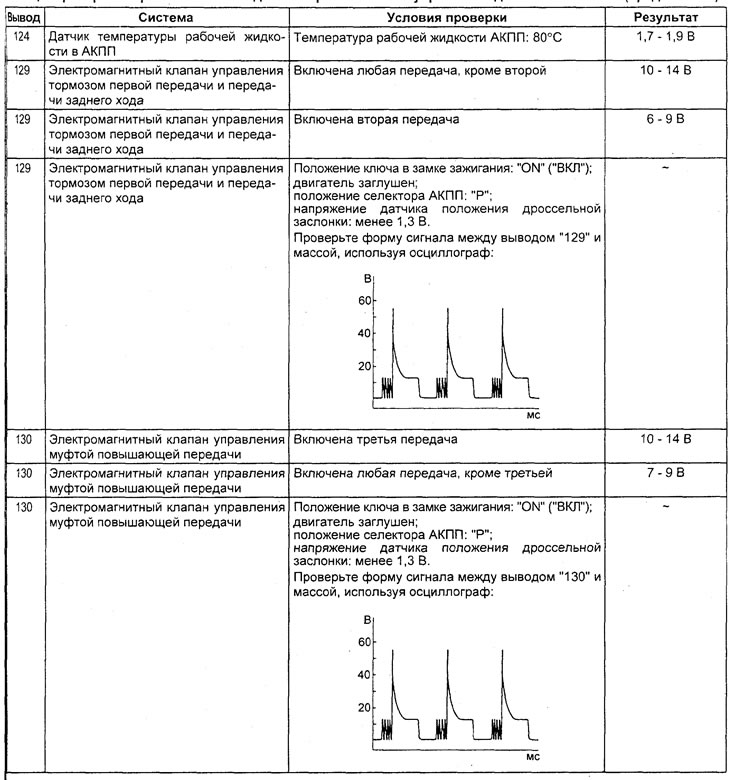
6) Check the crankshaft position sensor and communication with the engine control unit when the accelerator pedal is released (tachometer readings match tester readings) and pressed half way (gradually increases).
V) When translating the automatic transmission selector from the position "N" V "D" and from "N" V "R" make sure that there are no malfunctions at the beginning of the movement (there should be no sudden shocks when shifting gear, the gear engagement time should not exceed 2 seconds).
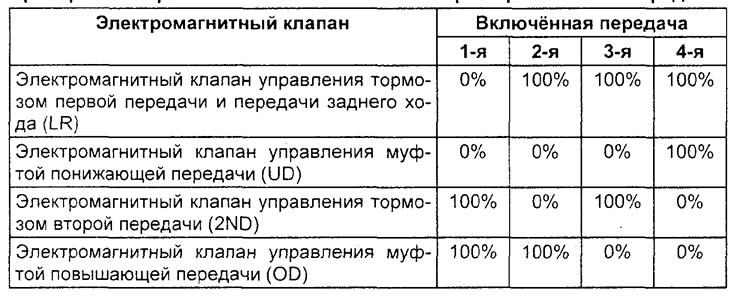
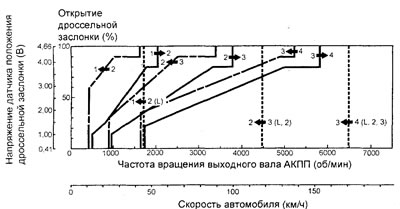
6. Check up correspondence of the included transfers to the specified speed and check up a condition of electromagnetic valves. The test is carried out on a straight horizontal section of the road, the initial position of the selector: "N" (see table "Checking the automatic transmission solenoid valves when shifting gears"). The following conditions must be met for 10 seconds or more.
Checking the solenoid valves of the automatic transmission when shifting gears.
Automatic transmission diagram.
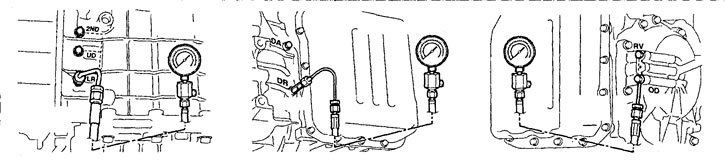
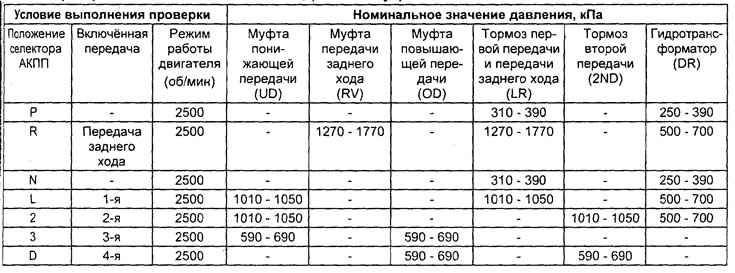
Holes for measuring pressure in the lines of the automatic transmission hydraulic control system. 2ND - second brake, UD - low clutch, LR - first and reverse brake, DR - torque converter output pressure, DA - torque converter input pressure, RV - reverse clutch, 0D - overdrive clutch.
A) The engine is idling (selector in position "L"; the car is retarded).
b) The car is moving at a constant speed of 10 km/h (in 1st gear).
V) A car is moving at a constant speed of 20 km/h (in 2nd gear).
G) A car is moving at a constant speed of 40 km/h (in 3rd gear).
d) A car is moving at a constant speed of 50 km/h (in 4th gear).
7. When specified in clause 6, paragraphs. "A" And "d" conditions, check the vehicle speed sensor (0 km/h and 50 km/h respectively).
8. When referred to in paragraph 6 p.p. "G" conditions, check the serviceability of the automatic transmission input shaft speed sensor and the automatic transmission output shaft speed sensor (nominal value).
Rated value - 1400 - 1700 rpm
9. Carry out the test when the automatic transmission selector is in position "D" and the vehicle is moving on a straight, level road. Make sure there are no faults when shifting gears (for example, the gear does not turn on or does not switch from one gear to another) and no shifting shift points. Use the tester to stop working in INVECS-II mode.
A) Accelerate the vehicle to 4th gear with a throttle position sensor signal voltage of 1.5 V (throttle valve open at 25%).
b) Slowly brake until the vehicle stops.
V) Accelerate the vehicle to 4th gear with throttle position sensor signal voltage of 2.5 V (throttle valve 50% open).
G) Accelerate the car from 1st to 4th gear.
d) When driving in 4th gear at 45 km/h, shift to 3rd gear (move the automatic transmission selector to the position "3").
e) When driving in 3rd gear at 25 km/h, shift to 2nd gear (move the automatic transmission selector to the position "2").
and) When driving in 2nd gear at 15 km/h, shift to 1st gear (move the automatic transmission selector to the position "L").
Note:
- When checking point by point "A", "b" And (V) the values read must correspond to the nominal value of the speed of the output shaft of the automatic transmission (vehicle speed) and there should be no sudden shocks.
- When checking point by point "G", "d", "e" And "and" downshifting should occur immediately after the transfer of the automatic transmission selector.
10. Move the automatic transmission selector from position "N" V "R" and check that reverse gear is engaged. When the vehicle is moving at a speed of 5 km/h on a straight and level road, check that the ratio between the signal values of the transmission speed input speed sensor and the transmission speed output speed sensor is equal to the gear ratio when the reverse gear is engaged.
Fully braked test (stall test)
The purpose of this test is to measure the maximum engine speed with the transmission output shaft fully braked on ranges "D" And "R". By the value of this frequency, it is possible to determine the performance of the overrunning clutch of the torque converter stator, as well as the presence of slip in the friction clutches and the first gear and reverse gear brake.
Attention:
- Do not allow anyone in front of or behind the vehicle during this check.
- The test should be carried out by two technicians: one should observe the wheels outside the car, and the second should carry out the test itself inside the car.
- The duration of each check should not exceed 5 seconds.
1. Measurement of revolutions on a fully braked car:
- A) Check the automatic transmission fluid level and temperature, as well as the engine coolant temperature. The automatic transmission fluid must be warmed up to normal operating temperature (70 - 80°C). The fluid level must be in the range "NOT" probe. The engine coolant must also be warmed up to normal operating temperature (80 - 100°C).
- b) Place chocks under the rear wheels of the vehicle.
- V) Apply the parking brake and depress the brake pedal all the way.
- G) Start the engine.
- d) Move the selector to position "D". Press the accelerator pedal all the way. Take a quick reading of the tachometer and compare it with the nominal values.
Attention:
- During this test, do not hold the accelerator pedal fully depressed for longer than necessary to determine the maximum engine speed, or for more than eight seconds.
- If this test needs to be carried out more than once, then after each test, move the automatic transmission selector to the position "N" and let the engine run at 1000 rpm to cool the fluid in the automatic transmission between checks.
Nominal value of the engine speed when the vehicle is fully braked (selector in position "D") — 2200 - 2700 rpm
e) Repeat the test with the selector position in the range "R".
Nominal value of the engine speed when the vehicle is fully braked (selector in position "D") — 2200 - 2700 rpm
2. Analysis of the test results on a fully braked vehicle.
A) If the engine speed is greater than the nominal value when the selector is in the position "D" or "R", the reason could be:
- torque converter slip;
- low pressure in the main line;
- slippage of the brake of the first gear and reverse gear.
b) If the engine speed is greater than the nominal value when the selector is in the position "D", the reason could be:
- underdrive clutch slip.
V) If the engine speed is less than the nominal value when the selector is in the position "R", the reason could be:
- reverse clutch slippage.
G) If the engine speed is less than the nominal value when the selector is in the position "D" or "R", the reason could be:
- torque converter malfunction;
- malfunction of the electronic engine control unit.
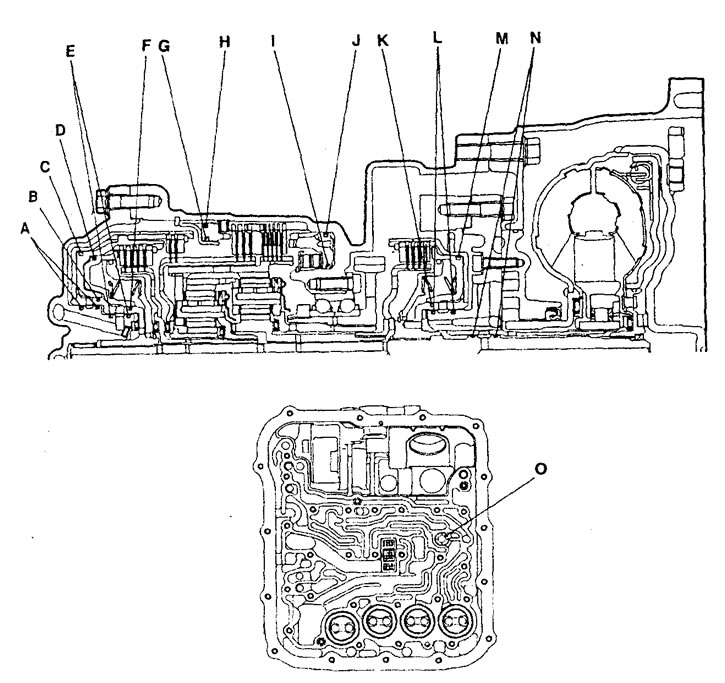
Location of automatic transmission seals.
Checking the pressure in the automatic transmission control hydraulic system (hydraulic test)
Note: checking the pressure in the automatic transmission control hydraulic system is the main one for determining the causes of automatic transmission malfunction. Perform basic checks and adjustments before carrying out (check the level of the working fluid in the variator and its condition, etc.). Checking the pressure in the hydraulic system should be carried out at normal temperature of the working fluid of the variator (70 - 80 °C).
1. Checking the pressure in the lines.
A) Warm up the automatic transmission fluid to operating temperature (70 - 80°C).
b) Place chocks under the rear wheels of the vehicle.
V) Apply the parking brake and depress the brake pedal all the way.
G) Start the engine.
d) Connect the adapter to the appropriate hole, connect the pipes and pressure gauge.
Note: when checking the pressure, use a pressure gauge with a measurement limit of 3000 kPa.
e) Verify that the data obtained corresponds to the nominal values (see table "Checking the nominal pressures in the automatic transmission control hydraulic system").
Table. Checking the nominal pressures in the automatic transmission control hydraulic system.
2. Analysis of the results of checking the pressure in the hydraulic control system of the variator.
A) High pressure in all lines can be caused by:
- pressure regulator failure.
b) Low pressure in all lines can be caused by:
- malfunction of the working fluid pump;
- malfunction of the working fluid filter;
- malfunction of the working fluid cooler;
- malfunction of the solenoid valve;
- malfunction of sealing rings;
- improper installation of each of the solenoid valves.
- improper installation of the solenoid valve block.
V) Incorrect pressure only on the range "R" (reverse) can be caused:
- switching valve malfunction,
- pressure regulator failure.
G) Inappropriate pressure only in 3rd or 4th gear can be caused by:
- pressure regulator failure.
d) Incorrect pressure in the underdrive clutch line only (UD) can be caused:
- gland defect "TO", "L" or "M",
- a malfunction of the solenoid valve for controlling the underdrive clutch,
- malfunction of the pressure control valve in the line of the downshift clutch, malfunction of the ball valve,
- line clogging;
- improper installation of the solenoid valve block.
e) Incorrect pressure in reverse clutch line only (RV) can be caused:
- gland defect "A", "IN" or "WITH",
- ball valve failure
- line clogging;
- improper installation of the solenoid valve block.
and) Incorrect pressure in the overdrive clutch line only (OD) can be caused:
- gland defect "D", "E" or "F"
- a malfunction of the solenoid valve for controlling the overdrive clutch,
- malfunction of the pressure control valve in the overdrive clutch line,
- ball valve failure
- line clogging;
- improper installation of the solenoid valve block.
h) Inappropriate pressure; only in the brake line of the first gear and reverse gear (LR) can be caused:
- gland defect "1" or "J",
- a malfunction of the solenoid valve for controlling the brake of the first gear and reverse gear,
- malfunction of the pressure control valve in the brake line of the first gear and reverse gear,
- switching valve malfunction,
- ball valve failure
- valve malfunction "A" emergency operation,
- line clogging;
- improper installation of the solenoid valve block.
And) Incorrect pressure in the 2nd gear brake line only (2ND) may be caused by:
- gland defect "G", "H" or "O",
- a malfunction of the solenoid valve for controlling the brake of the second gear,
- malfunction of the pressure control valve in the second gear brake line,
- valve malfunction "IN" emergency operation,
- line clogging;
- improper installation of the solenoid valve block.
To) Incorrect pressure only in the torque converter feed line (DR) can be caused:
- malfunction of the automatic transmission fluid cooler,
- seal failure "N",
- a malfunction of the pressure control valve in the torque converter clutch line,
- line clogging;
- improper installation of the solenoid valve block.
l) Incorrect pressure only in the torque converter feed line (DR) can be caused:
- improper adjustment of the automatic transmission control cable;
- malfunction of the solenoid valve for manual range selection;
- improper installation of the solenoid valve block.
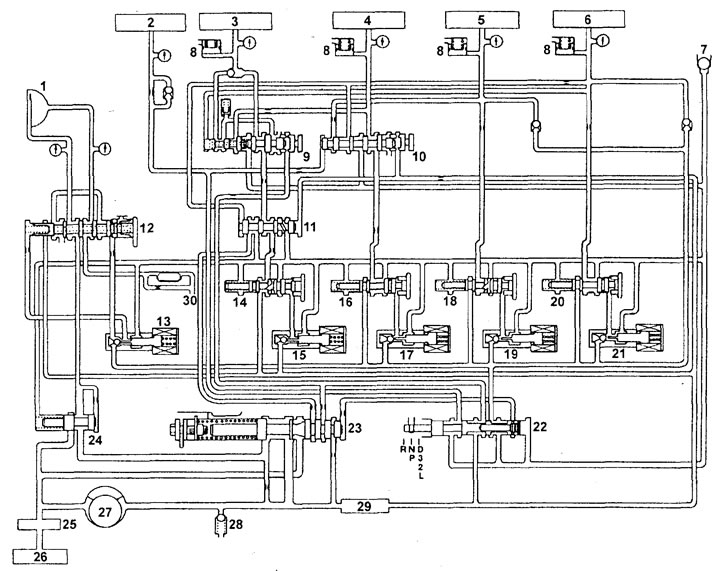
Scheme of the hydraulic part of the automatic transmission control system. 1 - torque converter lock-up clutch, 2 - reverse clutch, 3 - first and reverse brake, 4 - second brake, 5 - underdrive clutch, 6 - overdrive clutch, 7 - ball valve, 8 - hydraulic accumulator, 9 - valve "A" emergency operation, 10 - valve "IN" emergency operation, 11 - switching valve, 12 - torque converter clutch control valve, 13 - torque converter clutch control solenoid valve, 14 - pressure control valve in the first gear and reverse clutch line, 15 - first gear brake control solenoid valve and reverse gear, 16 - pressure control valve in the second gear brake line, 17 - solenoid valve for controlling the second gear brake, 18 - pressure control valve in the downshift clutch line, 19 - solenoid valve for controlling the downshift clutch, 20 - pressure control valve in overdrive clutch lines, 21 - overdrive clutch control solenoid valve, 22 - manual range valve, 23 - pressure regulator, 24 - torque converter pressure control valve, 25 - oil filter, 26 - oil sump, 27 - CVT fluid pump, 28 - safety valve, 29 - mesh filter, 30 - lubrication system line.
Main line pressure regulation
1. Drain the automatic transmission fluid and remove the control solenoid valve cover.
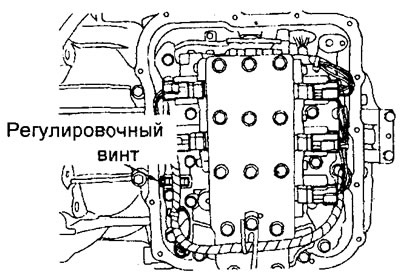
2. Turn the pressure regulator adjusting screw and adjust the pressure in the underdrive clutch line (UD) so that it corresponds to the nominal value. When turning the adjusting screw of the pressure regulator clockwise, the pressure in the line decreases, and when turned counterclockwise, it increases.
Rated value - 1010 - 1050 kPa
Attention: when the adjusting screw is turned 1 turn, the pressure of the working fluid in the automatic transmission hydraulic system changes by 35 kPa.
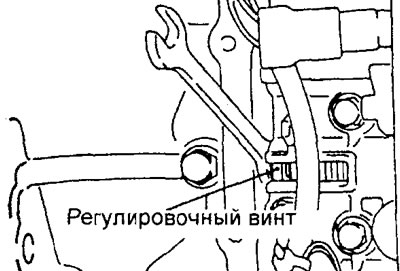
3. Replace the control solenoid valve block cover.
4. Fill in the working fluid in the automatic transmission.
5. Check the pressure in the automatic transmission control hydraulic system. Repeat pressure adjustment if necessary.
