Removal and disassembly
Removal of parts is carried out in the order of the numbers indicated in the figure "Removing the piston and connecting rod ".
Note: the operation to remove the piston pin is given in subsection "Repair".
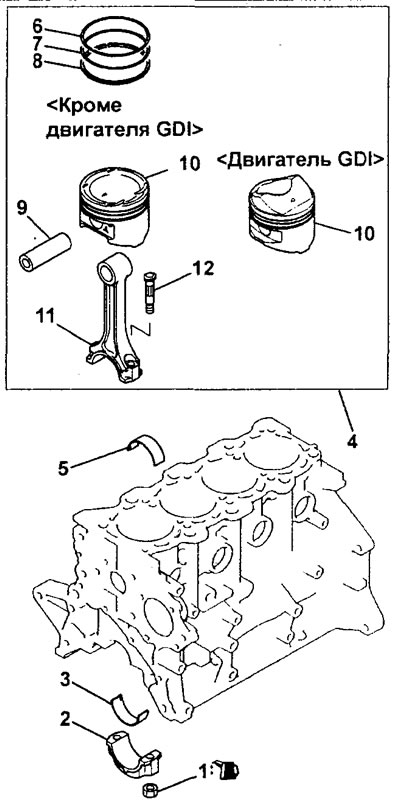
Removing the piston and connecting rod.1 - nut, 2 - lower connecting rod cap, 3 - lower connecting rod bearing, 4 - piston, connecting rod assembly, 5 - upper connecting rod bearing, 6 - compression ring No. 1, 7 - compression ring No. 2, 8 - oil scraper ring, 9 - piston pin, 10 - piston, 11 - connecting rod, 12 - bolt.
When removing parts, pay attention to the operation to remove the connecting rod cap.
A) Loosen the nut, remove the connecting rod cap and remove the piston and connecting rod from the cylinder.
Attention: be careful when removing the piston with connecting rod assembly, do not hit the connecting rod on the cylinder surface and the crankshaft journal.
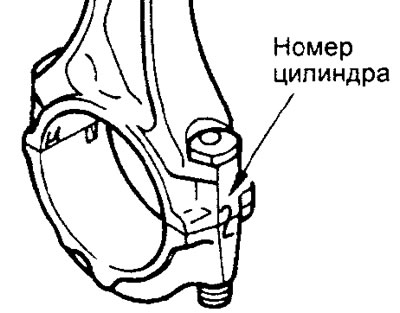
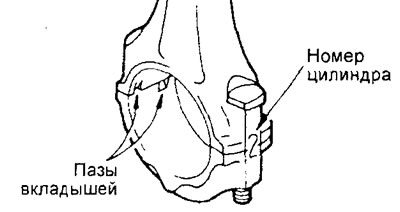
b) Mark the cylinder number on the side of the connecting rod for ease of reassembly.
V) Lay out the removed parts (connecting rods, pistons, liners, etc.) in order of their corresponding cylinder numbers.
Examination
Piston and piston pin
Attention: The piston and piston pin must be replaced as a set.
1. Replace the piston if there are scratches or scuffs on its surfaces (especially on hard surfaces). Replace piston if cracked.
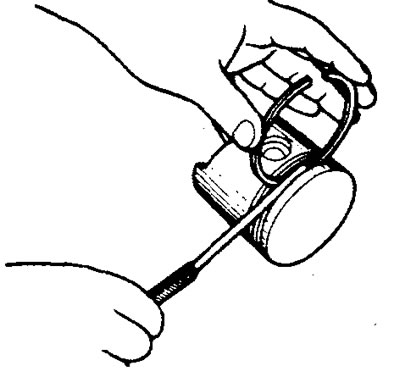
2. Try to insert the piston pin into the piston bore with thumb force. There should be resistance to this. Replace the pin if it slides easily into the hole or if there is significant play.
Piston rings
Attention: if the piston is replaced with a new one, the piston rings must also be replaced with new ones.
1. Check piston rings for damage, kinks or significant wear.
2. Measure the clearance between the piston ring and the piston groove. If the gap exceeds the allowable value, then replace the ring, or the piston, or both.
Note:
- Remove carbon deposits from all piston grooves before taking measurements.
- Measurement of the gap between the ring and the piston groove, perform around the entire circumference of the ring
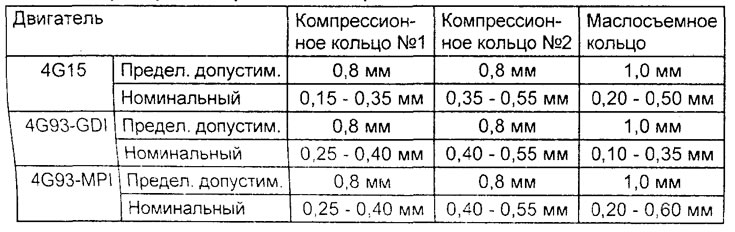
Gap between compression ring and groove for it:
Rated value:
- Ring No. 1 - 0.03 - 0.07
- Ring No. 2 - 0.02-0.06
- Maximum allowable - 0.1 mm
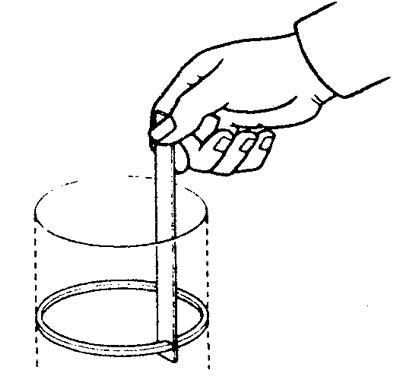
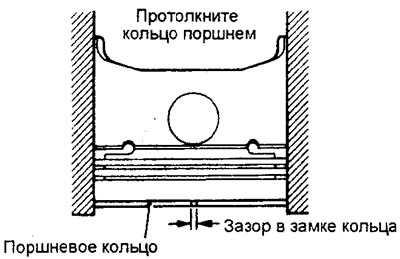
3. Install the piston ring in the cylinder bore. Move the ring with the piston as shown in the figure, this will allow the ring to stand at right angles to the generatrix of the cylinder wall. Then measure the gap in the lock of the ring, and if the gap is greater than the allowable value (see table), then replace the ring.
Connecting rod bearing shells
1. Checking the condition of the connecting rod bearing shells.
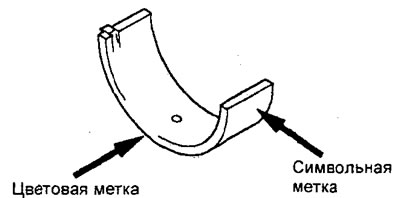
A) Visually inspect the surface condition of the connecting rod bearing shell (uneven contact, stripes, scratches, scuffs, etc.). If defects are evident, replace the connecting rod bearing shells.
b) If defects (stripes and streaks) significant, then check the corresponding crankshaft journals. If there are defects on the crankshaft journals, replace the crankshaft.
2. Checking the clearance in the connecting rod bearing.
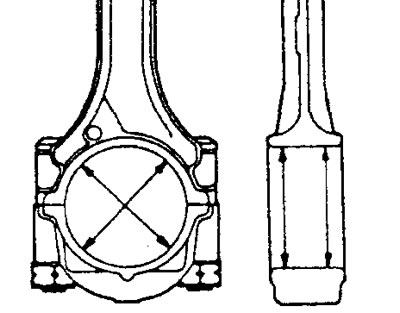
A) Measure the inner diameter of the connecting rod bearing and the outer diameter of the connecting rod journal of the crankshaft, then determine the clearance in the connecting rod bearing.
Note: A plastic gauge can be used to measure the clearance in the connecting rod bearing.
Nominal outer diameter of the connecting rod journal of the crankshaft:
- 4G15 engine - 42.0mm
- 4G93 engine - 45.0 mm
Connecting rod bearing clearance:
- Nominal - 0.02 - 0.05 mm
- Maximum allowable - 0.10 mm
Table. Checking the clearance in the piston ring lock.
b) If the oil clearance exceeds the maximum allowable value, then replace, if necessary, the connecting rod bearing shells, or the crankshaft, or both.
3. Measuring the clearance in the connecting rod bearing using a plastic gauge.
A) Clean the crankshaft journals and liners from oil and dirt,
b) Cut a piece of plastic gauge as long as the bushing width and place it parallel to the axis of the shaft journal away from the oil passage hole.
V) Install the bearing and connecting rod cap and tighten the nuts.
Attention:
.
- Follow the procedure for tightening the connecting rod cap nuts in accordance with the special operation in subsection "Assembly and installation".
- Do not rotate the crankshaft during the clearance measurement procedure
G) Remove the connecting rod cap and use the scale printed on the package of gauges to determine the clearance in the bearing.
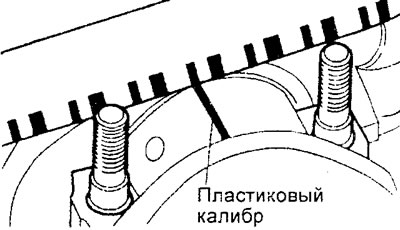
If the gauge on the shaft neck.
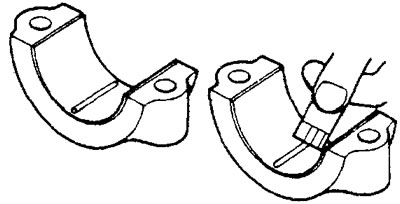
If the gauge on the shaft bearing cap.
Connecting rod
1. Install the piston pin in the connecting rod, if it was removed.
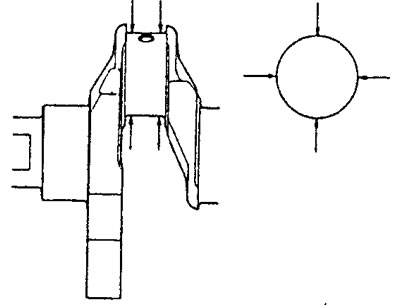
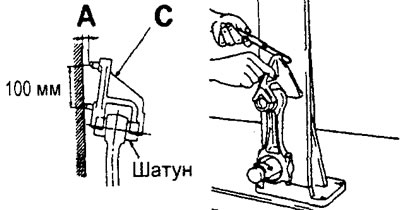
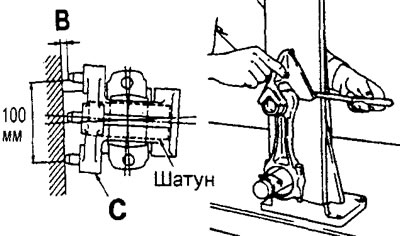
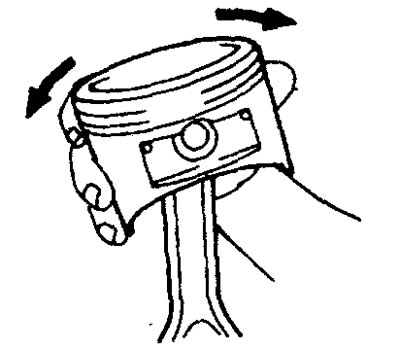
2. Using a special connecting rod tester "WITH" and a flat feeler gauge, check for bending and twisting of the connecting rod as shown in the illustration.
Limit value (per 100 mm length):
- bend - 0.05 mm
- twist - 0.10 mm
Attention:
- Install the connecting rod in a special tool "WITH" together with the upper and lower connecting rod bearing shells installed.
- Tighten the connecting rod cap bolts according to the special procedure in subsection "Assembly and installation".
3. If the bending or twisting of the connecting rod has exceeded the maximum allowable value according to the specifications, then replace the connecting rod assembly with the cover.
Repair
Piston pin selection
Attention:
- If the engine cylinders have not been machined, then if it is necessary to replace the piston, select it so that the mark on its upper part corresponds to the size mark of the cylinder on the cylinder block according to the table below.
- The piston size mark is located at the top of the piston.
| Dimensional mark of the cylinder | Dimensional mark of the piston |
| A | A |
| IN | no label |
| WITH | WITH |
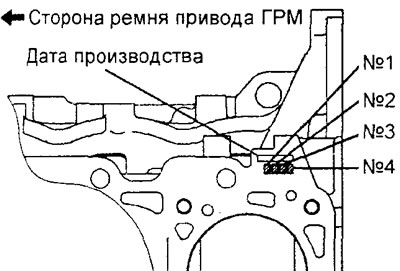
The rear of the cylinder block of the 4G15 engine (mounting surface for cylinder head).
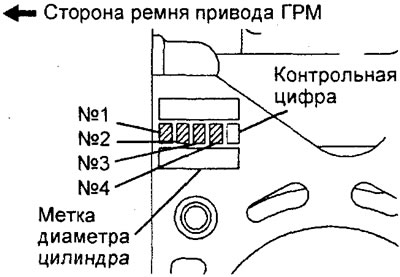
The rear of the cylinder block of the 4G93 engine (mounting surface for cylinder head).
Piston pin replacement
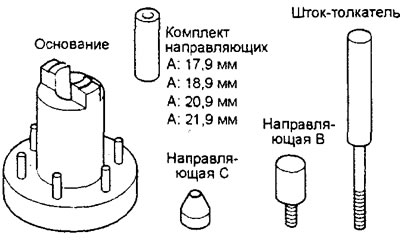
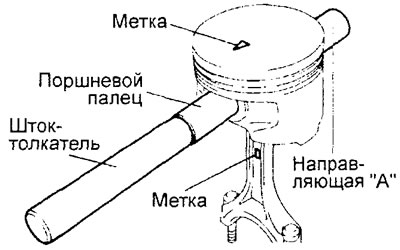
A) Perform all necessary assembly and disassembly work on the connecting rod and piston group using a special tool (kit for assembly and disassembly of piston kits), shown in the figure.
b) Insert the push rod into the piston from the side of the label "front" (in the form of an arrow), applied to the bottom of the piston.
V) Install the piston and connecting rod on the base with marks "front" up as shown.
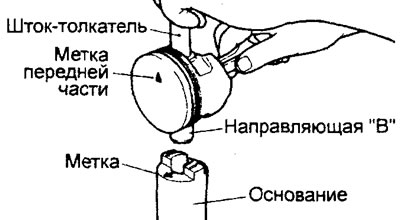
G) Using a press, remove the piston pin.
Note: To facilitate reassembly, keep disassembled parts separate from other similar parts.
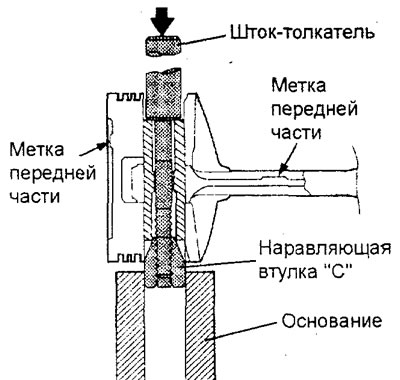
MPI engines.
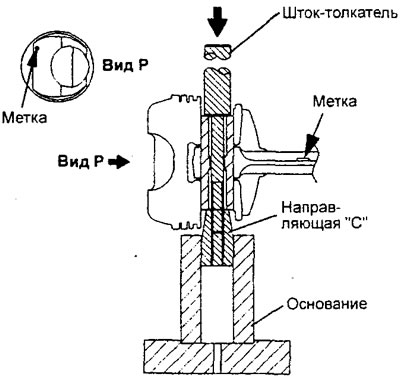
GDI engines.
d) Preparing a special tool:
- Measure the following values: A - the length of the hole for the piston pin; B is the distance between the piston bosses; C is the length of the piston pin; O - the width of the upper head of the connecting rod.
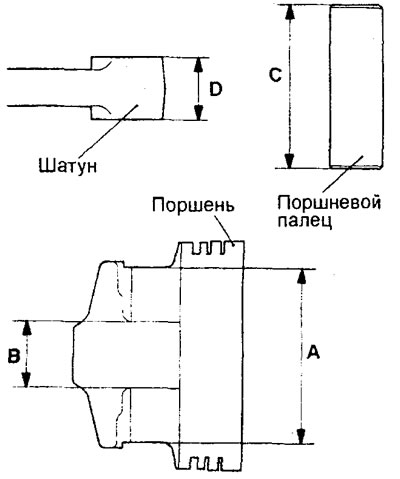
e) Determine the value "L" using the following formula:
L = { (A-C) - (B-D) }/2
and) Put the piston pin on the pusher rod and screw the guide sleeve "A" at the end of the stem.
h) Place the piston and connecting rod together with marks "front" up to the base of the fixture.
And) Apply engine oil to the surface of the piston pin.
To) Insert node (push rod with piston pin and guide sleeve "A" complete) sleeve in the combined hole of the piston and connecting rod (for piston pin) from the label side "front".
l) Screw in the guide bush "IN" into the guide bush "A" so that between these guide bushings a distance is formed equal to that measured in subparagraph "e" size "L" + 3 mm.
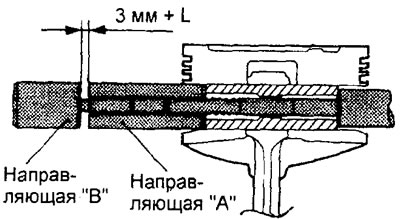
m) place piston and connecting rod together "front" up to the base of the fixture.
n) Press down on the pusher rod to install the piston pin. If the force developed during pressing is less than the nominal value, then replace the piston with a piston pin assembly and / or connecting rod.
Nominal pressing force:
- 4G15 engines - 4900 - 14700 N
- 4G93 engines - 4500 - 14700 N
Note: The piston pin is pressed in at room temperature.
Nominal outer diameter of piston pin:
- 4G15 engine - 18.0 mm
- 4G93 engine - 19.0 mm
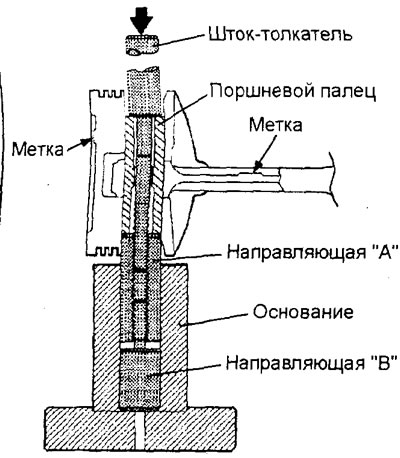
MPI motors
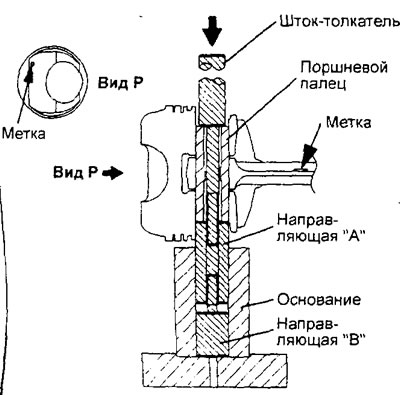
GDI engines.
Table. Color marks for oil scraper ring sizes.
| Engine | Nominal size (STD) | Repair size (0.50 mm) | Repair size (1.00 mm) |
| MPI | No | Blue | Yellow |
| GDI | No | Blue | Yellow |
O) Check that the piston moves smoothly without binding.
Assembly and installation
Installation of details is made in an order, the return to removal.
Pay attention to the following operations when installing parts.
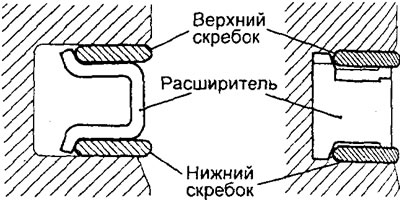
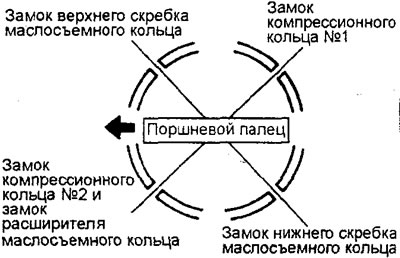
1. Installing the oil scraper ring.
A) Install the oil scraper ring expander into the ring groove in the piston.
Note:
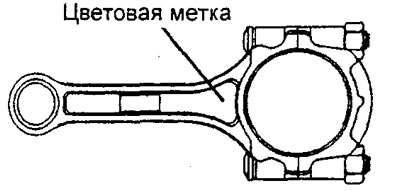
- Make sure that the gaps in the locks of the scrapers and expander are located as shown in the figure.
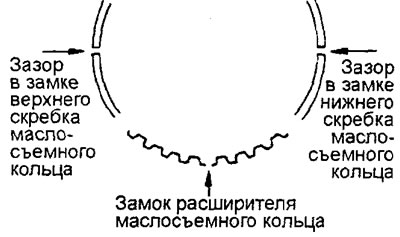
- New parts (expander and scrapers) are color-coded according to their size (see corresponding table).
b) Install the top oil ring scraper.
To install the top scraper, first install one end of the scraper into the piston groove, then slide the rest of the scraper with your finger as shown in the figure.
Caution: Do not use a piston ring expander. Unlike other parts of the piston rings, the scraper of the oil scraper ring can break when it is expanded with an expander.
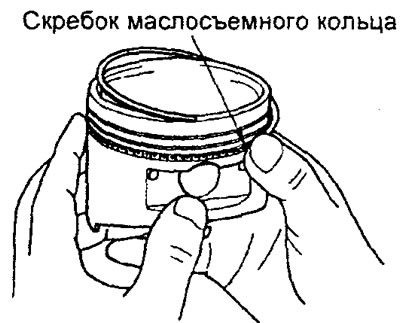
MPI motors
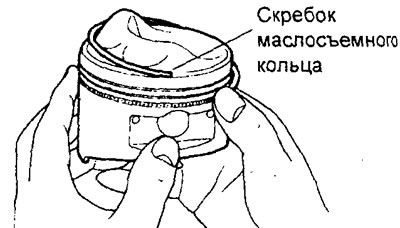
GDI engines.
V) Install the lower ring scraper in the same way as the upper one.
G) Check the correct installation of the oil scraper ring, which consists of three parts. When the oil scraper ring is correctly installed, it should rotate smoothly in any direction.
2. Installation of compression rings No. 1 and No. 2.
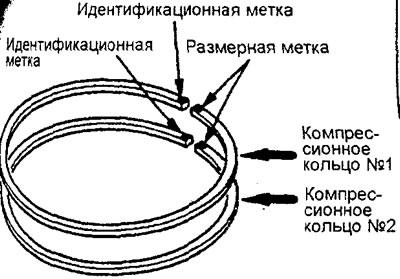
Using a compression ring expander, install compression rings #1 and #2 with the identification mark up.
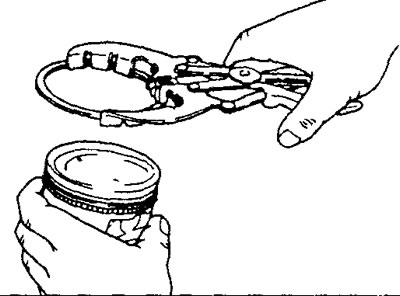
Note:
- Each compression ring has a size and identification marks stamped on the ends of the ring. When installing, position the ring so. so that the mark is on top.
Identification label:
4G15 engines:
- Ring #1 —— 1R, 1T or T
- Ring #2 - 2R, 2T or T2
4G93 engines:
- Ring #1 - T
- Ring #2 - 2T or T2
- The size group of the compression ring is determined by the table:
| Size | Dimension mark |
| Nominal (STD) | No |
| repair (0.50 mm) | 50 |
| repair (1.00 mm) | 100 |
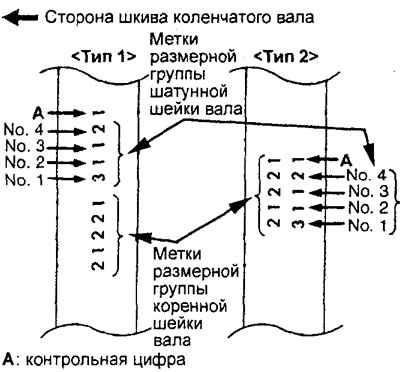
(Engine 4G 15) Selection of connecting rod bearing shells.
When replacing the connecting rod bearing shells, select them according to the table in accordance with the size group (character or color labels) crankshaft, size group (color labels) connecting rod and size group (character or color labels) connecting rod bearing shells.
The nominal diameter of the hole of the lower head of the connecting rod is 45.000 -45.015 mm
Attention: The size group mark of the crankshaft journal is applied only to the part supplied as a spare part.
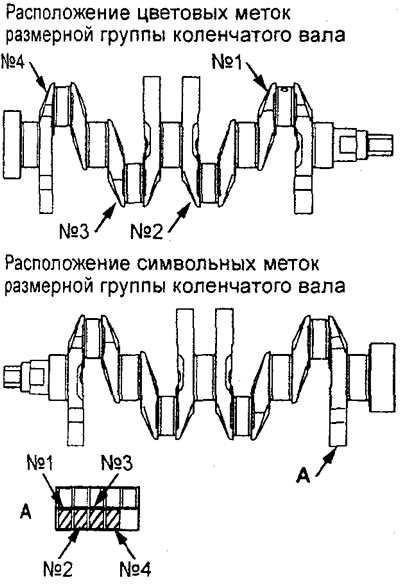
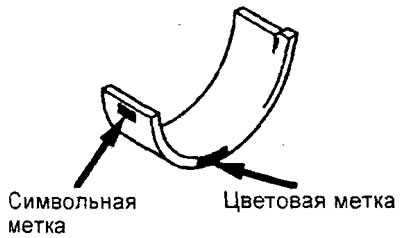
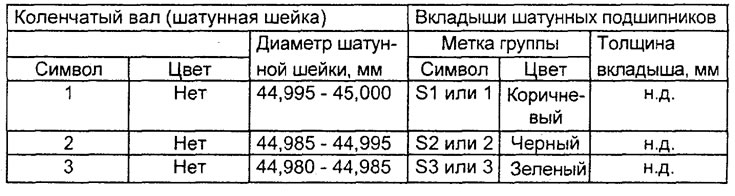
4. (Engine 4G93) Selection of connecting rod bearing shells.
When replacing the connecting rod bearing shells, select them according to the table in accordance with the size group (character or color labels) crankshaft and size group (character or color labels) connecting rod bearing shells.
The nominal diameter of the hole of the lower head of the connecting rod - 48.000 - 48.015 mm
Attention: The size group mark of the crankshaft journal is applied only to the part supplied as a spare part.
Table. Selection of connecting rod bearing shells for the 4G15 engine.
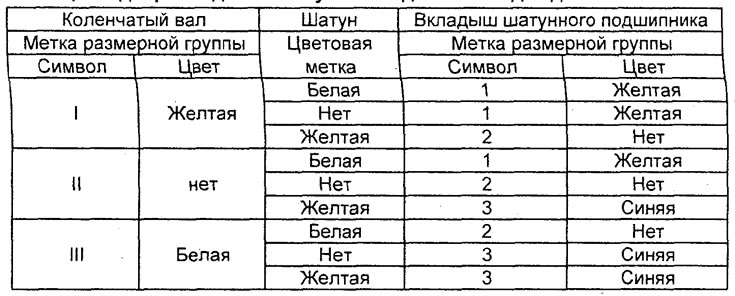
Table. Selection of connecting rod bearing shells for the 4G93 engine.
5. Installation of the piston and connecting rod assembly.
A) Lubricate the surfaces of the piston and piston rings with engine oil.
b) Position the locks of the compression rings and the oil scraper ring (expander and scrapers), as it shown on the picture.
V) Turn the crankshaft so that the connecting rod journal of the shaft is in the middle of the cylinder bore.
G) Use suitable protectors on the connecting rod bolt threads before installing the piston and connecting rod assembly into the cylinder bore. This will avoid damage to the working area of the crankshaft journals.
d) Using a ring compressor, install the piston and connecting rod assembly into the cylinder bore of the block.
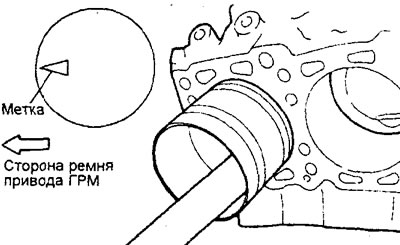
Attention: the piston with connecting rod assembly must be installed in the cylinder block so that the mark on the piston is directed towards the front of the engine (to the timing belt).
6. Installing the connecting rod cap and checking the axial clearance of the connecting rod bottom head.
A) Align the appropriate caps with the appropriate connecting rods, taking into account the markings made (cylinder number) and the method of fixing the liners (slots for inserts). If a new connecting rod without alignment marks is installed, then position the grooves for fixing the liners on the connecting rod and cover on one side.
b) Use a feeler gauge to check the bottom end end play of the connecting rod.
Axial clearance:
- nominal - 0.10-0.25 mm
- maximum allowable - 0.40 mm
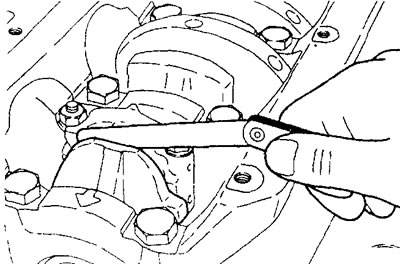
7. Tightening the connecting rod cap nuts.
A) The connecting rod cap bolt and nut are tightened "yield strength". Before installing the bolt, make sure that the thread of the bolt/nut is not deformed. The presence of deformation of the bolt-nut connection is checked by manually screwing the nut onto the bolt until the end of the thread. If the nut is difficult to screw onto the bolt by hand, the bolt thread is deformed and the bolt must be replaced.
b) Before installing the nut, lubricate the threaded parts of the nut and bolt with a small amount of engine oil) Screw the nuts onto the appropriate bolts by hand. Then tighten each nut individually to make sure the connecting rod cap is properly seated.
G) Alternately tighten the cap nuts to the specified torque.
Torque:
- 4G15 engines - 17 N.m
- 4G93 engines - 20 N.m
d) Tighten the nuts securing the covers at an angle of 90 - 94°.
Attention:
- If the nut is turned at an angle of less than 90°, then the tightening of the cap fastening nuts will be insufficient.
- If the nut is turned more than 94°, then unscrew the nut and repeat the tightening procedure from pp. "A".
