Disassembly
The main preliminary operations that you need to pay attention to are given in the sections "Replacement of oil seals" And "Replacing the cylinder head gasket" chapters "GDI Engines - Mechanical".
Removal of parts is carried out in the order of the numbers indicated in the figure "Removing rocker arms and camshafts".
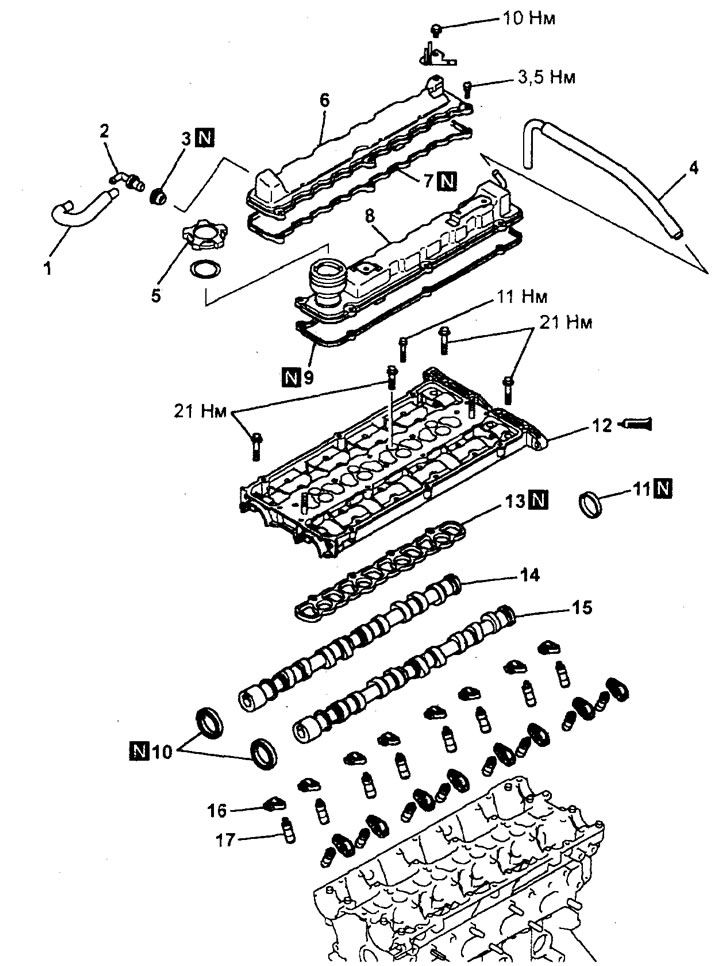
Removing rocker arms and camshafts (engine 4G93-GDI). 1 - positive crankcase ventilation hose, 2 - positive crankcase ventilation valve, 3 - positive crankcase ventilation valve gasket, 4 - ventilation hose, 5 - oil filler cap, 6 - cylinder head inlet valve cover, 7 - cylinder head inlet valve cover gasket cylinders, 8 - cylinder head exhaust valve cover, 9 - cylinder head exhaust valve cover gasket, 10 - camshaft oil seal, 11 - round plug, 12 - camshaft bearing cap block, 13 - camshaft cover block gasket, 14 - intake camshaft, 15 - exhaust camshaft, 16 - rocker arm, 17 - hydraulic compensator.
When removing parts, pay attention to the operation to remove the camshaft bearing cap assembly.
Gradually, in 2 - 3 steps, unscrew the bolts securing the camshaft bearing cap block.
Examination
Checking the camshaft
Each camshaft is checked in the same way as the corresponding check for MPI engines (see section "Rocker axles and camshaft (MPI engine)").
Below are the technical data for GDI engines required for verification.
Nominal bearing journal diameter:
- 4G15 engine - 25.95 - 25.97 mm
- 4G93 engine - 26.0 mm
Maximum allowable oil clearance (between each journal and bearing) — 0.05 - 0.09 mm
Jaw height:
Engine 4G15:
| Cam | Rated | Limit. |
| Inlet | 34.85 mm | 34.35 mm |
| High school graduation | 34.59 mm | 34.09 mm |
Engine 4G93:
| Cam | Rated | Limit. |
| Inlet | 35.49 mm | 34.99 mm |
| High school graduation | 34.73 mm | 34.23 mm |
Camshaft runout:
- Nominal value less than - 0.02 mm
- Limit value - 0.10 mm
Checking the rocker arms
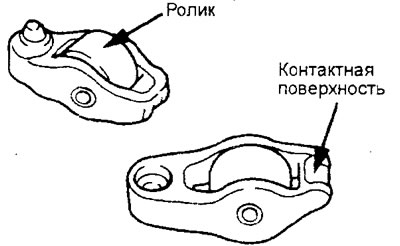
1. Check the surface of the valve rocker roller, replace the rocker if there are local wear, damage, scuffing.
2. Check roller rotation and replace valve rocker if present; seizing or increased play.
3. Check the surface condition of the rocker pusher (point of contact with the end face of the valve stem) for damage or scratches. Replace rocker if significant wear is found.
Leak test and cleaning of hydraulic lifters
Attention:
- The hydraulic compensator is a precision part. Keep dust, dirt and other foreign particles out of it.
- Do not disassemble the hydraulic lifter.
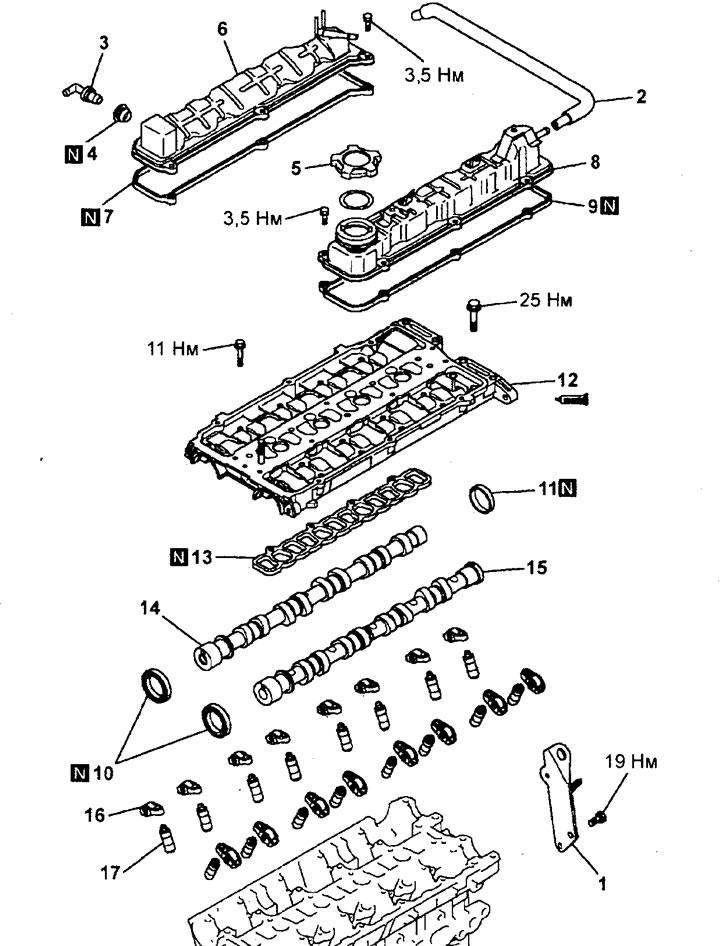
Removing rocker arms and camshafts (engine 4G15-GDI). 1 - engine suspension bracket, 2 - ventilation hose, 3 - positive crankcase ventilation valve, 4 - bushing, 5 - oil filler cap, 6 - cylinder head intake valve cover, 7 - cylinder head intake valve cover gasket, 8 - cover exhaust valves of the cylinder head, 9 - cylinder head exhaust valve cover gasket, 10 - camshaft oil seal, 11 - round plug, 12 - camshaft bearing cap block, 13 - camshaft cover block gasket, 14 - intake camshaft, 15 g exhaust camshaft, 16 - rocker arm, 17 - hydraulic compensator.
- When flushing the hydraulic compensator, use only clean diesel fuel.
1. Prepare three containers ("A", "IN" And "WITH") with enough clean diesel fuel (about 5 liters), to fully submerge the hydraulic compensator when vertical.
2. Place the hydraulic lifter in the container "A" and clean it outside. If deposits are difficult to remove, use a nylon brush.
3. Cleaning the internal cavities of the hydraulic compensator.
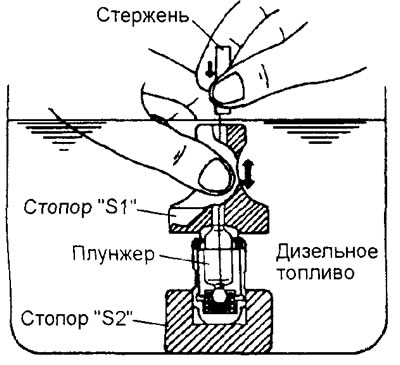
A) Immerse the hydraulic lifter in a container "IN" as it shown on the picture.
b) Slightly pressing down the steel inner ball of the hydraulic lifter with a special rod, at the same time move the plunger up and down (5-10 times), until the plunger moves smoothly. As a result, plunger sticking will be eliminated and contaminated oil will be removed.
Attention: the steel ball spring is weak, so the performance of the hydraulic compensator may deteriorate if the rod is pressed hard when air is removed.
Note: If the plunger remains stationary or another mechanism failure is found, replace the hydraulic compensator.
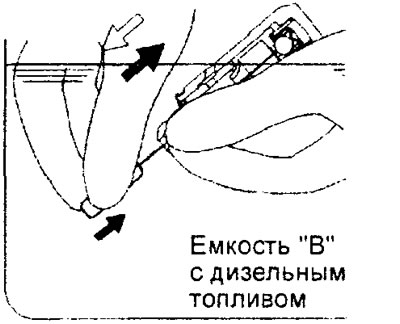
V) Remove the hydraulic compensator from the container, then lightly press the steel ball to force the plunger to push the diesel fuel out of the pressure chamber.
Attention: make sure that the oil hole in the body of the hydraulic compensator is directed towards the container "IN".
G) Repeat the operations according to p.p. "A" - "V" again to complete flushing.
4. Removal of air from the hydraulic compensator.
A) Immerse the hydraulic lifter in a container "WITH" plunger up.
b) Slightly pressing down the steel inner ball of the hydraulic lifter with a special rod, at the same time move the plunger up and down (four or five times) to remove air until the plunger moves smoothly.
Note: use of special tools (stoppers) to compress the hydraulic compensator facilitates the process of removing air.
Attention: the steel ball spring is weak, so the performance of the hydraulic compensator may deteriorate if the rod is pressed hard when air is removed.
V) Remove the special tool from the hydraulic lifter. Click on the plunger. If it is difficult to move the plunger, then the hydraulic compensator is in good condition. If the plunger moves freely, then the air removal operation must be repeated. If after that the plunger moves freely, then replace the hydraulic compensator.
Attention: After completing the bleed operation, install the hydraulic compensator vertically upwards to prevent diesel fuel from escaping.
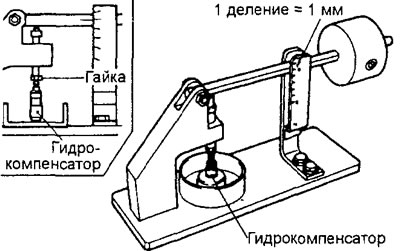
5. After carrying out the operation to remove air, install the hydraulic compensator in a special tool (stand for checking the tightness of the hydraulic compensator).
Note: when installing the hydraulic compensator on the test bench, use the adjusting nut of the bench to adjust the device to the height of the hydraulic compensator, as shown in the figure.
6. After the hydraulic compensator plunger has lowered by about 0.2-0.5 mm, measure the time for lowering the plunger by 1 mm. Replace the hydraulic compensator if the measured time does not match the nominal value.
The nominal value is 4-20 sec. (At diesel fuel temperature 15-20°C)
Assembly
Installation of details is made in an order, the return to removal.
Caution: When assembling, apply engine oil to all moving parts.
When installing parts, pay attention to the following operations:
1. Installation of hydraulic lifters.
A) If hydraulic lifters are reused, clean them (see paragraph "Leak test and cleaning of hydraulic lifters").
b) Bleed air from hydraulic lifters (see paragraph "Leak test and cleaning of hydraulic lifters").
V) Install the hydraulic lifters in the cylinder head, being careful not to let diesel fuel flow out of the hydraulic lifters.
G) Install the valve rocker in place so that it rests on the hydraulic compensator.
2. Installation of camshafts.
A) Check that each valve rocker is on one side of the hydraulic compensator and on the other side is on the end of the valve stem.
b) Lubricate the cams and camshaft bearing journals with clean engine oil.
V) Install the intake and exhaust camshafts to the cylinder head.
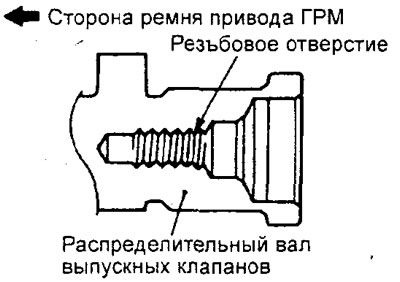
Attention: do not confuse the camshafts - at the end of the rear of the exhaust camshaft there is a hole for the camshaft position sensor rotor mounting bolt.
G) Turn the crankshaft so that the piston of the first cylinder is in the top dead center position (TDC).
d) Position the camshafts in the cylinder head so that their guide pins are in the position shown in the figure.
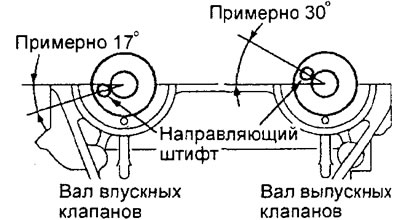
Engine 4G15.
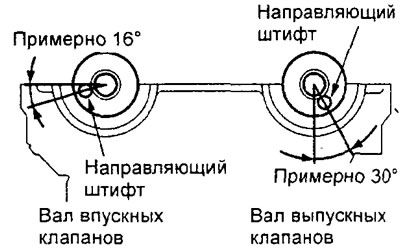
Engine 4G93.
3. Installation of the block of covers of bearings of camshafts.
A) Before installation, make sure that the camshafts are correctly positioned in the cylinder head.
b) Clean the mating surfaces of the cylinder head and the block of the camshaft bearing caps from the remnants of the old sealant. After cleaning, degrease surfaces to be sealed.
Attention: do not allow the remnants of the old sealant to enter the engine.
V) Apply the specified sealant in a continuous bead of approximately 3 mm diameter to the bottom of the camshaft bearing cap assembly (into a groove) in the places shown in the figure.
Sealant - 3M ATD Part #8660, Three Bond 1207F or equivalent
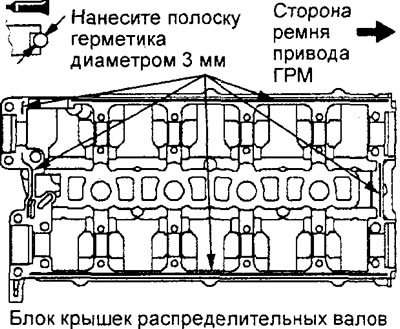
Engine 4G15.
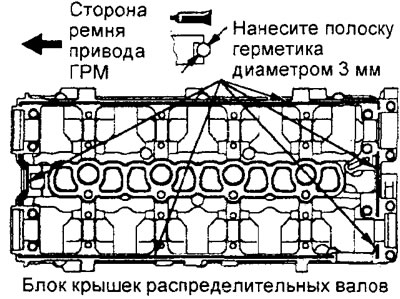
Engine 4G93.
G) Apply the specified sealant in a continuous bead of approximately 3 mm in diameter to the mating surface of the cylinder head at the locations shown in the figure.
Sealant - 3M ATD Part #8660, Three Bond 1207F or equivalent
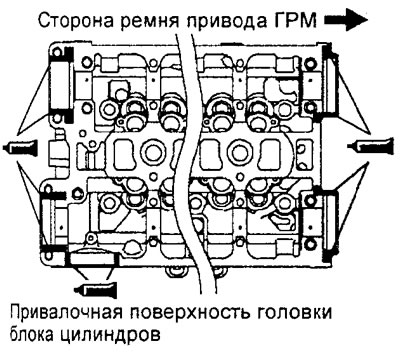
Engine 4G15.
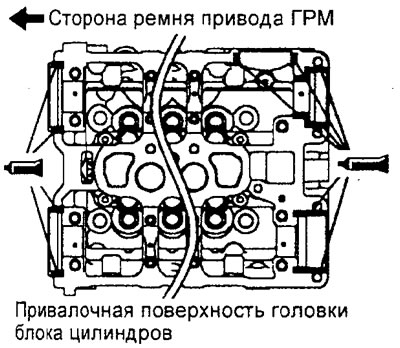
Engine 4G93.
d) Install the camshaft bearing cap gasket to the cylinder head.
e) Install the camshaft bearing cap assembly to the cylinder head before the sealant hardens (dry up),
and) Gradually tighten the camshaft cover assembly bolts in two or three steps in the order shown in the figure. Tighten the bearing cap assembly bolts to the specified torque in the final tightening sequence.
Torque:
- bolt M6 - 10-12 Nm
- bolt M8
- 4G15 engine - 24-26 Nm
- Engine 4G93 —19-23 Nm
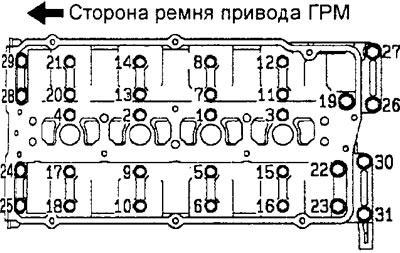
Engine 4G15.
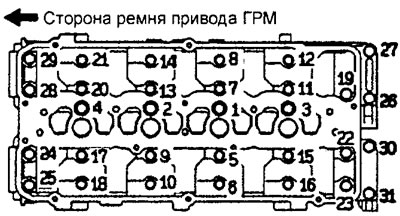
Engine 4G93.
h) Apply engine oil to the lip of the camshaft oil seal.
And) Press in the camshaft seals using the special tool before the sealant hardens.
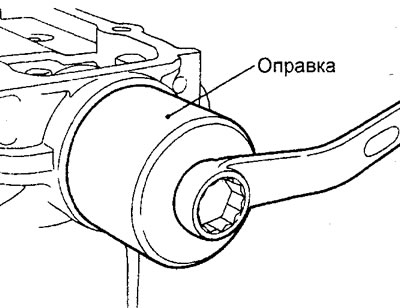
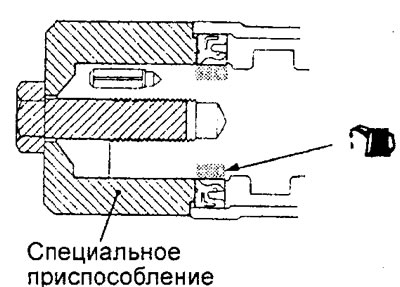
To) Wipe excess extruded sealant around the periphery of the camshaft bearing cap assembly before it hardens.
