Disassembly
Attention: Lay out the removed parts according to the cylinder number and intake / exhaust valves so as not to mix them up during assembly.
Removal of parts is carried out in the order of numbers indicated in the corresponding figure.
When removing parts, pay attention to the following operations:
1. Removing the valves.
A) Using a special puller, compress the valve spring and remove the crackers.
b) Remove the puller carefully. Remove the spring plate, spring and its seat. Take out the valve.
Note: Store parts for each valve separately.
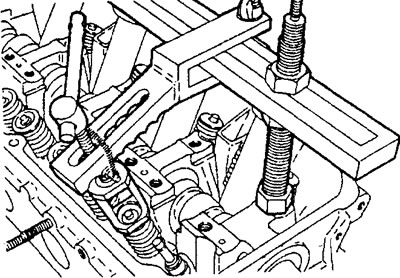
MPI engine
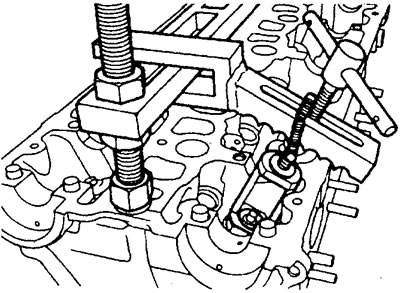
GDI engine.
2. Removing valve stem seals.
Remove the valve stem seals from the cylinder head using special pliers as shown in the figure.
Caution: Do not reuse valve stem seals.
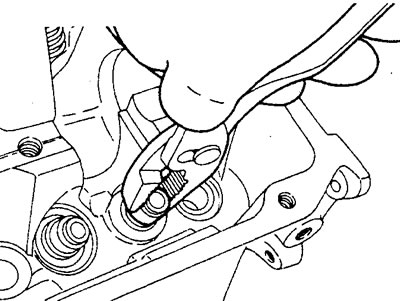
MPI engine.
Examination
Checking the cylinder head
1. Before cleaning, check the cylinder head for damage and cracks, coolant and oil leaks, exhaust gases and air.
2. Completely remove oil deposits, scale, gasket residues, soot deposits from the surface of the cylinder head. After cleaning, blow out the oil passages of the cylinder head with compressed air.
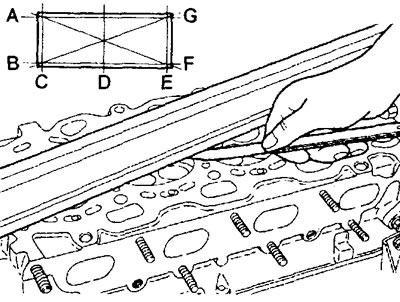
3. Checking the non-flatness of the attached surface of the cylinder head.
A) Using a precision ruler and a flat feeler gauge, check the non-flatness of the mating surface of the cylinder head under the gasket in directions from "A" before "G", shown in the figure.
Not flatness (for head):
- Nominal - 0.03 mm
- Maximum allowable - 0.20 mm
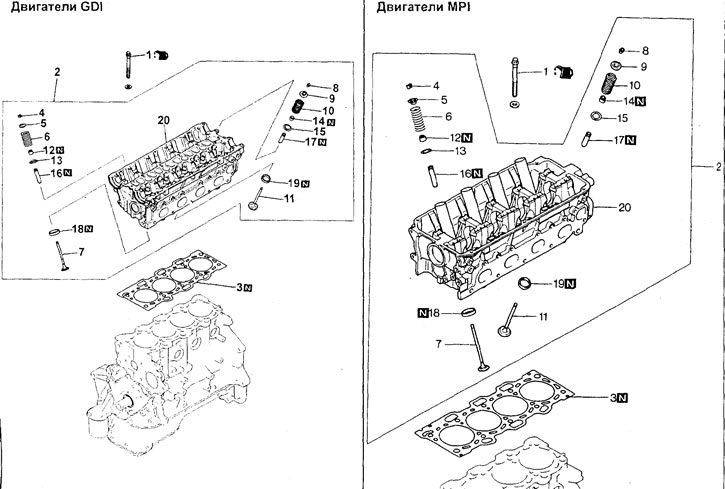
Cylinder head and valves. 1 - cylinder head bolt, 2 - cylinder head assembly, 3 - cylinder head gasket, 4 - crackers, 5 - valve spring plate, 6 - valve spring, 7 - inlet valve, 8 - crackers, 9 - plate valve springs, 10 - valve spring, 11 - exhaust valve, 12 - valve stem seal, 13 - valve spring seat, 14 - valve stem seal, 15 - valve spring seat, 16 - intake valve guide, 17 - exhaust valve guide, 18 - inlet valve seat, 19 - exhaust valve seat, 20 - cylinder head.
b) If the flatness exceeds the limit, grind the surfaces of the cylinder head and cylinder block.
Rated Height (new) cylinder heads (+0.1 mm):
- GDI Engine - 132.0mm
- MPI Motor - 120.0mm
- Maximum permissible grinding depth - 0.20 mm
Attention: the total thickness of the metal removed from the mating surfaces of the cylinder head and cylinder block must not exceed 0.20 mm in total.
V) Using a precision ruler and a flat feeler gauge, check the flatness of the mating surface of the cylinder head under the gasket on the side of the intake and exhaust manifolds.
Non-flatness (for collectors):
- Nominal value no more than - 0.15 mm
- Limit value - 0.20 mm
G) If the flatness exceeds the maximum permissible value, grind the mating surface of the cylinder head from the manifold side.
4. Inspect the inner surfaces under the camshaft bearings, check for scoring and other damage. If there is damage, replace the cylinder head.
Checking the valve and valve seat
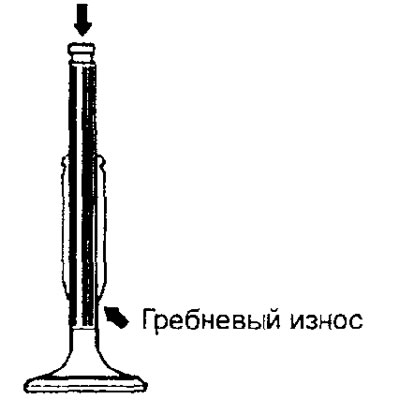
1. The valve must be replaced if the valve stem is worn (ridge wear) or damaged, or if the end of the valve stem (the point of contact of the end face with the adjusting screw of the rocker arm of the valve) dents have formed.
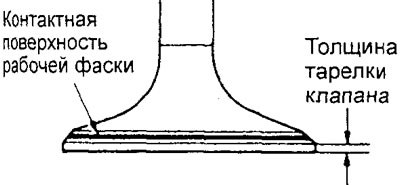
2. Check the contact patch of the chamfer of the valve disc with the valve seat. The contact patch should be located evenly in the center of the working chamfer of the valve disc. In case of improper contact of the valve with the seat, grind the chamfer of the valve disc.
Note: Before checking the contact patch, make sure that the valve and guide sleeve are in good condition.
3. Check the thickness of the valve disc in its cylindrical part. If the valve disc thickness is less than the limit, replace the valve.
Valve plate thickness (mm):
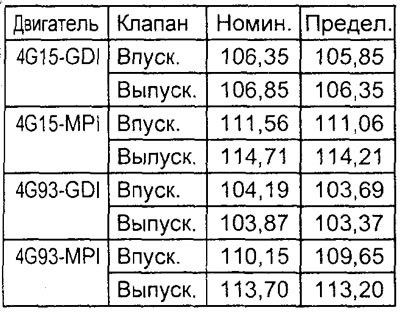
4. Measure the overall length of the valve. If the measured value is out of range (more than 0.5 mm or less than 0.5 mm from the nominal value), then replace the valve.
Table. Overall valve length (mm).
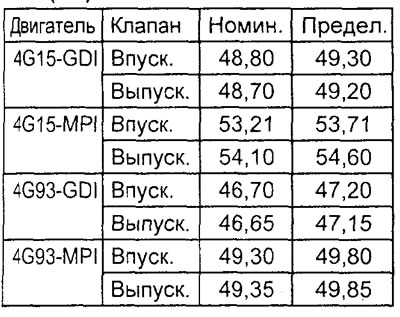
5. Insert the valve into the guide sleeve in the cylinder head and, pressing it against the seat, measure the protrusion of the valve stem from its end to the seat surface of the valve spring seat. If the measured value exceeds the allowable value, replace the valve seat.
Table. Valve stem protrusion (mm
).
Checking the valve spring
1. Measure the height of the valve spring in the free state, and if it is less than the allowable value, then replace the spring.
Table. Valve spring height.
| Engine | Rated | Limit. |
| 4G15-GDI | 49.1 mm | 48.6 mm |
| 4G15-MPI | 50.9 mm | 50.4 mm |
| 4G93-GDI | 44.8 mm | 43.8 mm |
| 4G93-MPI | 50.9 mm | 49.9 mm |
2. Measure the deflection of the valve spring axis from perpendicular to the bearing surface. If the deviation exceeds the maximum allowable value, then replace the spring.
Spring axis deflection:
nominal - 2°or less
maximum allowable - 4°
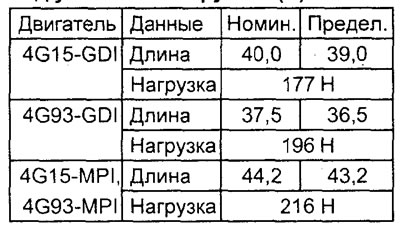
3. Using a spring tester, measure the force required to compress the spring to its installation length. If the force is less than the maximum allowable value, then replace the spring.
Spring setting length (mm) under specified load (H):
Checking the valve guide
1. Measure the clearance between the valve guide and valve stem at several points along the length.
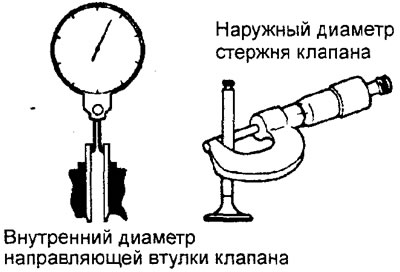
Clearance between valve guide and valve stem:
Rated value:
- Inlet - 0.02 - 0.05 mm
High school graduation:
- Engine 4G15 - 0.03 - 0.06 mm
- Engine 4G93 - 0.05 - 0.09 mm
Maximum allowable value:
- Inlet - 0.10 mm
- Graduation - 0.15 mm
Nominal valve stem diameter:
- 4G15 engine - 5.5mm
- 4G93 engine - 6.0mm
Nominal valve guide bore:
- 4G15 engine - 5.52mm
- 4G93 engine - 6.02 mm
2. If the clearance is greater than the allowable value, replace the valve guide or valve or both.
Repair
Valve seat rebuild
1. Check clearance between valve stem and valve guide before performing valve seat rebuilds. If necessary, replace the valve guide.
2. With a special tool (shell milling cutter with 30°, 45°, 60°or other bevel angle) machine the valve seat to obtain the width of the contact surface and the angle of the inclination of the working chamfer to the specifications.
Note: It is recommended to re-geometry the valve seat on machine tools.
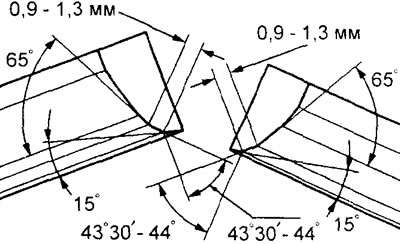
Engine 4G93
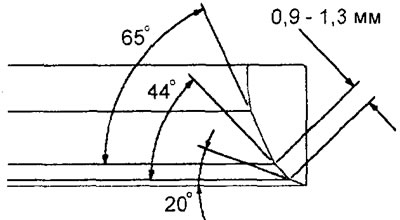
Engine 4G15-GDI - intake valve seat.
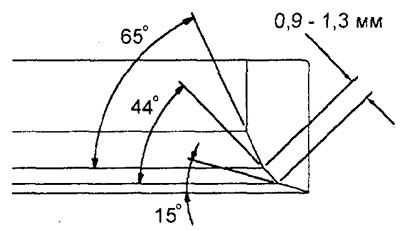
4G15-GDI engines - exhaust valve seat.
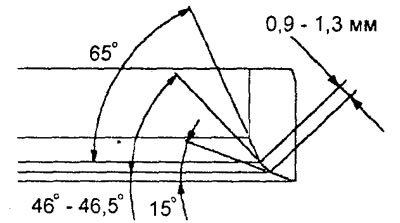
Engine 4G15-MPI.
3. After reshaping the valve seat, the valve and valve seat should be lapped using lapping paste.
4. Check the amount of protrusion of the valve stem above the surface of the cylinder head (see the corresponding paragraph in paragraph "Checking the valve and valve seat").
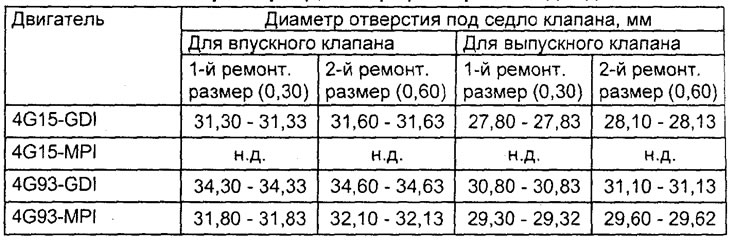
Valve seat replacement
Note: Valve seat replacement must be done on machine tools.
1. Machine (cut off) replaceable valve seat from the inside to reduce the thickness of its walls. Then remove the valve seat.
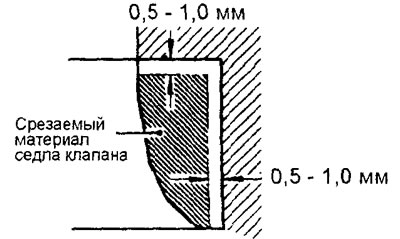
2. Bore a hole in the cylinder head to install an oversized valve seat (repair size).
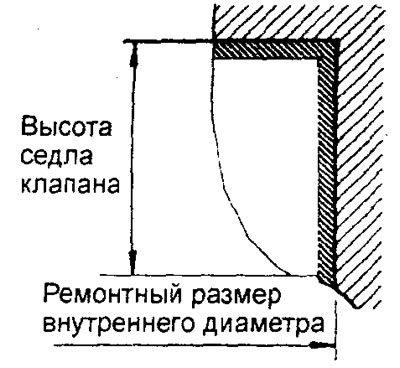
3. Before installing the valve seat, either heat the cylinder head to approximately 250°C or cool the valve seat in liquid nitrogen to prevent mechanical damage (scuffing) holes in the cylinder head when installing the seat.
4. Use a valve seat cutter to machine the seat to the required contact surface width and bevel angle as specified (see paragraph "Valve seat rebuild").
Valve Guide Replacement
1. Using the special tool and a press, press out the valve guide in the direction of the cylinder head gasket surface.
2. Bore a hole in the cylinder head to install the oversized valve guide (repair size).
Note: Do not install a valve guide of the same diameter again after boring the hole to oversize.
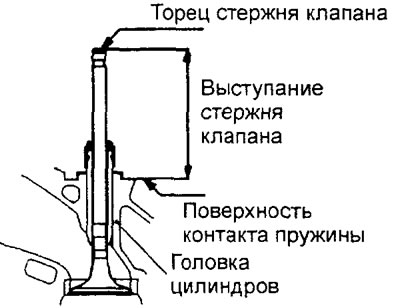
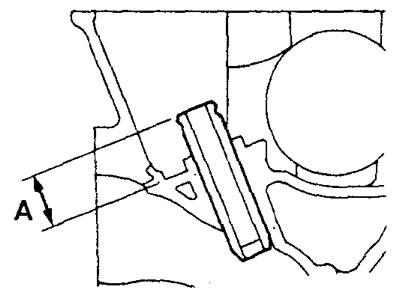
3. Press in the new valve guide from the side of the upper surface of the cylinder head so that its protrusion from the end to the seat of the valve spring seat is equal to "A" (see picture).
Rated value "A":
- 4G15 engines - 23.0mm
- Engine 4G93-GDI - 19.0 mm
- 4G93-MPI engine - 14.0mm
Note:
- Press in the guide bushings from the side of the upper surface of the cylinder head (from the side of the lid).
- Pay attention to the difference in the length of the guide bushings:
4G15 engines:
- for intake valve - 48.0 mm
- for the exhaust valve - 55.0 mm
4G93 engines:
- for the intake valve - 45.5 mm
- for the exhaust valve - 50.5 mm
4. After installing the guide sleeve, fit a new valve to it and check that the valve moves freely, without binding or excessive play.
5. After replacing the valve guide, check the valve seat contact pattern. In case of incorrect contact, correct the valve seat (lap valve i valve seat).
Valve fix
1. Grind the valve to remove carbon deposits and scratches.
2. Verify that the angle of inclination of the working chamfer corresponds to the nominal value.
Attention:
- Valve grinding should be minimal.
- If the thickness of the valve disc: after grinding is less than the maximum allowable value, then replace the valve.
- After grinding, lap the valve and valve seat to ensure the correct contact pattern.
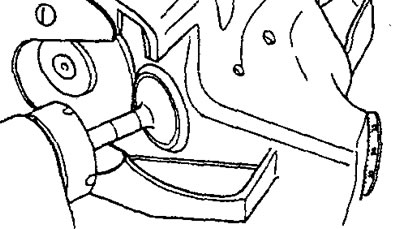
Lapping valve to seat
1. Apply a thin layer of lapping paste evenly to the valve seat seating surface.
Attention:
- Do not allow lapping paste to come into contact with the valve stem.
- Use a medium-grained paste first (grain size 120 -150), and then fine grinding paste (grit over 200). - To apply the lapping paste evenly, use a mixture of the lapping paste with a small amount of engine oil.
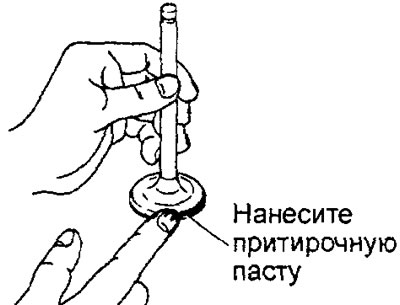
Table. Repair dimensions (inner diameters) valve guide holes.
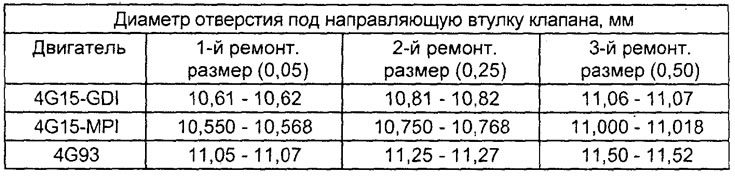
Table. Repair dimensions (diameters) valve seat holes.
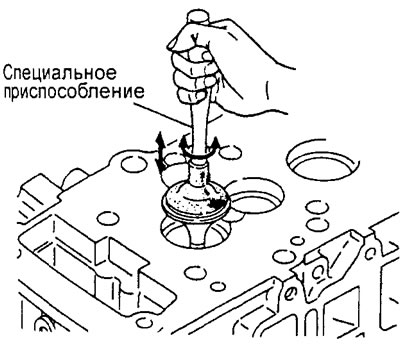
2. Hit the valve against the seat several times, turning the valve a little with the special tool.
3. Wash off the lapping paste with kerosene.
4. Apply a light coat of engine oil to the valve seat contact surface.
5. Check valve seat contact. Repair or replace the valve seat if necessary.
Assembly
Installation of details is made in an order, the return to removal.
Pay attention to the following operations when installing parts.
Note: Apply engine oil to all moving parts before installation.
1. Installing the valve stem seal.
A) Install the valve spring seat.
b) Using a special mandrel, install the valve stem seal on the valve guide.
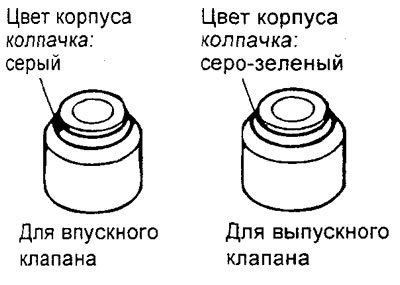
Note: for the 4G15-GDI engine, do not confuse the installation locations of the valve stem seals for the intake and exhaust valves, the valve stem seals differ in color marks:
Symbol mark on the cap:
- inlet valve no
- exhaust valve - SD
Cap body color:
- intake valve - gray
- exhaust valve - grey-green
Attention:
- Incorrect installation of the valve stem seal will result in increased oil flow through the valve guide.
- Do not install a valve stem seal that has been used.
GDI engine
MPI engine
2. Installation of the valve, valve spring and crackers.
A) Lubricate the valve stem with engine oil and insert it into the guide bush. Check the freedom of movement of the valve.
Attention: do not apply force when passing the valve stem through the valve stem seal.
b) Install the valve spring in place so that the colored identification mark is located near the spring seat (up).
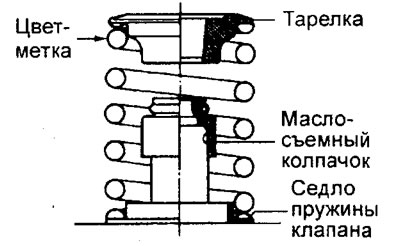
V) With a puller, compress the spring and install crackers in the groove of the valve stem.
Attention: if the spring is overcompressed, the spring seat may abut against the valve stem seal and damage it.
G) Check the correct installation of the crackers after removing the puller.
