Removing
Removal of parts is carried out in the order of the numbers indicated in the figure "Removing the crankshaft and torque converter drive plate".
Lay out the removed parts (thrust half rings and liners of main bearings, etc.) in order of their corresponding cylinder numbers.
Examination
Crankshaft
Attention: if the clearance between the crankshaft journals and the liners is out of range, then replace the liners and, if necessary, the crankshaft.
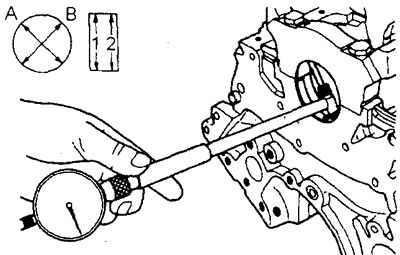
1. Checking the clearance in the main bearings of the crankshaft.
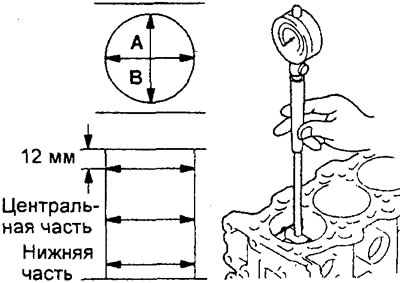
A) Measure the outside diameter of the crankshaft main journal and the inside diameter of the crankshaft main bearing shell in two mutually perpendicular directions (marked in the figure "A" And "IN") and in two sections along the length (marked in the figure "1" And "2").
Nominal outer diameter of the crankshaft main journal:
- 4G15 engine - 48.00 mm
- 4G93 engine - 50.00 mm
Main bearing clearance:
- nominal - 0.02-0.04 mm
- maximum allowable - 0.1 mm
b) If the clearance exceeds the maximum allowable value, then replace the main bearing shells and, if necessary, the crankshaft.
2. Determination of the clearance in the main bearings of the crankshaft using a plastic gauge.
Note: The use of this method greatly simplifies the procedure for determining the clearances in the crankshaft bearings.
A) Clean the surfaces of the cylinder block and the bed of the crankshaft, the main journals of the crankshaft and the bearing shells from deposits» oils, greases and other contaminants,
b) Place the crankshaft carefully into the cylinder block.
V) Cut a piece of gauge plastic wire that is the same length as the width of the journal, then place it on the crankshaft journal along the axis of the crankshaft.
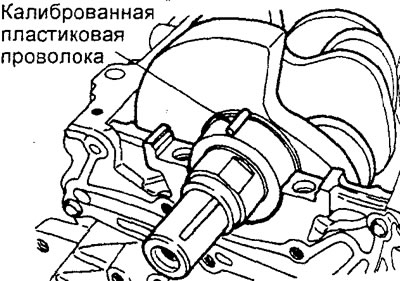
G) Carefully install the crankshaft bed on the cylinder block and tighten the mounting bolts, but with a minimum tightening torque.
d) Unscrew the fastening bolts, carefully remove the bed with the pole of that shaft.
e) Measure the width of the crushed plastic gauge wire at its widest point using the scale printed on the plastic gauge package.
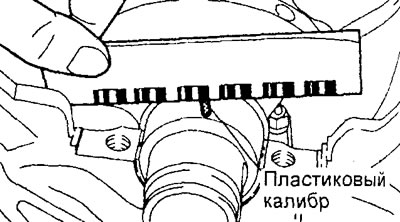
If the gauge on the shaft neck
If the caliber is on the bed of the shaft.
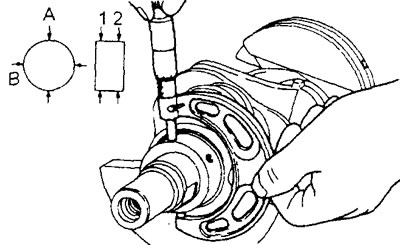
3. Check for out-of-roundness and taper» main and connecting rod journals.
A) Check the out-of-roundness and taper of the main and connecting rod journals as shown in the figure.
Maximum permissible values:
- Out-of-roundness - no more than 0.005 mm
- Taper - no more than 0.01 mm
b) If the out-of-roundness or taper is greater than the limit, replace the crankshaft.
Rear crankshaft oil seal
1. Check the crankshaft seal lip for wear or damage.
2. Check the rubber part of the gland for hardening or deterioration.
3. Check the condition of the stuffing box housing for cracks or damage.
Torque converter drive plate
Check the torque converter drive plate for deformation, damage or cracks. Replace if necessary.
Cylinder block
1. Preparation for inspection after removing all parts.
A) Before cleaning the cylinder block, check for signs of coolant leaks or any obvious damage.
b) Clean the parts of dirt, oil, carbon residue, scale and other types of deposits, after which you can proceed with the inspection and repair operations.
V) Remove sediment from oil holes and make sure these holes are not clogged with dirt. If necessary, blow out the holes in the channels of the lubrication and cooling systems with compressed air.
G) All parts must be neatly laid out in accordance with the order of assembly.
2. Assessment of the state of the cylinder block.
A) Visually inspect the cylinder block for gasket residue or other foreign matter, damage, rust or corrosion. If defects are found, repair them or replace the cylinder block.
b) Check the cylinder block with a liquid solution to determine the presence of cracks. If defects are obvious, then replace or repair the block of cylinders.
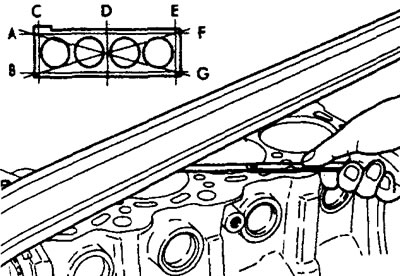
3. Checking the warping of the mating plane of the cylinder block.
A) Using a straightedge and a feeler gauge, check the degree of warping of the cylinder block running surfaces in the directions shown in the figure. The surface of the cylinder block must be free of foreign particles.
Nominal value - 0.05 mm or less
Maximum allowable value - 0.1 mm
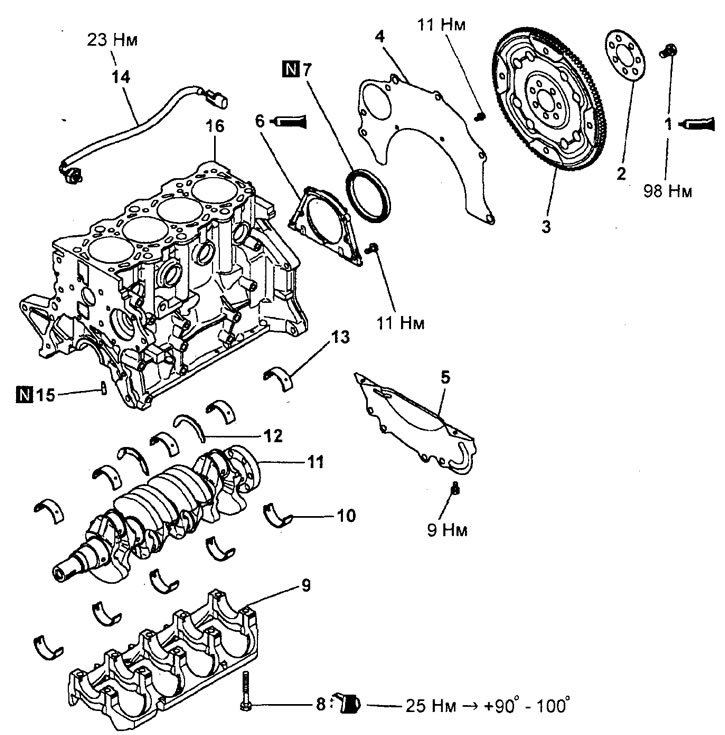
Removing the crankshaft and torque converter drive plate (4G93 engines). 1 - bolt; 2 - adapter plate; 3 - torque converter drive plate; 4 - rear plate of the cylinder block; 5 - protective casing of the gearbox housing; 6 - housing of the rear oil seal of the crankshaft; 7 - rear crankshaft seal; 8 - a bolt of fastening of a bed of a cranked shaft; 9 - bed of the crankshaft; 10 - the lower loose leaf of the main bearing of the shaft; 11 - crankshaft; 12 - upper thrust half rings; 13 - the upper loose leaf of the main bearing of the shaft; 14 - knock sensor; 15 - oil nozzle; 16 - cylinder block.
b) If warping is significant, then correct the defect to an acceptable value or replace the cylinder block.
Maximum grinding depth - 0.20 mm
Attention: the total thickness of the removed metal from the cylinder head and cylinder block must not exceed 0.2 mm in total.
Block height (new):
- 4G15 engines - 256.0 mm
- 4G93 engines - 263.5 mm
4. Checking the cylinder mirror.
Check the cylinder mirror for scratches and signs of sticking (badass). If defects are evident, repair (squander) to oversize or replace the cylinder block.
5. Piston clearance check (with connecting rod assembly) and a cylinder.
Use a bore gauge to measure the bore and taper (cylindricity) cylinder. In the presence of severe wear, bore the cylinder to the repair size, replace the piston and piston rings as a set.
Take measurements at the places shown in the figure.
Rated value:
Engine cylinder inner diameter
- 4G15 engines - 75.50 - 75.53 mm
- 4G93 engines - 81.00 - 81.03 mm
- Maximum allowable taper (cylindricity) - 0.01 mm
Repair
Cylinder boring
Attention: bore all four cylinders to the same repair size. Do not bore only one cylinder to oversize.
1. According to the largest diameter of the cylinder of the engine being repaired, obtained as a result of measurements, determine the number of the repair size of the pistons.
Attention: the oversize number of the piston is stamped on the piston head.
Repair dimensions of the piston and the corresponding piston rings:
| Repair size | Label |
| №1 (+0.50 mm) | 0.50 |
| №2 (+1.00 mm) | 1.00 |
2. Measure the outside diameter of the piston to be used at the location shown in the figure.
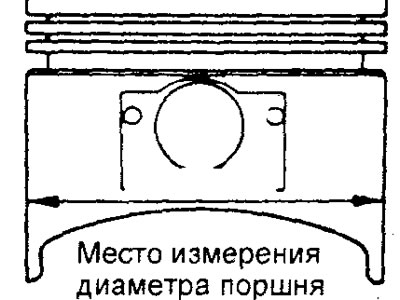
3. Based on the measured value of the outer diameter of the piston, calculate the bore diameter of the cylinder.
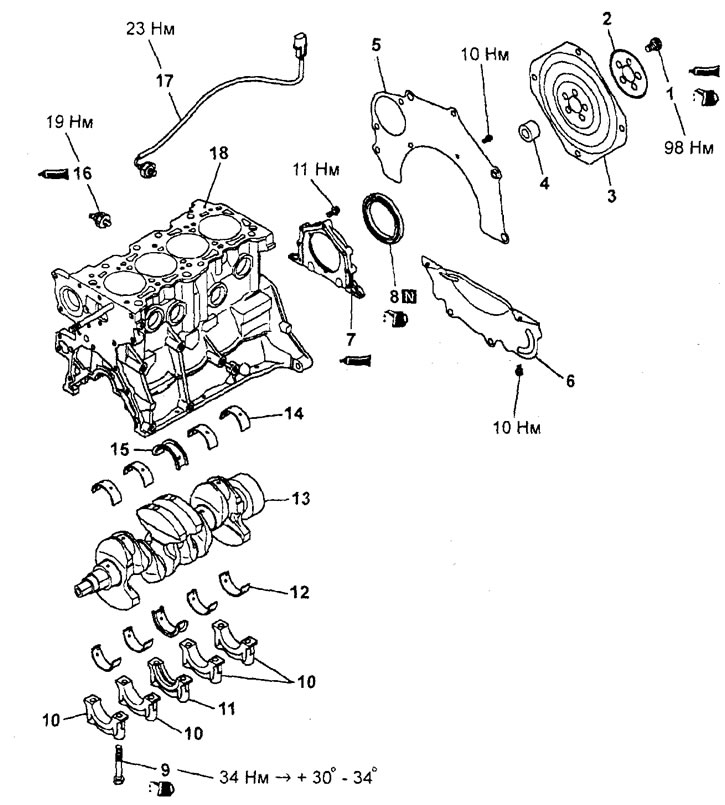
Removing the crankshaft and torque converter drive plate (4G15 engines). 1 - bolt; 2 - adapter plate; 3 - torque converter drive plate; 4 - crankshaft bushing; 5 - rear plate of the cylinder block; 6 - protective cover of the gearbox housing; 7 - housing of the rear oil seal of the crankshaft; 8 - rear crankshaft oil seal; 9 - a bolt of fastening of a cover of the main bearing of a cranked shaft; 10 - crankshaft main bearing cap; 11 - cover No. 3 of the main bearing of the crankshaft; 12 - the lower loose leaf of the main bearing of the shaft; 13 - crankshaft; 14 - the upper loose leaf of the main bearing of the shaft; 15 - main bearing shell No. 3 (with iterated thrust rings); 16 - engine oil emergency pressure sensor; 17 - knock sensor; 18 - cylinder block.
Cylinder bore diameter = Piston outside diameter + (gap between piston and cylinder) - 0.02 mm (honing allowance).
4. Bore all cylinders to design diameter.
Attention: to prevent temperature deformations during boring, bore the cylinders in the following sequence: No. 2, No. 4, No. 1, No. 3.
5. Honed cylinders to final finish size (piston outer diameter + clearance between piston and cylinder).
Attention: to prevent temperature deformations during boring, bore the cylinders in the following sequence: No. 2, No. 4, No. 1, No. 3.
6. Check up a backlash between the piston and the cylinder.
Clearance between piston and cylinder - 0.02 - 0.04 mm
Installation
Installation of details is made in an order, the return to removal.
Pay attention to the following operations when installing parts.
Note: Apply engine oil to all moving and sliding parts before assembly and installation.
1. Selection of liners of main bearings of the crankshaft.
Note: If the liner needs to be replaced, select and install the correct size liner.
A) If the crankshaft is supplied as a spare part, then identify the color or symbol marks on the crankshaft main journals that are stamped in the location shown in the figure. If identification of the crankshaft by marks is not possible (no tags), then measure the diameter of each crankshaft main journal.
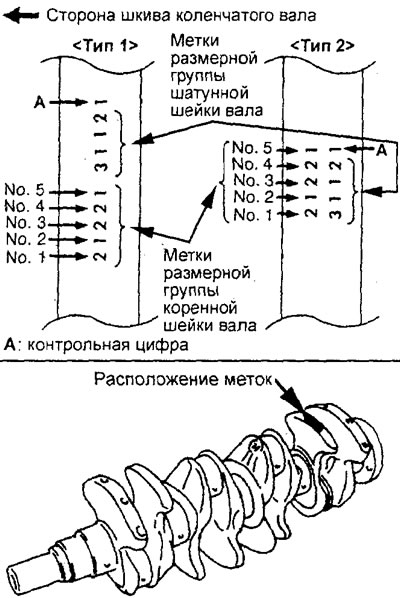
4G93 engine crankshaft marks.
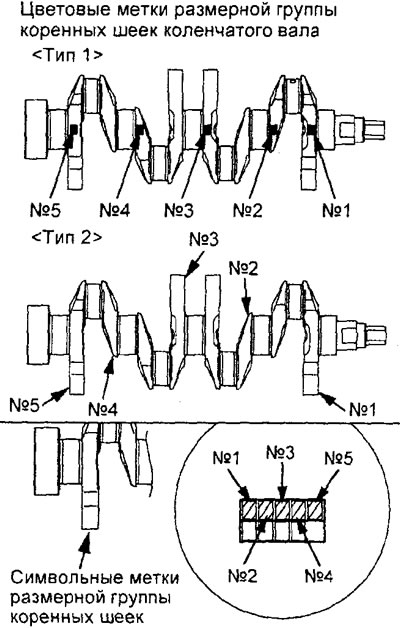
4G15 engine crankshaft marks.
b) Determine the character identification marks on the cylinder block (size groups of bore diameters for main bearings), which are stamped at the location shown in the figure, in the direction from the front to the back of the unit. The mark for the neck No. 1 is located on the side of the front of the engine (from the timing belt side).
Note: for 4G93 engine see picture "Character identification marks for the selection of shells of main bearings of the crankshaft of the 4G93 engine".
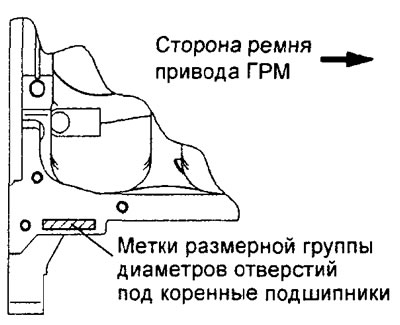
Symbolic identification marks for the selection of the main bearing shells of the crankshaft of the 4G15 engine.
V) The crankshaft main bearing shells are identified by color and/or symbol labels, which are located as shown in the figure.
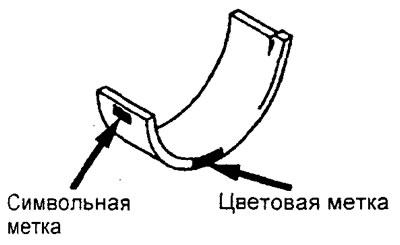
Engine 4G15.
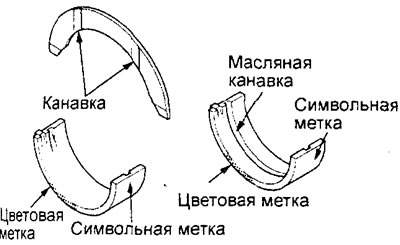
Engine 4G93.
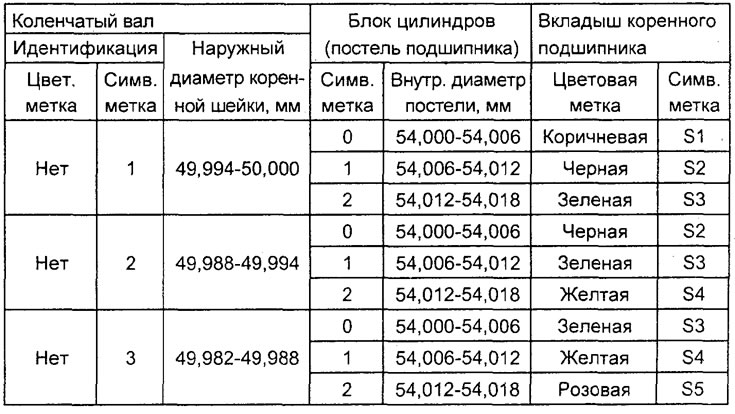
G) In accordance with those defined in paragraphs. "A" - "V" marks on the crankshaft (or the results of measurements of the main journals of the shaft) and identification marks on the cylinder block, select the correct main bearing shells from the table below.
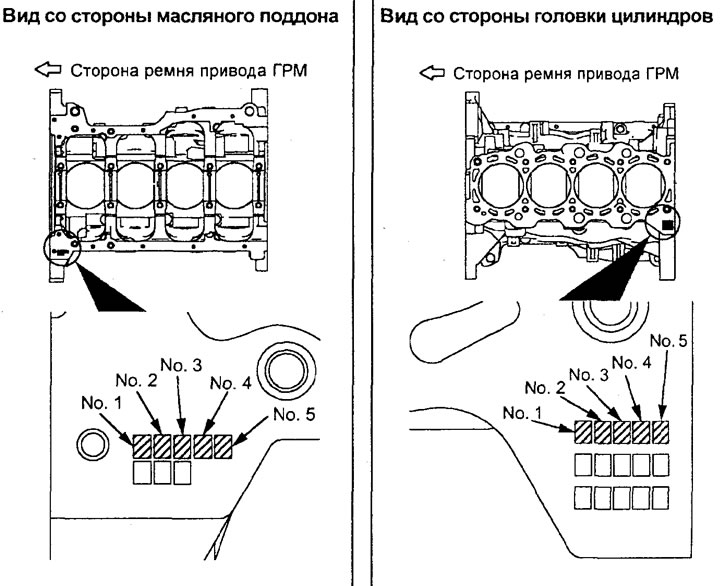
Symbolic identification marks for the selection of the main bearing shells of the crankshaft of the 4G93 engine.
Table. Selection of liners of main bearings of the crankshaft of the 4G15 engine.
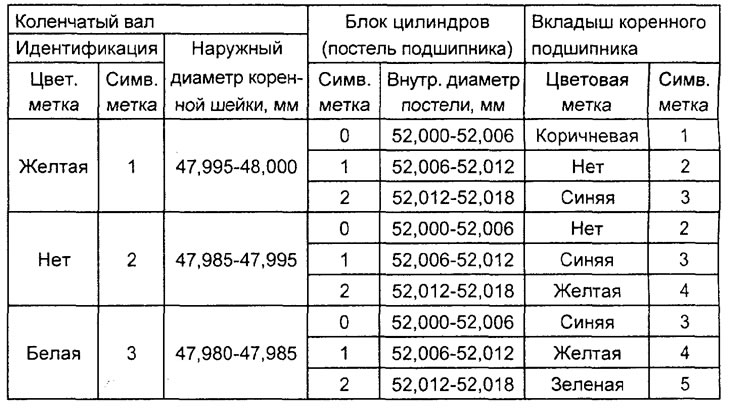
Table. Selection of liners of main bearings of the crankshaft of the 4G93 engine.
2. Installing the crankshaft main bearing shells.
A) Install the upper main bearing (No. 1, 2, 4 and 5 for the 4G15 engine) crankshaft into the cylinder block.
Attention: there is a groove in the upper shell of the main bearing of the crankshaft for supplying lubricant.
b) Install the lower main bearing (No. 1, 2, 4 and 5 for the 4G15 engine) crankshaft to the bed of the crankshaft.
V) (Engine 4G15) Install the No. 3 upper and lower main bearing shells.
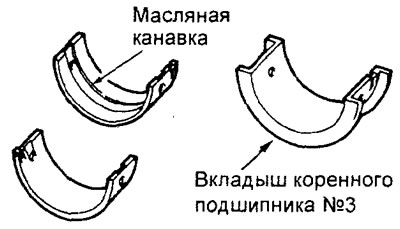
G) (Engine 4G93) Install the thrust washers on both sides of the No. 3 main bearing with the grooves facing out (to the cheek of the counterweight).
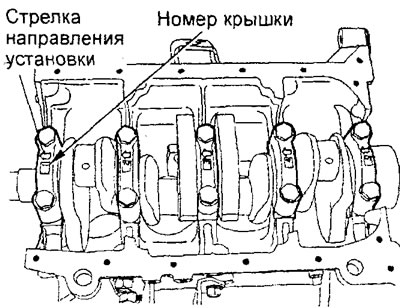
3. (Engine 4G15) Installing crankshaft bearing caps and mounting bolts.
A) When installing, it is necessary to arrange the covers so that the arrows of the covers are directed to the crankshaft pulley and the numbers of the covers correspond to the numbers of the shaft journals.
b) Apply engine oil to the threads of the bolts and under their heads.
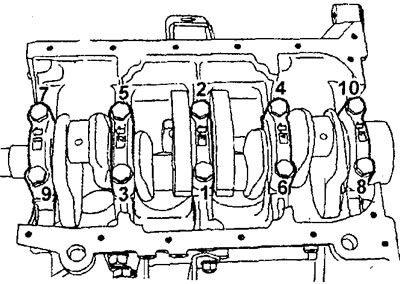
V) Tighten the main bearing cap bolts to the specified tightening torque in the sequence shown in the figure.
Tightening torque - 34 Nm
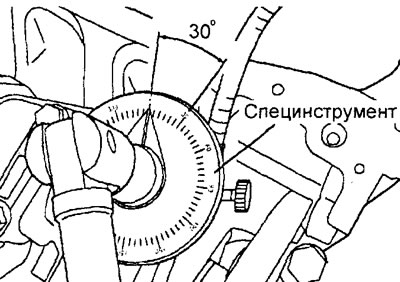
G) Tighten the main bearing cap bolts by 30°in the above sequence.
Attention:
- If the bolt is turned at an angle of less than 30°, then the fastening of the crankshaft bed will be insufficient.
- If the bolt is turned more than 34°, then unscrew the bolt and repeat the tightening procedure from paragraphs. "A".
d) Make sure the crankshaft rotates smoothly.
e) Check the end clearance of the crankshaft as shown in the figure.
Axial clearance of the crankshaft:
- nominal - 0.05-0.18 mm
- maximum allowable - 0.25 mm
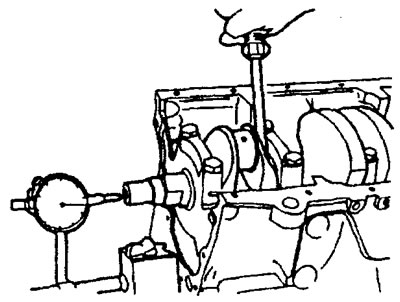
and) If the clearance exceeds the maximum allowable value, then replace the No. 3 main bearing shells.
4. (Engine 4G93) Installing the crankshaft bed and its fastening bolts.
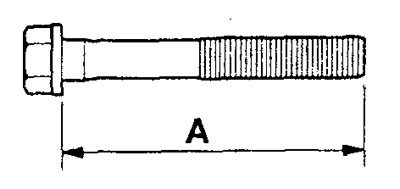
A) Before installing the mounting bolts, check that the length of the rod "A" for each bolt does not exceed the maximum allowable value. If the limit value is exceeded, replace the bolt.
Maximum allowable value - no more than 71.1 mm
b) Install the crankshaft bed on the cylinder block so that the arrow on it is located on the side of the timing belt.
V) Apply engine oil to the threads of the bolts and under their heads.
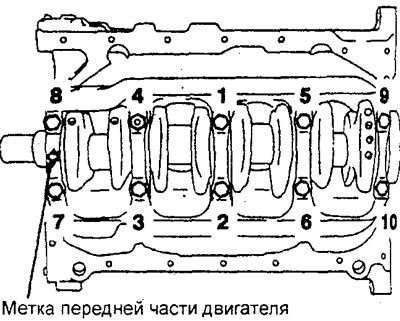
G) Tighten the crankshaft bed mounting bolts to the specified tightening torque in the sequence shown in the figure.
Tightening torque - 25 Nm
d) Tighten the crankshaft bed mounting bolts (bearing cap) at an angle of 90° (1/4 turn) in the above sequence.
Attention:
- If the bolt is turned at an angle of less than 90°, then the fastening of the crankshaft bed will be insufficient.
- If the bolt is tightened by an angle of 100°, then unscrew the bolt and repeat the tightening procedure from paragraphs. "A".
e) Make sure the crankshaft rotates smoothly.
and) Check the end clearance of the crankshaft as shown in the figure.
Axial clearance of the crankshaft:
- nominal - 0.05-0.25 mm
- maximum allowable - 0.40 mm
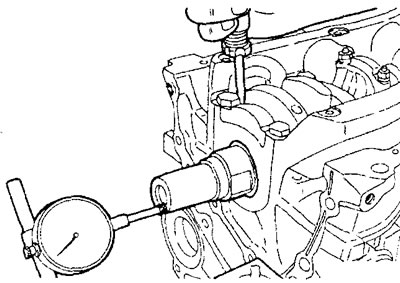
h) If the clearance exceeds the maximum allowable value, then replace the thrust half rings.
5. Installing the rear crankshaft oil seal.
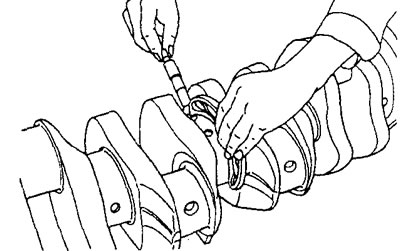
Install the new oil seal into the oil seal housing using a special mandrel as shown in the figure.
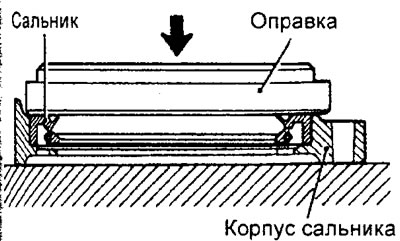
Engine 4G15
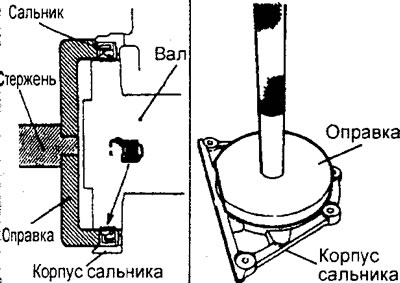
Engine 4G93
6. Installing the crankshaft rear oil seal housing.
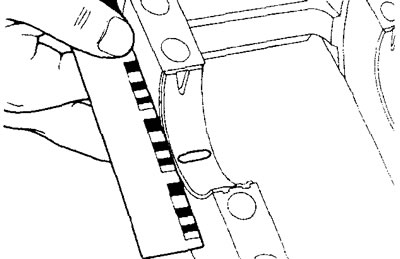
A) Apply the specified sealant to the stuffing box at the locations shown in the illustration.
Sealant MITSUBISHI GENUINE Part No. MD 970389, Three Bond No. 1207F or equivalent
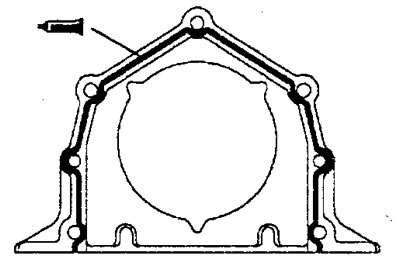
Engine 4G15
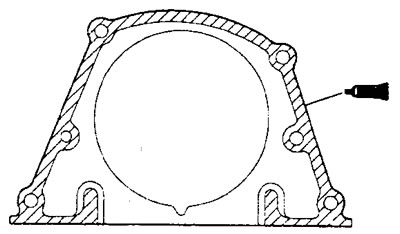
Engine 4G93
b) Apply a small amount of engine oil to the lip of the oil seal around its entire circumference and install the oil seal housing on the cylinder block.
Tightening torque - 11 Nm
Note:
- Install the packing case within 15 minutes of applying the sealant.
- After installation, do not allow oil and coolant to come into contact with sealant-coated surfaces of the stuffing box.
7. Installing the torque converter drive plate.
See the corresponding paragraph of the section "Replacement of oil seals" chapters "Engines - Mechanical".
