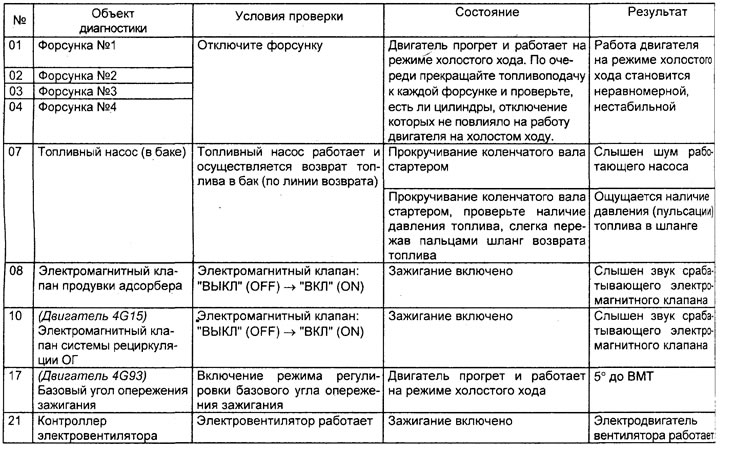
General information
1. Type of self-diagnosis system.
A) Models use an EOBD or OBD-II type self-diagnosis system, the standard diagnostic code of which consists of one letter and 4 digits (For example: "P0000"). The numbering of such codes is continuous, i.e. fault codes for various systems are not repeated.
b) On models with an OBD-II system, a new function has been added to the engine control unit "freeze" data (freeze frame data). If a malfunction is detected, the self-diagnosis system will record the appropriate diagnostic code and record the current parameters of the main components and engine systems at the moment ("freeze" data). This data, read by the tester, can make it easier to analyze the fault conditions.
2. Features of diagnostics using a tester.
A) The algorithm of the Mitsubishi diagnostic system is slightly different from the standard algorithm (OBD2 protocol), therefore, it is recommended to use the MUT-II tester to perform correct diagnostics.
b) It is recommended to connect a tester (MUT-II) with the ignition off, as a malfunction may occur on some types of electronic control units.
V) Before connecting the tester to the diagnostic connector, make sure that the condition and shape of the connector pins are correct.
3. Diagnostic connector.
One standard 16-pin main diagnostic connector was installed in the car (located under the instrument panel).
4. Explanations on the operation of the indicator "CHECK ENGINE" (check the engine):
- A) The indicator lights up for a few seconds immediately after the ignition is turned on to indicate that the indicator itself is functioning properly.
- b) Further (after starting or with the engine running) indicator lights up to alert the driver that a malfunction has been detected by the self-diagnosis system.
Attention: if the indicator lights up due to a malfunction of the electronic control unit, then communication between the tester and the electronic control unit cannot be established, and there is no possibility to read diagnostic codes.
V) Periodic blinking of the indicator indicates the presence of a temporary malfunction. It may continue as long as a major fault affects the emission control system or other systems (e.g. skipped flashes damage the catalytic converter).
G) In the event of a critical failure (a serious defect in the fuel injection or emission control system) the indicator will remain lit while the vehicle is moving until the fault code is cleared after the fault has been corrected (those. after repair).
Note: Clearing the DTC is not a troubleshooting.
d) The indicator will turn off when the ignition is turned off (key: "OFF").
5. Conditions under which the indicator is lit "CHECK ENGINE" may go out at the signal of the electronic control unit when the ignition is on (fault code stored).
Note: for any malfunction, the cycle means engine start-stop or three trips (road test car), during which this fault is monitored
A) For a fault in the transmission: if the electronic engine control unit has not detected a fault within three cycles under the appropriate modes and conditions (see code occurrence conditions).
b) For a fault in the exhaust emission system (skip flashes in cylinders): if the electronic engine control unit during the cycle did not detect a malfunction under similar engine operating conditions (engine speed, coolant temperature, etc.), at which the fault was first detected.
6. Explanations on the operation of the self-diagnosis system.
A) The electronic engine control unit monitors the input and output signals (some permanently, others only under certain conditions). If a permanent or for a predetermined period of time a malfunction of the system is detected, or if, after the first incorrect signal, several more similar signals are received by the electronic engine control unit, the engine control unit will perceive this as a malfunction and write the corresponding fault code to memory and send a signal to the output of the self-diagnosis system.
Note:
- Usually, if the electronic control unit has detected a malfunction, then the indicator "CHECK ENGINE" will illuminate and the fault code will be stored only after the engine is restarted and the same fault is detected again.
- − In the event of a malfunction of the ignition coil (power transistor) indicator "CHECK ENGINE" will light up and the P0300 fault code will be stored the first time it is detected (this fault is critical; because the catalytic converter is damaged).
b) Since the storage device (RAM of the electronic engine control unit) is powered directly from the battery, the diagnostic results are stored even when the ignition key is turned to the "OFF" (OFF). Trouble codes will be cleared when the battery terminal or ECM connector is disconnected. In addition, fault codes are erased if, with the ignition on, (key in position "ON" (ON)) a signal will be sent from the tester to the electronic engine control unit to clear the trouble codes.
Attention: if with the ignition on (key in position "ON") disconnect the connector of any sensor, then the electronic control unit will perceive this as a malfunction and the corresponding code will be written to the memory of the control unit. In this case, clear the trouble codes.
Standard Troubleshooting Chart
1. Simulate symptoms of a malfunction to check for their presence and determine the nature and conditions of occurrence (engine operating mode, operating conditions, etc.).
2. Read the fault codes and determine the causes of the fault, the components to be tested and the order in which they should be tested.
3. Check the input signals of the electronic engine control unit using a tester or motor tester. If the signals are normal, then the corresponding sensor (element) serviceable. Move on to the next component.
4. Check the output signals of the electronic engine control unit using a motor tester and check the operation of the actuators (drives) using the menu item ACTUATOR TEST of the tester. If the signals of the electronic engine control unit and the drive are normal, then the drive control is normal. Move on to the next component.
5. If the signals of the electronic engine control unit are normal, then check and, if necessary, repair the electrical wiring of the system components. After repair, check the signals of the electronic engine control unit again. If the signals are OK this time, then check the input and output signals for the next component to be tested.
6. If the wiring is in order, but the input and output signals of the electronic engine control unit are not correct, then check the individual components of the system and, if necessary, repair or replace them. After repair, check the signals of the electronic engine control unit again. If the signals are OK this time, check the signals for the next component to be tested.
7. Recheck for symptoms and repair.
If, as a result of checking the suspect wiring circuit and specific components, no defects are found, but the input and output signals of the engine control unit deviate from the norm, then carefully evaluate the symptoms of the malfunction (the initial diagnosis may have been incorrect or incomplete). When checking further, try to expand the troubleshooting area to other groups of components (repair if necessary).
8. Try to simulate the symptoms of the problem to be sure that the problem has been fixed. Eliminate the cause of the malfunction to prevent the defect from reappearing.
Checking the indicator "CHECK ENGINE" (check the engine)
1. Turn on the ignition (key position "ON") and make sure the indicator "CHECK ENGINE" lights up for about 5 seconds and then goes out.
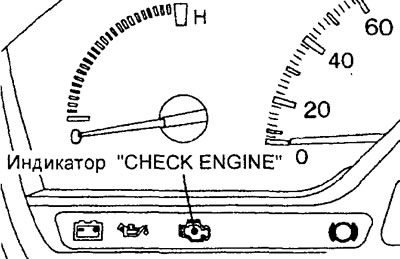
2. If the indicator does not light, then check the wiring, fuse and indicator lamp.
Reading diagnostic trouble codes with a tester
1. Prepare the vehicle for inspection as follows.
A) Make sure the battery is in good condition, as fault detection is not possible when the battery voltage is low.
b) Turn off all additional equipment.
V) Set the CVT or automatic transmission selector lever to position "N".
Attention: do not disconnect the battery until the diagnostic results are completely read, as the fault code will be deleted from the memory of the electronic control unit when the battery or the connector of the electronic control unit is disconnected.
Note: If DTCs have been cleared, then the fault information "freeze frame" data will also be erased from memory. Therefore, if necessary, before deleting fault codes from the memory of the electronic control unit, read the fault "freeze frame" data.
2. Turn the ignition key to the position "OFF" (OFF).
3. Connect a tester to a diagnostic socket under the panel of devices.
Attention: to prevent damage to the tester when connecting or disconnecting "ignition" should be off (ignition key in position "OFF" (OFF)).
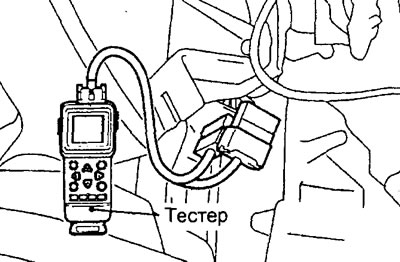
4. Turn on the ignition and read the diagnostic codes.
Note: Fault codes are shown in the table "Diagnostic Trouble Codes".
5. After completing the test, turn the ignition key to the position "OFF" (OFF) and then disconnect the tester from the diagnostic socket.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Note: after repair, delete the trouble codes from the memory of the electronic engine control unit.
1. Turn the ignition key to position "OFF".
2. If a tester is used, then connect it to the diagnostic socket and erase the codes,
3. If the tester is not being used, disconnect the cable from the negative battery terminal for 10 seconds or more.
Attention: after disconnecting the wire from the negative terminal of the battery, the contents of the memory of electronic control units of other systems will be lost.
4. Turn the ignition key to position "ON", then verify that the normal status code is displayed.
5. After warming up the engine, let it idle for at least 10 minutes.
Car diagnostics
1. Prepare the vehicle for inspection (see "Reading diagnostic trouble codes with a tester").
2. Connect a tester to a diagnostic socket under the panel of devices.
Attention: before connecting the tester, turn off the ignition.
3. Turn on the ignition and read the diagnostic codes.
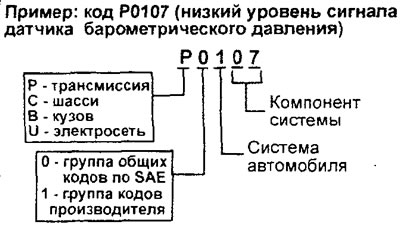
4. Description of the structure of the standard DTC for system type 0E3D-II.
A) The letter shows the purpose (application area) faulty device: P - transmission (engine and gearbox), C - chassis, B - body, U - on-board electrical network, b) The first digit of the code after the letter indicates either a group of common SAE codes (0), or a group of specialized manufacturer codes (1).
V) The second digit of the code after the letter indicates the specific vehicle system in which the malfunction is present. For example, if the application is transmission (R), then the following 8 systems are defined for it: 1 - fuel system and air supply system, 2 - fuel system and air supply system (only types of malfunctions in the injector circuit), 3 - ignition system or misfiring in cylinders, 4 - additional emission control system (emission), 5 - vehicle speed control system and idle speed control system, 6 - circuits of various electronic control systems, 7 and 8 - transmission (Transmission).
G) The remaining 2 digits indicate the specific component of the system.
Recommendations for troubleshooting by codes
1. Before looking for the cause of the malfunction, check that the battery voltage is 10V or more, then check the circuit "masses" engine control unit.
2. If the DTC continues to appear even though testing has shown that the systems/circuits being tested are OK (no faults found), substitute a known-good engine-ECU, road test, and recheck.
3. Replace the engine control unit only after checking the voltage at its outputs to confirm that there is no open or short circuit in the circuits.
4. If the DTC does not set and the engine stalls or the engine does not start, if the diagnostic circuit is OK, replace the engine control module.
5. For most items diagnosed using codes, the main causes of the malfunction are:
- A) Corresponding element defect (specified in code detail, see code table);
- b) Poor contact in the cell connector, broken wiring or short circuit in the cell circuit (power chains, "masses", signal);
- V) Defective electronic engine control unit.
Checking with functions "SERVICE DATA" And "ACTUATOR TEST" tester
1. Check using the menu item "SERVICE DATA" And "ACTUATOR TEST" tester. In the event of a malfunction, check the vehicle's electrical wiring, relevant components and parts.
Attention: when moving the selector lever to the position "D", keep the brake pedal depressed to prevent the vehicle from moving.
Note: the time of the open state of the injector is determined when the crankshaft is rotated by the starter at a frequency of not more than 250 rpm, when the supply voltage is not less than 11V.
2. After the repair, recheck with a tester to make sure that the incorrect input and output signal is correct as a result of the repair.
3. Delete diagnostic codes of malfunction from memory of the electronic control unit of the engine.
4. Start the engine and carry out a road test to ensure that the problem is corrected.
Data of the current state of the engine ("freeze")
In case of detection of several faults, the memory of the control unit will store "freeze" data only for the fault that was detected first. Table "freeze frame" This data lists the components, information about the state of which will be recorded in the memory of the electronic engine control unit in the event of a malfunction.
Road test troubleshooting
1. Ready for road testing.
A) The electronic engine control unit constantly determines the status of the following parameters for their compliance with the norm, while storing the received data in memory:
- (Engine 4G15) oxygen sensor (code P0130), oxygen sensor heating element (code P0135).
- (Engine 4G15) oxygen sensors (codes P0130 and P0136), oxygen sensor heating elements (codes P0135 and P0141).
b) This data can be read with a tester (if the state of the parameter was determined earlier, then this is confirmed by the corresponding entry, for example "Complete").
Note: if the fault codes have been cleared or the wires from the battery have been disconnected, then these data will also be erased from memory.
2. Troubleshooting with a road tester.
A) Using a tester, switch the diagnostic mode of the electronic engine control unit to the mode "DIAGNOSIS 2".
b) Carry out road tests.
V) Read fault codes and determine the location of the fault.
G) Switch off and then switch on the ignition.
Note: after turning off the ignition, the engine control unit will automatically enter the diagnostic mode "DIAGNOSIS 1".
d) Erase the trouble codes.
Explanations on the operation of the system in emergency mode (replacement of incorrect signals)
When the self-diagnosis system detects a malfunction of one of the main sensors, the engine management system switches to emergency control mode (FAIL SAFE FUNCTION), replacing the incorrect signal with the signal previously stored in the memory of the electronic control unit so that the car can continue moving (to the place of repair).
1. If the intake manifold absolute pressure sensor is faulty (4G 15 engine) il mass air flow sensor (4G93 engine), That:
- A) Uses signals from throttle position sensor and crankshaft position sensor to determine injector opening base period (fuel supply) and basic ignition timing in accordance with a given program.
- b) The idle speed control servo is fixed in the programmed position, as a result, idle speed control is not performed.
Table. "Freeze" data.
| № | Parameter | Unit rev. |
| 21 | coolant temperature sensor | °C |
| 22 | crankshaft position sensor | rpm |
| 24 | Vehicle speed sensor | km/h |
| 81 | Long term fuel balance | % |
| 82 | short term fuel balance | % |
| 87 | Calculated load | % |
2. (Engine 4G15) If the air temperature sensor in the intake manifold is faulty, then the air temperature in the intake manifold is assumed to be 45°C.
3. (Engine 4G93) If the intake air temperature sensor is defective, the intake air temperature is assumed to be 25°C.
4. If the throttle position sensor is faulty, then there is no increase in fuel supply when the accelerator pedal is pressed (signal from the throttle position sensor).
5. If the coolant temperature sensor is faulty, then:
Engine coolant temperature is assumed to be 80°C (the system will continue to operate normally (even if the sensor signal becomes normal), until the ignition key is turned to the "LOCK" (OFF)).
6. If the camshaft position sensor is faulty, then:
Fuel is supplied to all cylinders at the same time (it is assumed that at the moment the ignition was turned on, the piston of the first cylinder was not at TDC).
7. If the barometric pressure sensor is faulty, then the air pressure is assumed to be 101 kPa (758 mmHg)
8. If the knock sensor is faulty, the electronic control unit switches the ignition timing from the value set for PREMIUM or SUPER gasoline (95 RON research method), to the value set for REGULAR or STANDARD petrol (91 RON by research method).
9. If the ignition coil is faulty (power transistor), then the fuel supply to the cylinders for which the ignition signal is incorrect is stopped.
10. (Engine 4G 15) If the oxygen sensor is faulty, then the air-fuel ratio will not be regulated (no feedback control).
11. If there is no signal from the FR output of the generator, then the output voltage of the generator is not controlled by the electrical load (works like a normal generator).
Table. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (4G15 engine).
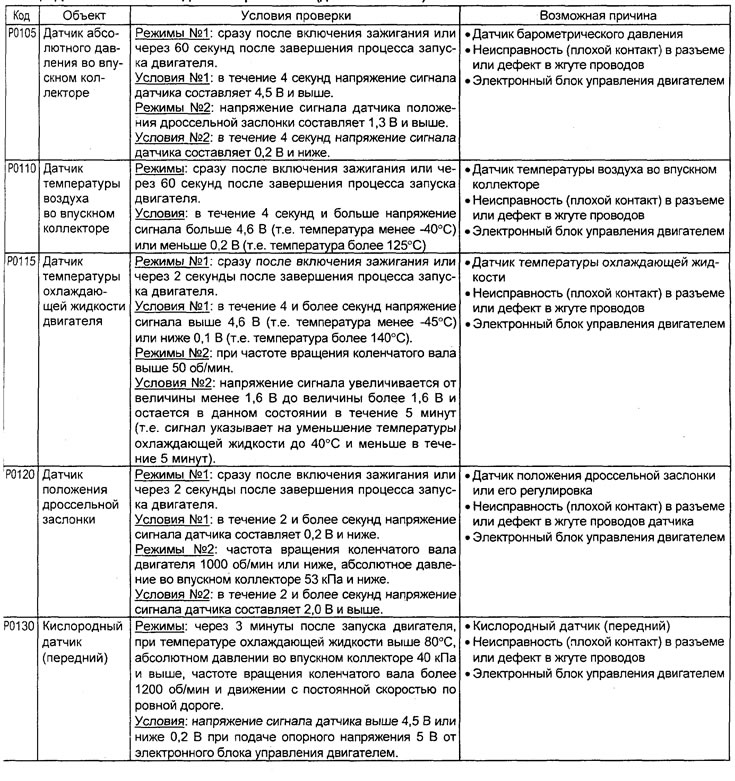
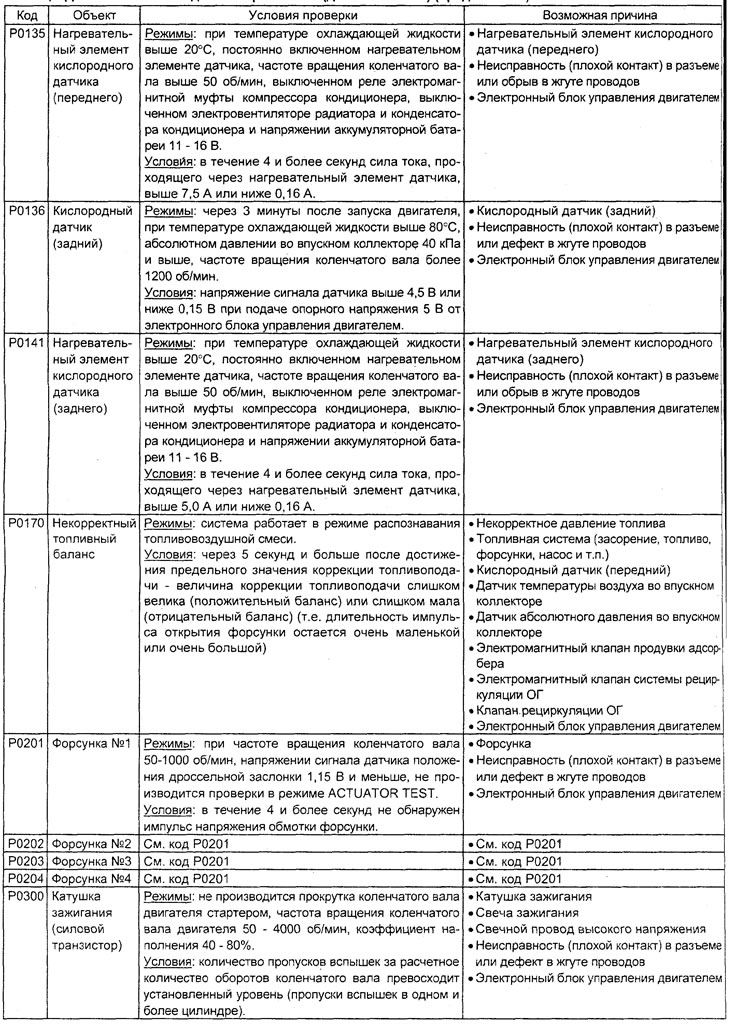
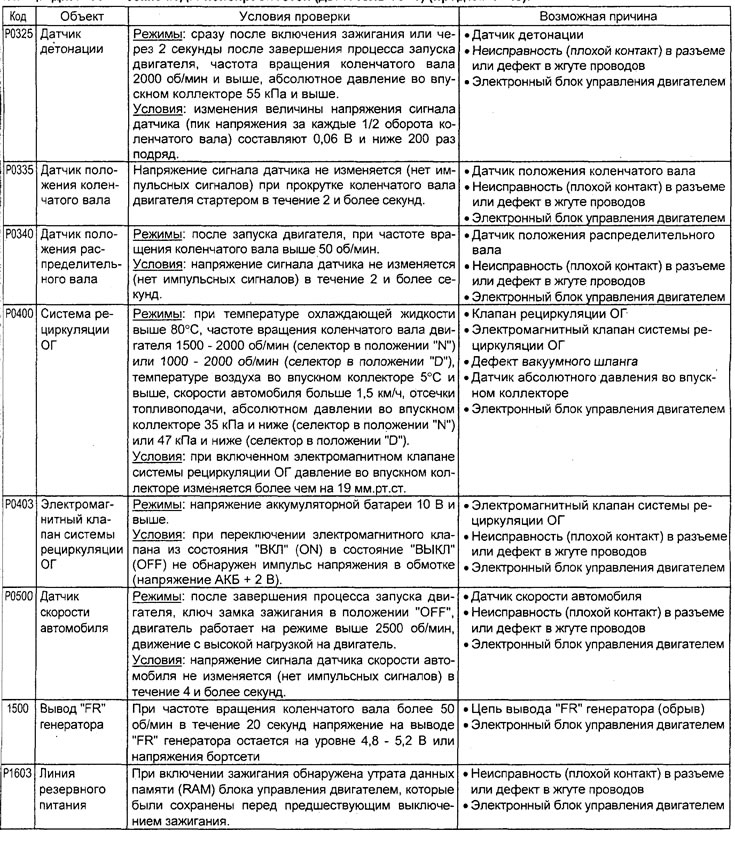
Table. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (4G93 engine).

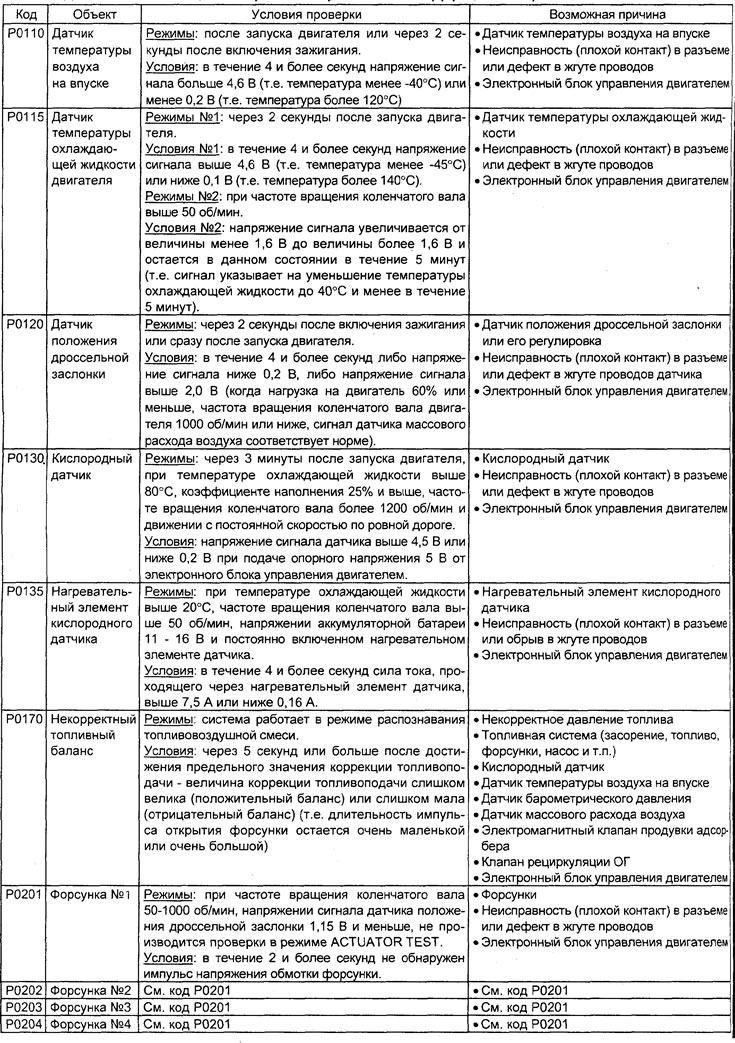
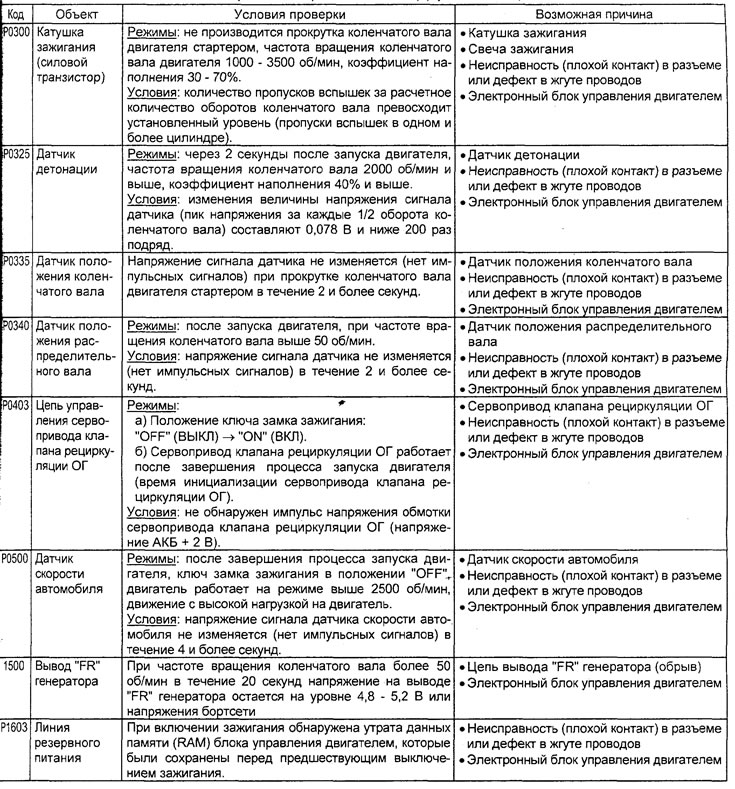
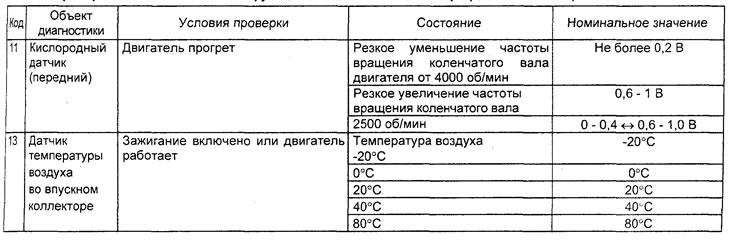
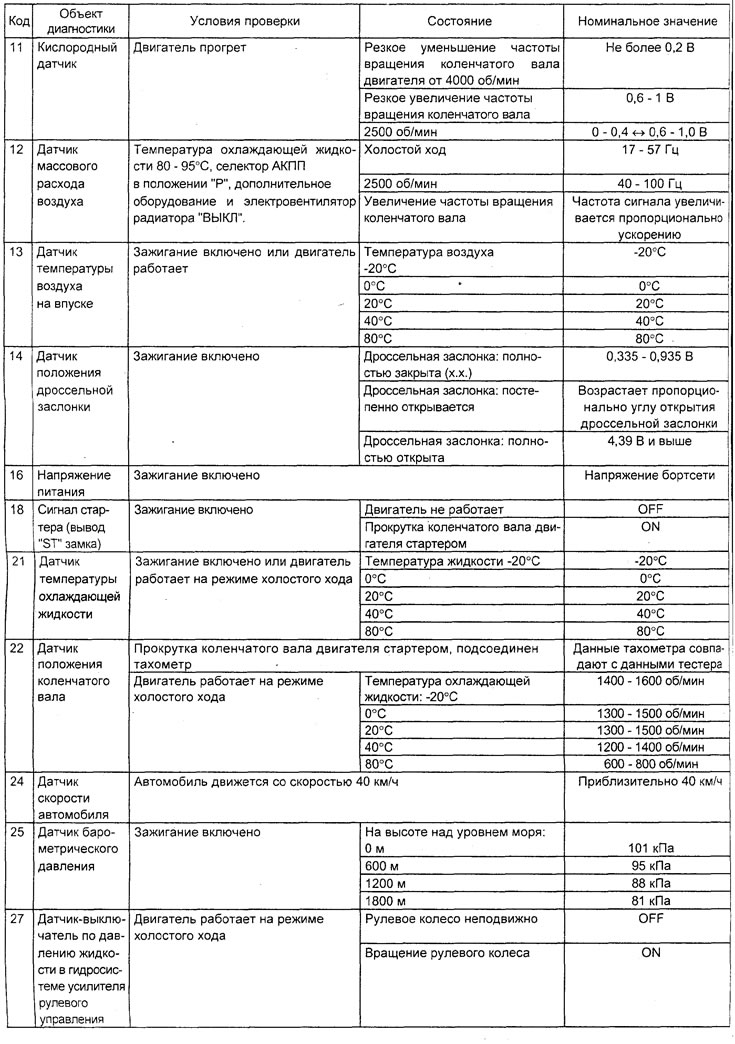
Table. Checking the system using the function "SERVICE DATA" tester (4G15 engine).
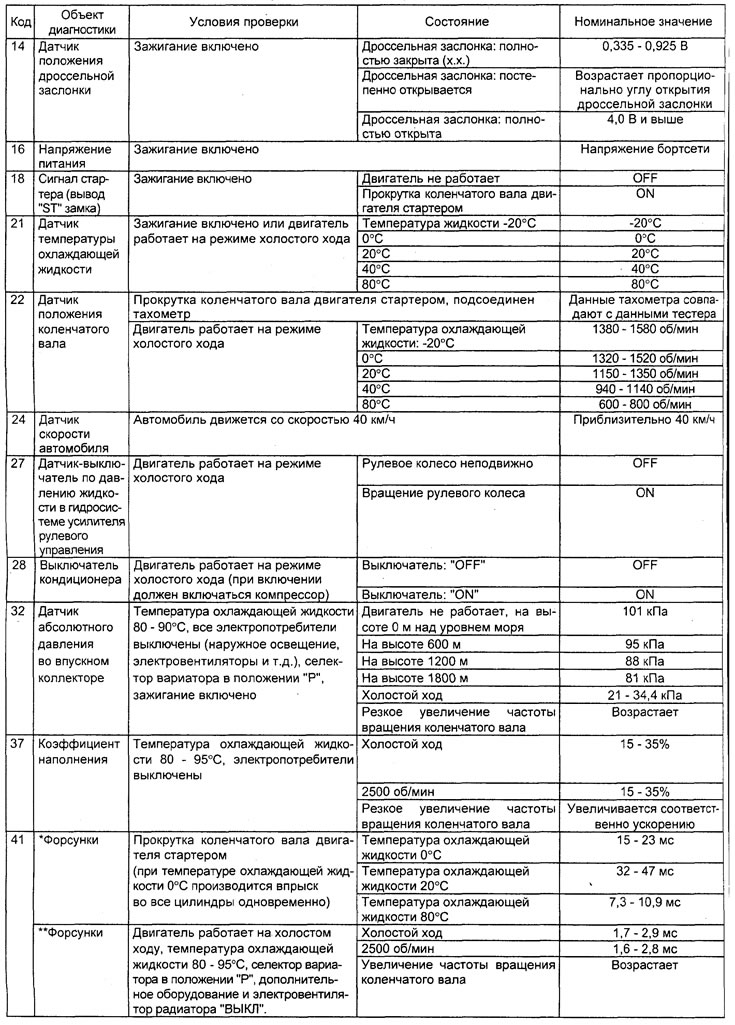
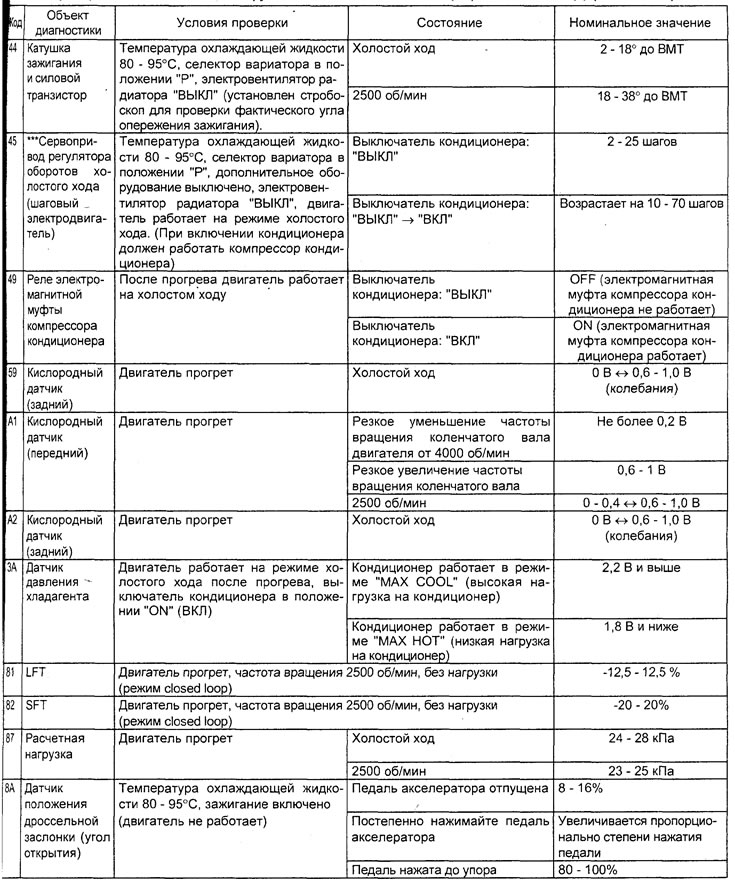
Note: in the table, symbols indicate:
- - When the selector lever of the variator or automatic transmission is moved to the position "D", keep the brake pedal fully depressed to prevent the vehicle from moving forward;
- The injector response time period is determined by the voltage supply time and the engine speed (250 rpm or less). With an increase in the frequency of rotation of the crankshaft, the response time of the nozzle decreases.
- On a new car (with a mileage of 500 km or less) the result can sometimes differ up to 10% from the nominal value.
- On a new car (with a mileage of 500 km or less) the result can sometimes differ up to 30 steps from the nominal value.
- − LFT - long-term fuel balance.
- SFT - short term fuel balance.
Table. Checking the system using the function "SERVICE DATA" tester (4G93 engine).
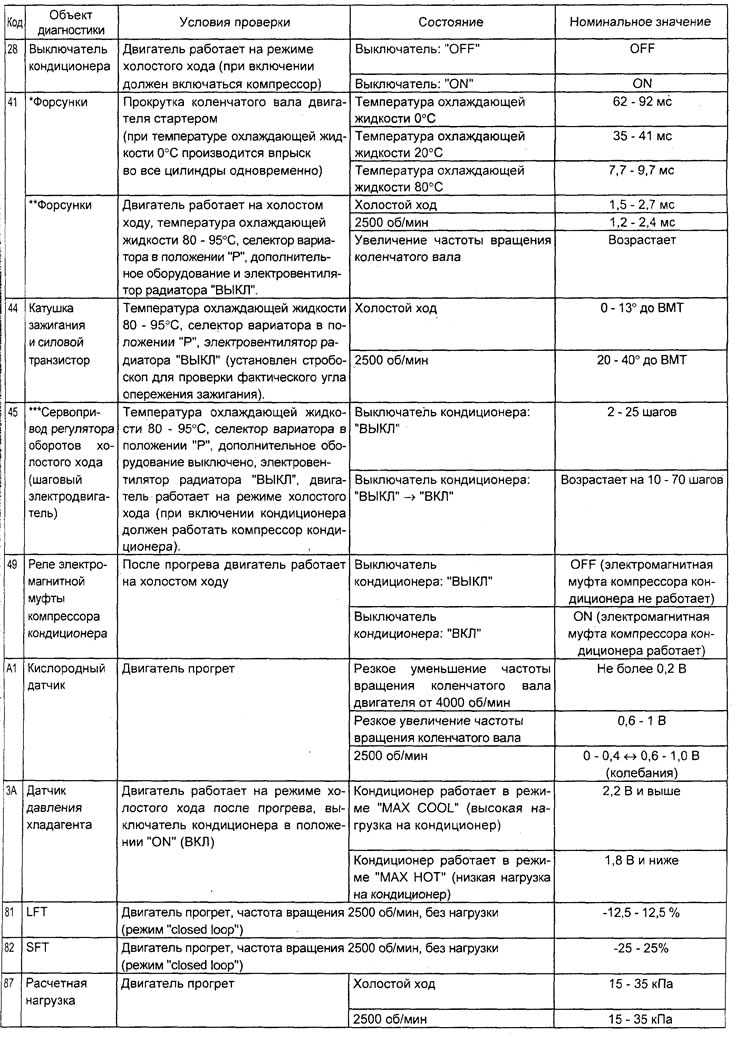
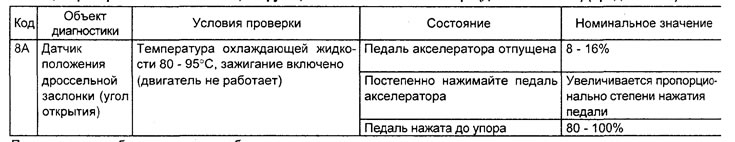
Note: in the table, symbols indicate:
- When moving the selector lever of the variator or automatic transmission to the position "D", keep the brake pedal fully depressed to prevent the vehicle from moving forward;
- The injector response time period is determined by the voltage supply time and the engine speed (250 rpm or less). With an increase in the frequency of rotation of the crankshaft, the response time of the nozzle decreases.
- On a new car (with a mileage of 500 km or less) the result can sometimes differ up to 10% from the nominal value.
- On a new car (with a mileage of 500 km or less) the result can sometimes differ up to 30 steps from the nominal value.
- LFT - long term fuel balance.
- SFT - short term fuel balance.
Table. Checking the system using the function "ACTUATOR TEST" tester.