GDI engine design
The main differences in the design of the GDI engine from the engine with distributed fuel injection (MPI).
1. Higher compression ratio (about 11 -12).
2. Specially shaped intake manifold (with resonator). The inlet ports are straight vertical to ensure the formation of a so-called. "reverse vortex" air charge, which directs the air-fuel mixture to the candle and improves the filling of cylinders with air.
3. Pistons with a concave bottom, with the help of which the air-fuel mixture is directed to the spark plug area.
4. In addition to the conventional fuel tank pump (low pressure pump) high pressure fuel pump installed (injection pump) with a mechanical drive from the camshaft, developing a pressure of 5.0 - 5.5 MPa. For dosing accuracy, a fuel pressure sensor is installed.
Note: since the normal operation of the injection pump requires thorough fuel cleaning, a multi-stage fuel filtration system is used: in addition to the filter at the pump inlet in the tank and the standard fuel filter, microfilters are installed inside the injection pump.
5. Nozzles with vortex atomizers that create a fuel spray jet of various shapes, depending on the engine operating mode (in power mode - conical, in the mode of combustion of an extra-lean mixture - a compact torch). For signal amplification (voltage 100 V) injector control, a driver for injector control signals is installed.
6. Electronic throttle (servo), controller and using the accelerator pedal position sensor signal. The driver does not directly control the damper, but only "involves" accelerator pedal position sensor. The throttle position is changed by the electronic control unit, depending on the engine operating conditions and sensor signals.
7. EGR unit with EGR valve actuator (stepper motor). Exhaust gas recirculation is carried out mainly when the engine is running in super-lean combustion mode.
8. Separate ignition coil for each candle. High voltage spark plug wires are not used.
9. An additional control lamp is installed on the instrument cluster to indicate the inclusion of the mode "GDI ECO" (super-lean combustion mode).
10. For the electronic control unit of the engine and the variator, except for the signals of the components marked in the figure "General scheme of the GDI fuel injection system", signals from the ignition switch are also used (conclusion "ST" And "IG"), power lines, air conditioner switch, air conditioner load, refrigerant pressure sensor, start inhibit switch, power steering hydraulic fluid pressure switch, output "FR" alternator, brake light switch, electrical control unit, throttle servo controller, accelerator pedal position sensor (channel #1), the sensor-switch of the fully released accelerator pedal and the signal for opening the injector circuit (control).
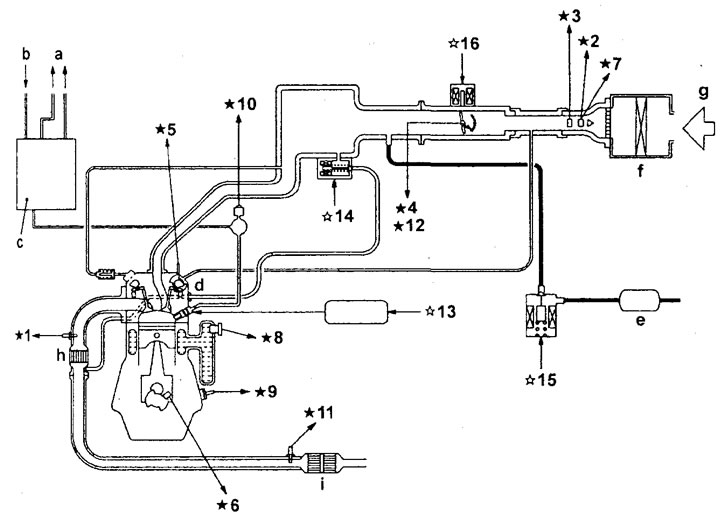
General scheme of the GDI fuel injection system. 1 - oxygen sensor, 2 - mass air flow sensor, 3 - intake air temperature sensor, 4 - throttle position sensor (channel #2), 5 - camshaft position sensor, 6 - crankshaft position sensor, 7 - atmospheric pressure sensor, 8 - engine coolant temperature sensor, 9 - knock sensor, 10 - fuel pressure sensor, 11 - catalytic converter temperature sensor, 12 - sensor throttle position (channel #1), 13 - injector control signal generator, 14 - EGR valve servo drive, 15 - canister purge solenoid valve, 16 - throttle valve servo drive; a - to the fuel tank, b - from the low pressure fuel pump, c - high pressure fuel pump (injection pump) and fuel pressure regulator (high pressure), d - injector, e - canister, f - air filter, g - air, h - pre-catalytic converter (on the exhaust manifold), i - main catalytic converter (under the car floor).
Note: the signals of the marked components are used by the electronic engine control unit; noted "☆ " components are executive devices.
11. Actuating devices are, along with the marked components, relays (#1 and #2) in-tank fuel pump, main injection system relay, A/C compressor magnetic clutch relay, indicator light "CHECK ENGINE" (check the engine), self-diagnosis circuit, ignition coils, output "G" alternator, oxygen sensor heating element, injector control relay, throttle servo relay, throttle servo controller, mode enable indicator "GDI ECO", electric fan controller.
12. Throttle position sensor signal (channel #1) used by the throttle servo controller. Signals from the power line, the accelerator pedal position sensor are also used (channel #2) and an electronic control unit for the engine and variator.
GDI engine operating modes
The GDI engine uses three fuel delivery modes to precisely control the combustion process.
Note: a - air/fuel ratio.
1. Mode of combustion of an extra-lean mixture (mode "GDI ECO").
This mode is active when the vehicle is moving at a constant speed (up to 120 km/h) or the engine is idling. Fuel is injected at the end of the compression stroke in a compact jet, bounces off the piston crown and is directed towards the spark plug area. Although the mixture in the main volume of the combustion chamber is extremely lean (a ~ 30-40), but the charge in the spark plug area is enriched enough to be ignited by a spark and ignite the rest of the mixture.
Note: when the engine is running in this mode, the mode enable indicator lights up "GDI ECO" on the instrument cluster.
2. Power mode.
This mode is active when the vehicle is moving at high speed or accelerating. Fuel is injected during the intake stroke, mixing with air and forming a homogeneous (homogeneous) mixture, as in a conventional port injection engine. The composition of the mixture is close to stoichiometric (a ~ 15).
3. Two-stage mode (Applies to left hand drive models only).
A) This mode is active when the vehicle is accelerating strongly to provide maximum torque at low revs. A smaller part of the fuel is injected first on the intake stroke, cools the air and forms an extra-lean mixture (a ~ 60). Most of the fuel is then injected on the compression stroke and the mixture is significantly richer (a ~ 12). When the mixture is burned, high power and engine torque are achieved,
b) This mode (in combination with a specially designed exhaust manifold) can be used to quickly warm up the three-way catalytic converter after starting the engine.
