General information
1. Exhaust gas recirculation system reduces nitrogen oxide emissions (NOx). At a high temperature of the air-fuel mixture burning in the combustion chamber, a large amount of nitrogen oxides is formed (NOx). The exhaust gas recirculation system directs part of the exhaust gases from the cylinder head outlet through the intake manifold back to the combustion chambers, thereby lowering the combustion temperature of the air-fuel mixture, resulting in a decrease in the concentration of nitrogen oxides.
2. The amount of bypassed exhaust gases is controlled by the EGR valve servomotor (except for 4G15-MPI engine) or EGR valve (4G15-MPI engine) so as not to degrade engine performance.
3. The EGR valve is closed and no EGR occurs under one of the following conditions: engine coolant temperature is low, the engine is idling, or the throttle is wide open. For everyone (In other modes, the EGR valve is open and exhaust gas recirculation takes place.
Checking the servomotor of the exhaust gas recirculation valve (except for 4G15-MPI engine)
Checking the servo by the sound of its operation
1. Check that the operating sound of the EGR valve servo is clearly audible (stepper motor) when the ignition is turned on (without engine start).
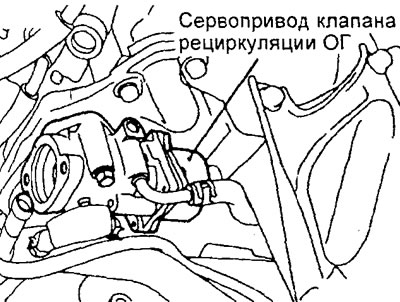
Engine 4G15-GDI.
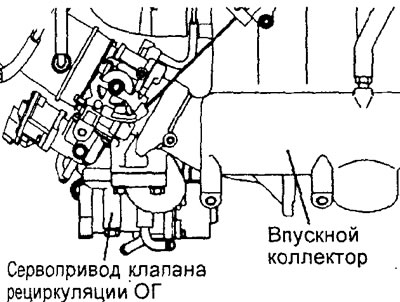
Engine 4G93-GDI.
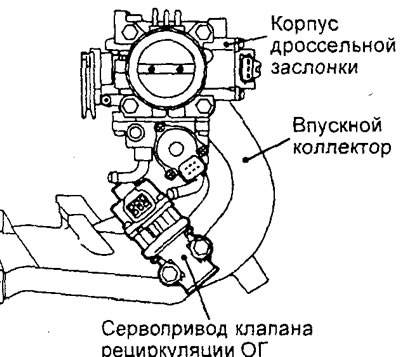
Engine 4G93-MPI.
2. If the sound of the operating EGR valve servo is not audible, then check the power supply circuits of the servo. If the power supply circuit is working, then the servo itself or the electronic engine control unit may be faulty.
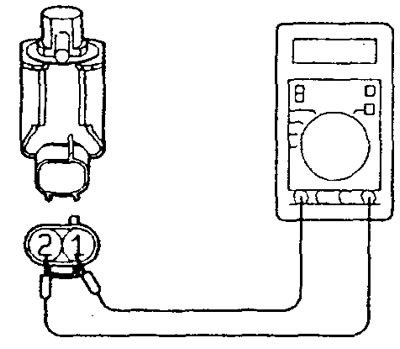
Checking the resistance of the servo winding
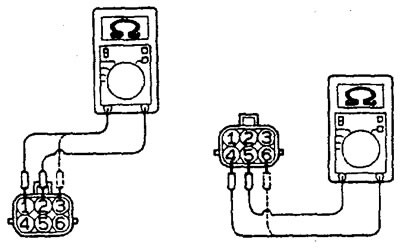
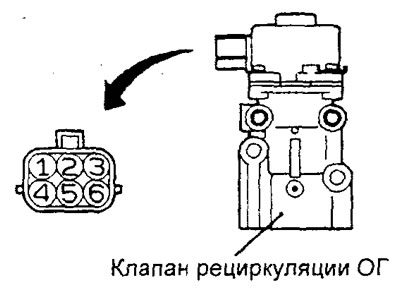
1. Disconnect the EGR valve servo connector.
2. Measure the resistance between the terminal "2" and output ''1'' or "3" servo connector.
Rated resistance:
- GDI - 10-20 Ohm (at 20°C)
- 4G93 - MPI 20 - 24 Ohm (at 20°C)
3. Measure the resistance between the terminal "5" and conclusion "4" or "6" servo connector.
Rated resistance:
- GDI - 10 - 20 Ohm (at 20°C)
- 4G93 - MPI 20-24 Ohm (at 20°C)
Checking the operation of the servo
1. Remove the EGR valve servomotor.
2. Connect the test lead harness to the EGR servo connector.
3. Connect the wire from the positive terminal of the power supply (voltage approx. 6 V) to the conclusion "2" servo connector.
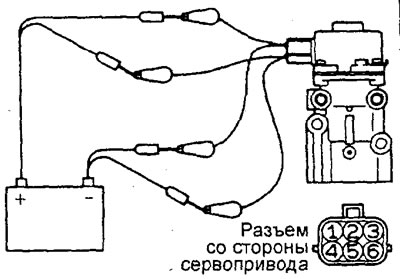
4. Connect a wire from the negative terminal of the 6V power supply to the terminals "1" And "3" connector. At the same time, check if you can feel a slight vibration of the running stepper motor.
5. Connect the wire from the positive terminal of the power supply (voltage approx. 6 V) to the conclusion "5" servo connector.
6. Connect a wire from the negative terminal of the 6V power supply to the terminals "4" And "6" connector. At the same time, check if you can feel a slight vibration of the running stepper motor.
7. If, as a result of these checks, a slight vibration of a working servo is felt, then it is considered serviceable.
8. Replace the gasket and tighten the valve mounting bolts to nominal torque.
Tightening torque - 16- 22 N.m
Cleaning the EGR valve
1. Remove and check the EGR valve for sticking or obstruction. If necessary, clean the valve with a wire brush.
Attention: Do not use solvent for cleaning, as it may cause malfunctions if it gets on the servomotor.
2. Replace the gasket and tighten the valve mounting bolts to nominal torque.
System check (4G15-MPI engine)
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (with green stripe) from the EGR valve (EGR) and then connect a hand vacuum pump through the tee between the valve and the hose.
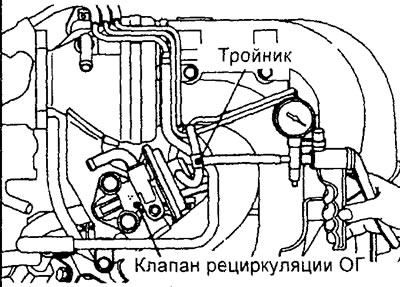
2. Perform the test when the engine is cold (coolant temperature 20°C or less).
Depress the accelerator pedal sharply, increasing the engine speed, and check that no vacuum is generated (atmospheric pressure 0 kPa).
3. Perform the check when the engine is warm (coolant temperature 80°C or more).
Depress the accelerator pedal sharply, increasing the engine speed, and check that the vacuum temporarily increases momentarily to 13 kPa (100 mmHg) or more.
4. Disconnect the tee and connect a hand vacuum pump directly to the EGR valve. Plug open vacuum hose.
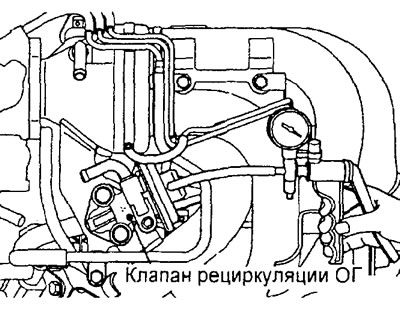
5. Create a vacuum of more than 27 kPa when the engine is idling, and check that the engine has stalled or its idling has become unstable.
Checking the vacuum control valve (4G15-MPI engine)
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (with white stripe) away from the valve and connect a hand vacuum pump to the valve port.
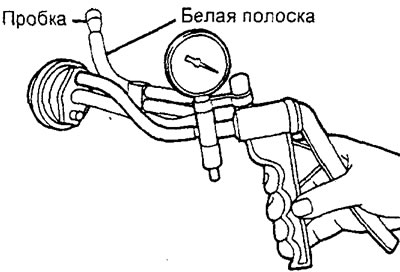
2. Plug the disconnected vacuum hose.
3. Start the engine and let it idle.
4. Check vacuum.
Nominal value - approx. 23 kPa
Exhaust gas recirculation valve test (4G15-MPI engine)
1. Remove the EGR valve and check for valve stem sticking, carbon deposits, etc. If deposits are present, clean the valve with solvent to ensure that the valve stem seats correctly.
2. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the EGR valve diaphragm connection.
Note: if there are two fittings on the valve diaphragm, then close the second fitting with a plug.
3. Using the pump, create a vacuum of 67 kPa and check that it is maintained.
4. Check the passage of air through the valve (through the exhaust gas channel).
A) Create a vacuum of less than 7 kPa and make sure that air does not pass through the valve.
b) Create a vacuum of more than 27 kPa and check that air passes through the valve.
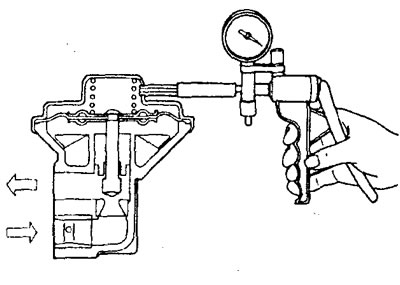
5. Replace the gasket and tighten the valve mounting bolts to nominal torque.
Tightening torque - 17 - 25 N.m
Checking the underpressure line of the exhaust gas recirculation valve (4G15-MPI engine)
Note: Before checking, warm up the engine so that the coolant temperature reaches 80-95°C.
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (with green stripe) from the EGR vacuum hose connection (on throttle body) and connect the hose to the hand vacuum pump.
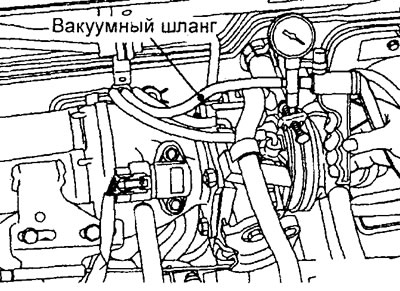
2. Start the engine and check that the amount of vacuum remains almost constant as the engine speed increases.
Note: If the vacuum value changes with increasing engine speed, then the EGR vacuum hose fitting in the throttle body is probably clogged and needs to be cleaned.

Checking the EGR solenoid valve (4G15-MPI engine)
Note: when disconnecting the vacuum hose, pre-mark the alignment marks so that the bull is in its original position when the hose is connected.
1. Disconnect the vacuum hoses from the solenoid valve.
2. Disconnect the harness connector from the solenoid valve.
3. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the "A", from which the hose was disconnected (with green stripe).
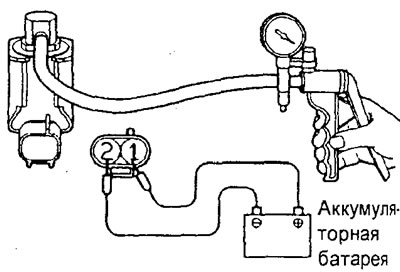
4. Create a vacuum with a vacuum pump and check the operation of the solenoid valve.
A) Check that the vacuum in the valve is maintained when battery power is connected to the valve terminals.
b) Check that the valve vacuum decreases when battery power is not connected to the terminals.
5. Measure the resistance between the solenoid valve leads.
Rated resistance - 29 - 35 Ohm (at 20°C)
Removal and installation of the EGR valve actuator (except for 4G15-MPI engine)
Before you start removing parts, do the following:
- A) (GDI engines) Drain the coolant.
- b) Remove the air filter assembly.
Removal of parts is carried out in the order of the numbers indicated in the figure "Removing the EGR valve actuator".
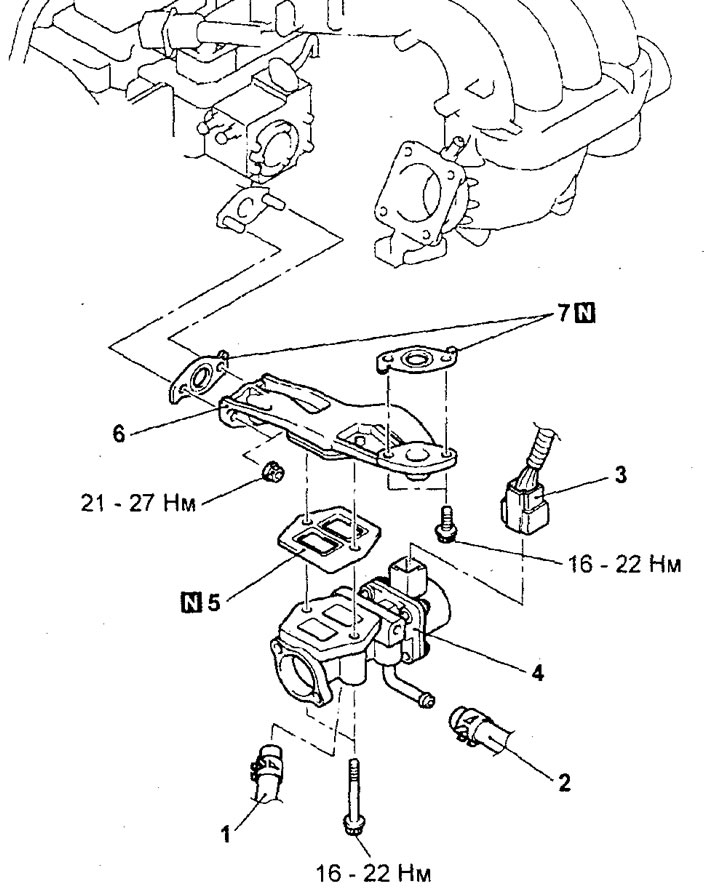
Removing the EGR valve actuator (4G15-GDJ engine). 1 - coolant hose, 2 - coolant hose, 3 - EGR valve servo harness connector, 4 - EGR valve servo, 5 - gasket, 6 - EGR pipe and EGR valve servo bracket, 7 - pipe gasket exhaust gas recirculation systems.
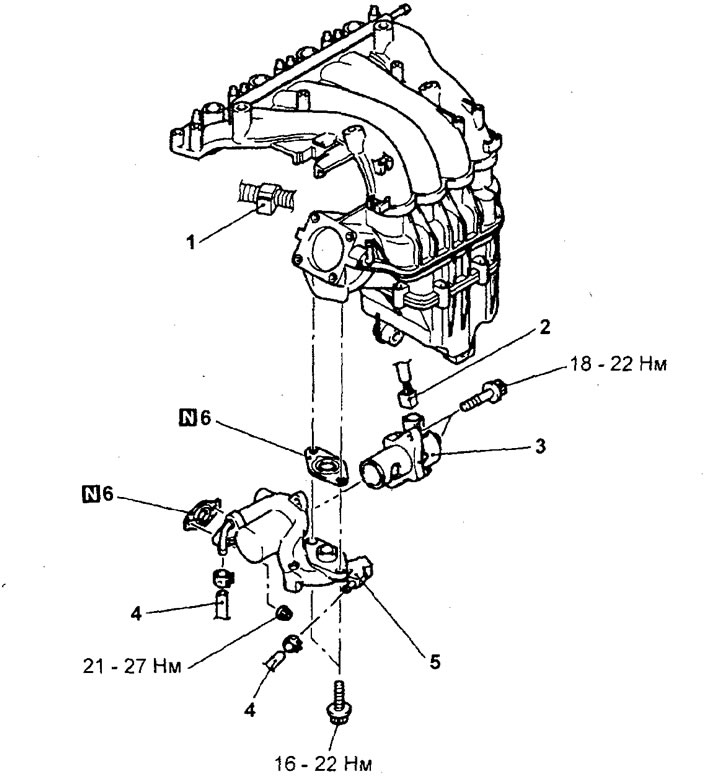
Removing the EGR valve actuator (engine 4G93-GDI). 1 - wire harness retainer, 2 - EGR valve servo harness connector (remove intake manifold), 3 - EGR valve actuator, 4 - cooling system hose, 5 - EGR pipe and EGR valve actuator bracket, 6 - EGR pipe gasket.
(GDI engine) When removing parts, pay attention to the operation to remove the fuel pump protective cover.
Raise the gearbox with the transmission telescopic rack, creating a gap between the engine and the windshield wiper panel, and remove the protective casing of the injection pump.
Installation of details is made in an order, the return to removal.
(Except 4G93-GDI engine) When installing the parts, pay attention to the installation procedure for the gasket and EGR valve servo.
A) Install the EGR valve servo gasket as shown in the illustration.
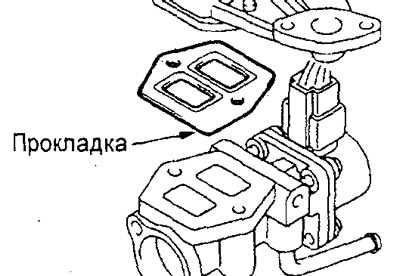
Engine 4G15-GDI.
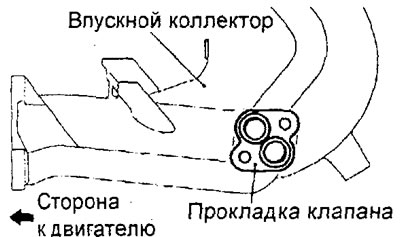
Engine 4G93-GDI.
b) Tighten the servo mounting bolts to the rated torque.
Tightening torques:
- GDI engine - 16-22 Nm
- MPI engine - 21 - 27 Nm
- After completing the installation of the parts, perform the following operations:
- A) Install the air filter assembly.
- b) (GDI engines) Fill with coolant
Removal and installation of the EGR valve (4G15-MPI engine)
Remove the air filter assembly before beginning to remove parts.
Removal of parts is carried out in the order of the numbers indicated in the figure "Removing the EGR valve".
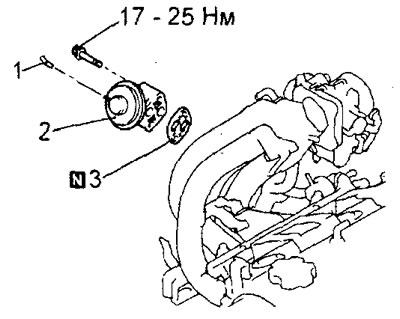
Removing the EGR valve. 1 - vacuum hose connection, 2 - EGR valve, 3 - EGR valve gasket.
Installation of details is made in an order, the return to removal.
After completing the installation of the parts, install the air filter assembly.
