General information
The three-way catalytic converter works in conjunction with the oxygen sensor feedback air-fuel ratio control system. The catalytic converter oxidizes carbon monoxide (SO) and hydrocarbons (CH) and reduces nitrogen oxide emissions (NOx). When the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio is maintained, the three-way catalyst provides the highest cleaning efficiency for three groups of substances, namely: CO, HC and NOx.
Removal and installation
- Parts are removed in the order of the numbers shown in the figure "Removing the catalytic converter".
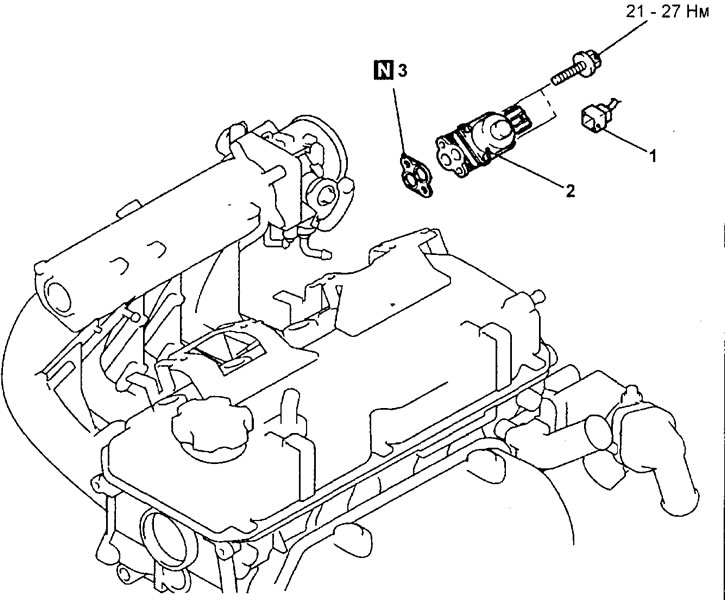
Removing the EGR valve actuator (engine 4G93-MPI). 1 - EGR valve servo harness connector, 2 - EGR valve, 3 - EGR valve gasket.
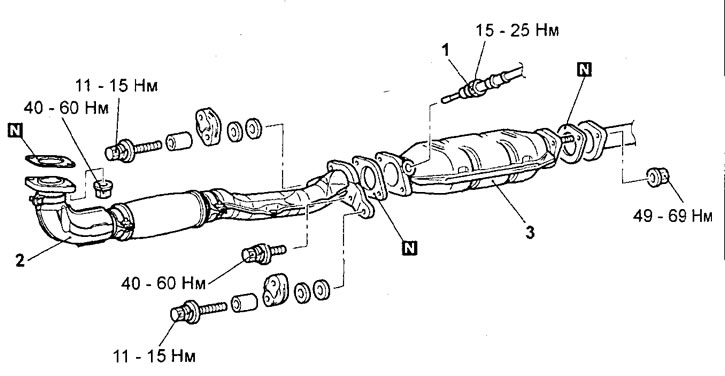
Removing the catalytic converter. 1 - catalytic converter temperature sensor (GDI engines) or oxygen sensor (rear, engine 4G15-MPI), 2 - downpipe of the exhaust system, 3 - catalytic converter.
− Installation of parts is carried out in the reverse order of removal.
Checking the catalytic converter
Check for damage, cracks or melting. Replace the catalytic converter if a malfunction is present.
Attention:
- - Necessary maintenance and adjustments in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications must be carried out as soon as possible.
- - Do not run the engine (including at idle), if the engine is misfiring, as the exhaust system will then have an abnormally high temperature that could damage the catalytic converter or parts under the vehicle body.
- - Change of design or deterioration of technical condition (destruction, aging, wear or oxidation) ignition or fuel system, or a change in the operating state of any other system that could cause the engine to misfire, must be corrected immediately to prevent overheating of the catalytic converters.
