Steering wheel play check
1. When the engine is idling (power steering works) Install the front wheels parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle.
2. Slightly turning the steering wheel in both directions until the front wheels begin to turn, measure the free play (backlash) steering wheel on its rim.
Maximum allowable value - 30 mm
3. If the steering wheel play exceeds the maximum allowable value, then check for clearances in the steering shaft connections and steering rods. Repair or replace worn parts.
4. If, as a result of checking on the item (3) If the steering wheel play still exceeds the limit, align the front wheels parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle with the engine off. Apply a force of 5 N to the steering wheel rim and check the play.
Rated value (with the engine off) - 10 mm or less
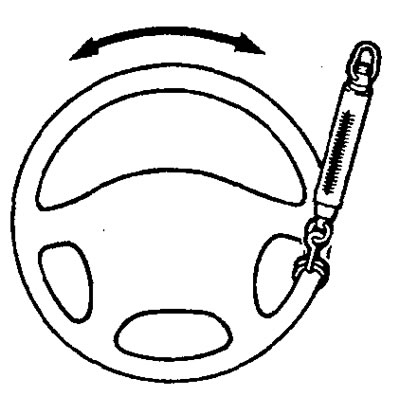
5. If the backlash exceeds the nominal value, then remove the steering gear and check the total torque of the steering gear drive gear.
Checking the angle of rotation of the steered wheels
1. Mount the front wheels on a turn radius measuring stand and measure the steering angles.
Rated value:
- Inner wheel - 40°40'±1°30'
- Outer wheel - 33°
2. If the steering angles do not correspond to the nominal values, then the amount of convergence of the front wheels is probably not adjusted. Adjust the toe and check the steering angles again.
Check of the moment of the beginning of rotation of the spherical joint of a tip of steering draft
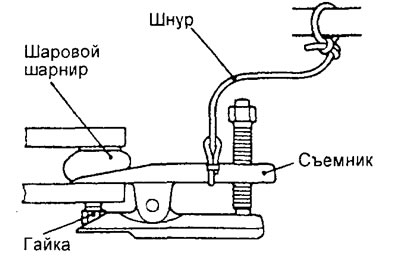
1. Disconnect the tie rod end from the steering knuckle using a puller.
Attention:
- To prevent the puller from jumping off, you must first tie it with a cord.
- Just loosen the fastening nut on the ball joint pin, do not unscrew the nut completely.
2. Move the ball joint pin several times and tighten the nut. Using a special tool, measure the start of rotation of the ball joint.
Nominal value - 0.5-2.5 N.m
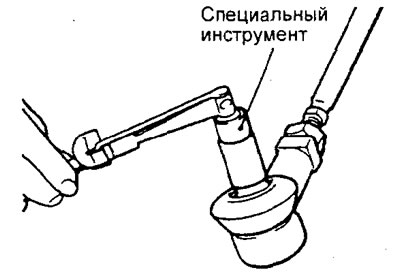
3. If the measured value exceeds the nominal value, then replace the tie rod end.
4. If the measured value is less than the nominal value, then check for increased clearances or jamming in the ball joint. In the absence of these faults, the ball joint is serviceable.
Checking the amount of effort when turning the steering wheel on a stationary vehicle
1. Place the car on a flat horizontal platform and install the front wheels parallel to the longitudinal axis of the car.
2. Start the engine and set its operating mode to 1000±100 rpm.
Attention: after checking the set speed, set the normal idle speed.
3. Install the spring dynamometer on the steering wheel rim. Measure the turning force required to turn the steering wheel from a straight position to the left and right (by 1.5 turns). Also check that there are no significant deviations in the amount of force required on the steering wheel.
Rated value - 29 N or less
Tolerance - 5.9 N or less
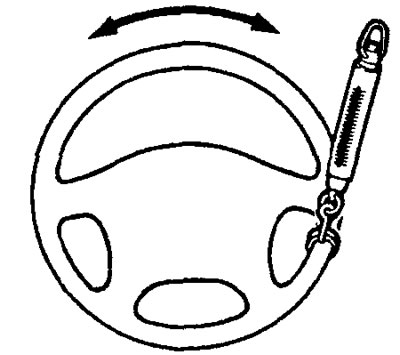
Checking the independent return of the steering wheel to the middle position
1. While driving, make several smooth and then sharp turns of the steering wheel to the right and left in order to check the absence of a difference in efforts on the steering wheel when turning left and right, as well as the presence of a returning moment.
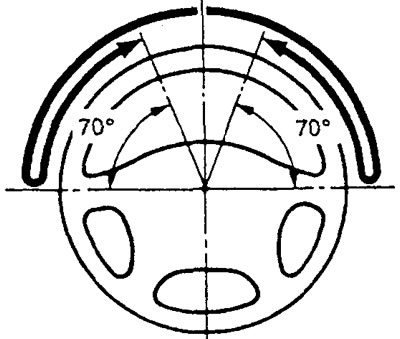
2. When driving at a speed of 35 km/h, turn the steering wheel 90°and release it after 1-2 seconds. If the steering wheel then turns 70°or more towards the center position on its own, then the return of the steering wheel is considered satisfactory.
Note: when turning sharply, there may be an instant sensation of some "gravity" steering wheel, but this is not considered a disadvantage (this feeling occurs due to the low performance of the power steering pump at low engine speeds).
Power steering hydraulic fluid replacement
1. Jack up the front wheels of the car and place the car on sliding (safety) racks.
2. Disconnect the return hose.
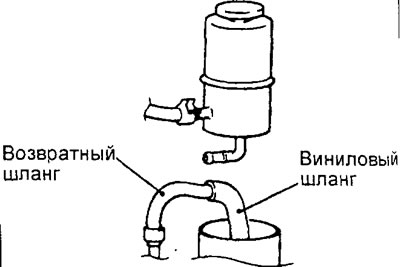
3. Connect the vinyl hose to the return hose and drain the fluid into a suitable container.
4. Disconnect high voltage spark plug wires.
Caution: Do not place high voltage spark plug wires near the fuel manifold.
5. To completely drain the working fluid, make several short-term starts of the starter while constantly turning the steering wheel left and right.
6. Put the return hose back in place and secure it with a clamp.
7. Fill the tank with the recommended liquid to the lower position of the filter, then bleed air from the power steering hydraulic system.
Recommended Fluid - Mitsubishi ATF-SPII
Attention: do not use ATF-SP II M and ATF-SP III fluid in steering.
Removal of air from the hydraulic system of the power steering
1. Jack up the front wheels of the car and place the car on sliding (safety) racks.
2. Manually rotate the power steering pump pulley several times..
3. Make 5 or 6 full turns of the steering wheel left and right.
4. Disconnect high voltage spark plug wires or wires from ignition coils.
Caution: Do not place high voltage spark plug wires near the fuel manifold.
5. Make several short turns on the starter while constantly turning the steering wheel left and right (five or six times within 15-20 seconds).
Attention:
- During bleeding, it is necessary to constantly top up the working fluid and make sure that its level does not fall below the lower position of the filter.
- If air is removed while the engine is running, then air will be sucked in and enter the working fluid. Therefore, the removal of air from the hydraulic system must be carried out only when the crankshaft of the engine is turned by the starter.
6. Connect spark plug wires or wires from ignition coils.
7. Turn the steering wheel to the right and to the left until the air bubbles in the power steering reservoir disappear.
8. Make sure that the working fluid is clear, without turbidity, and its level in the tank corresponds to the normal position on the dipstick.
9. Be convinced that the difference of liquid levels at the left and right turns of a steering wheel is insignificant.
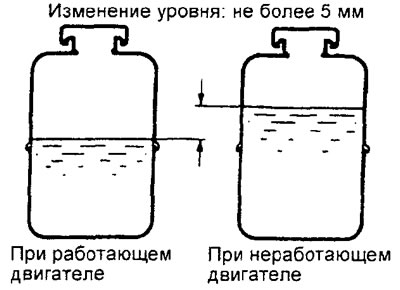
10. Make sure that the difference between the level of the working fluid in the tank when the engine is running and after the engine is stopped is within 5 mm.
11. If the difference in levels has reached 5 mm or more, then the air is not completely removed from the hydraulic system, so the operation of removing air should be repeated, starting from step 2.
Attention:
- If the fluid level rises sharply after stopping the engine, then the air from the hydraulic system is not completely removed.
- If air is not completely bled from the power steering hydraulic system, extraneous noise will occur from the pump and control valve, which will lead to a reduction in the life of the pump and other elements of the hydraulic system.
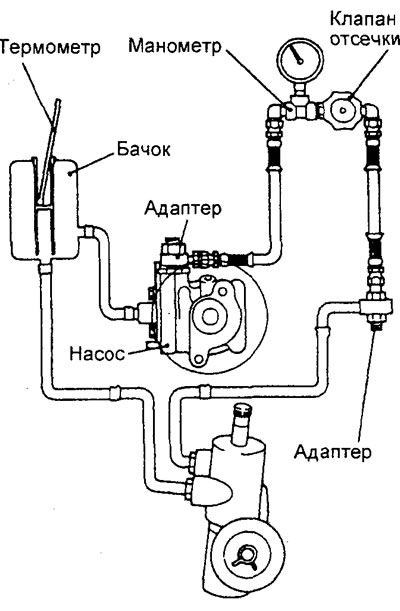
Checking the maximum supply pressure of the hydraulic booster pump
1. Disconnect the pressure hose from the power steering pump and connect the special tools.
2. Remove air from the power steering hydraulic system. Then, with the vehicle stationary, turn the steering wheel several times until the fluid temperature rises to about 50 - 60°C.
3. Start the engine and set its operating mode to 1000±100 rpm.
4. Completely close the shut-off valve on the measuring pressure gauge and measure the power steering pump supply pressure and check that it corresponds to the nominal value.
Rated value - 8.8 MPa
Caution: The shut-off valve should not be closed for more than 10 seconds.
5. If the measured pressure does not correspond to the nominal value, then disassemble and reassemble the power steering pump. Then re-measure the power steering pump supply pressure.
6. Check the pressure in the hydraulic system of the amplifier without load with the cut-off valve fully open.
Rated value - 0.2 -0.7 MPa
7. If the measured value of pressure does not correspond to the nominal value, then the cause of the malfunction should be sought in the steering mechanism or hydraulic hoses. After troubleshooting, re-measure the pressure value.
8. Turn the steering wheel all the way to the left or right and measure the holding pressure of the steering gears.
Rated value - 8.8 MPa
9. If the measured pressure is below the nominal value, then disassemble and reassemble the steering gear. If the measured pressure is higher than the nominal value, disassemble and reassemble the pump fluid flow control valve. Then measure the pressure again.
10. Disconnect gauges, connect pressure hose and tighten hose clamp to rated torque.
Tightening torque - 57±7 N.m
11. Remove air from the power steering hydraulic system.
Checking the fluid pressure switch in the power steering hydraulic system
1. Disconnect the pressure hose from the power steering pump and connect the special tools.
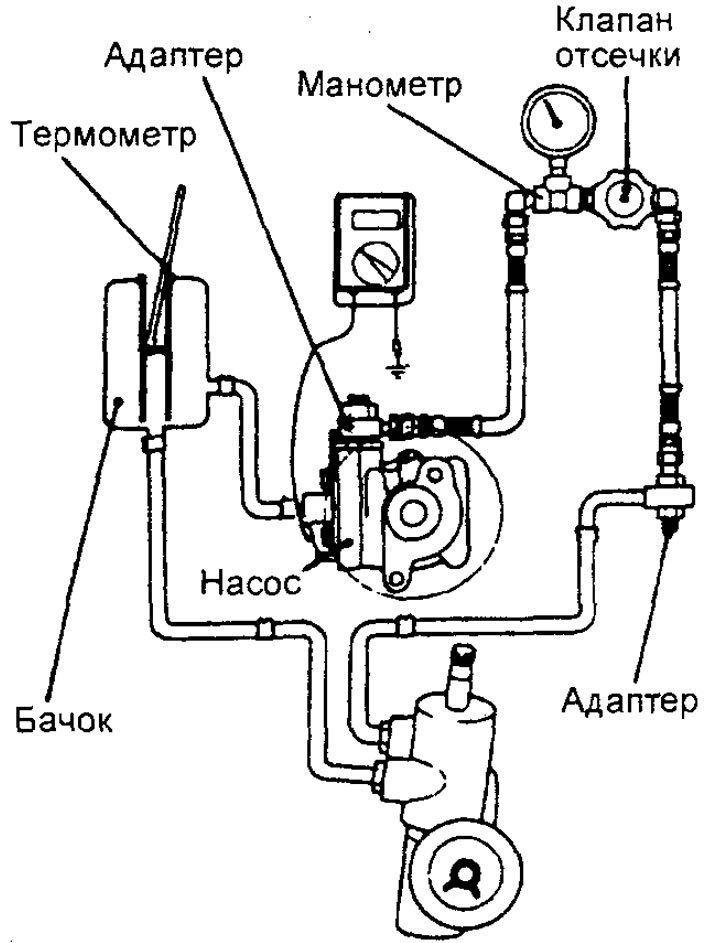
2. Remove air from the booster hydraulic system. With the vehicle stationary, turn the steering wheel left and right several times to raise the fluid temperature to about 50 - 60°C.
3. Start the engine and set the idle speed.
4. Disconnect the connector of the sensor-switch for the pressure of the working fluid in the hydraulic system of the booster and connect an ohmmeter to the connector.
5. Slowly close the cut-off valve on the gauge to increase the working pressure. Check the actuation pressure of the sensor-switch according to the pressure of the working fluid in the hydraulic system.
Rated value - 1.5 - 2.0 MPa
6. Slowly open the shut-off valve on the pressure gauge to decrease the operating pressure. Check the lower pressure threshold of the sensor-switch by the pressure of the working fluid in the hydraulic system.
Rated value - 0.7 -2.0 MPa
7. Disconnect the special tools, connect the pressure hose and tighten the hose fasteners to the specified torque.
Tightening torque - 57 N.m
8. Remove air from the power steering hydraulic system.
Checking the protective boot of the ball joint
1. Apply pressure to the ball joint boot with your finger and inspect the boot for wear, damage, cracks, abrasions or deterioration.
2. If mechanical damages of a protective cover are found out, then replace a tip of steering draft.
Note:
- Cracks and damage to the protective boot can damage the ball joint.
- If the protective cover has been damaged during maintenance work, the protective cover must be replaced with a new one and the test must be repeated.
