If the gap is too small, the distribution phases change, the sealing is poor, the engine power drops, the engine runs unevenly. In extreme cases, deformation of the valves or burning of the valve seats can occur. If the gap is too large, strong mechanical knocks occur, the distribution phases change, due to incomplete filling of the cylinders, the engine loses power and runs unevenly.
Valve clearance adjustment only brings the desired result when the valve seal is perfect, there is no unacceptable play in the guide bushings and the ends of the valve stems are not broken.
Valve clearances should be checked or adjusted after repairs or if valve knocking is present. In addition, it is necessary to check the valve clearance as part of maintenance. 16-valve engines have a hydraulic gap compensator that automatically compensates for gap of any size. Valve clearance adjustment is not required on these engines. If there are unusual noises in the valve train, check the valve clearance compensator, see paragraph 1.19.
Checking and adjusting the valves should be carried out on a hot engine, but can also be carried out on a cold engine. In this case, you have to re-check the valve clearance on a hot engine.
Examination
Start and warm up the engine to a coolant temperature of 80°-90°C.
Turn off the engine.
Petrol engines: Remove all spark plugs.
Diesel engine: Remove upper part of intake manifold, see point 1.10.
Diesel engine: To make work easier, unscrew the glow plugs, see point 9.4.
Remove cylinder head cover.
Set the transmission to neutral position, cock the handbrake.
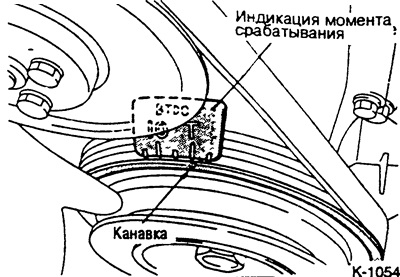
Turn the crankshaft at the central bolt clockwise until the groove on the pulley matches the mark "T". The pistons of the 1st and 4th cylinders are now at TDC. Cylinders are counted from left to right. Cylinder 1 is on the V-belt side of the engine.
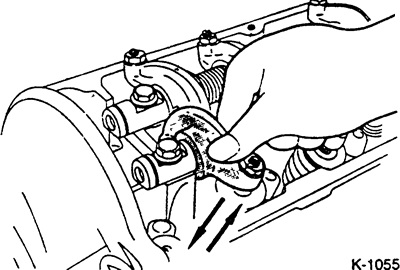
Check which cylinder is at TDC. To do this, move the rocker arms of cylinders 1 and 4 up and down by hand. The piston is at TDC when there is clearance in both the intake and exhaust valves.
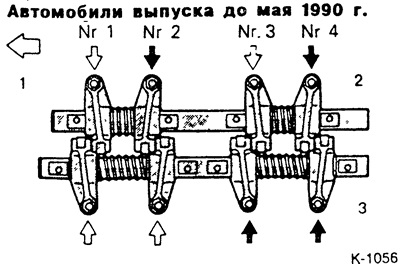
Gasoline engines
1 - camshaft gear side,
2 - the side of the exhaust valves,
3 - the side of the intake valves.
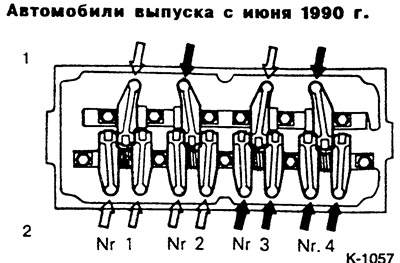
1 - the side of the exhaust valves,
2 - intake valve side
Diesel engine
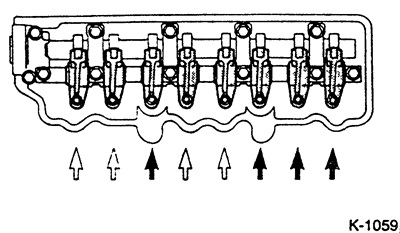
If the piston in cylinder 1 is in the ignition TDC position, then the clearance of the valves marked with white arrows can be adjusted.
If the piston in cylinder 4 is in the ignition TDC position, then the clearance of the valves marked with black arrows can be adjusted.
Attention: To change from one position to another, turn the crankshaft 1 turn clockwise.
Example: Cylinder 1 is at TDC. On vehicles with a petrol engine, the exhaust valves of cylinders 1 and 3 as well as the intake valves of cylinders 1 and 4 can be checked and adjusted "T" Cylinder 4 is now at TDC and the exhaust valves of cylinders 2 and 4 and the intake valves of cylinders 3 and 4 can be checked and adjusted.
Measure the valve clearance with a feeler gauge between the rocker arm and the valve surface.
The clearance is correctly adjusted if the feeler gauge is pulled through with interference, otherwise adjust the valve clearance.
Adjustment
Attention: On engines with a Jet valve, manufactured approximately from September 1986 to August 1988, the adjustment of the Jet valve is always carried out before adjusting the intake valve clearance, see also the subsection at the end of this chapter.
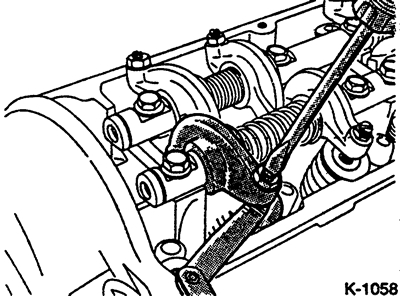
Loosen the locknut about ½ turn while holding the adjusting screw with a screwdriver.
Set the valve clearance by turning the adjusting screw while constantly moving the feeler gauge.
Tighten the locknut.
Check the valve clearance again, readjust if necessary.
Turn the crankshaft one more turn and check and, if necessary, adjust the clearances in other valves.
Attention: It is advisable to mark the rocker arms of already adjusted valves with chalk.
After adjustment, check whether the fixing screws and rocker brackets are well inserted or tightened.
Caution: When adjusting valve clearances on a cold engine, the valve clearances must be checked on a hot engine.
Install the cylinder head cover.
Petrol engine: Screw in the spark plugs, see point 5/32.1.
Diesel engine: Screw in the glow plugs, see point 9.4.
Diesel engine: Install the upper part of the intake manifold, see point 1.10.
Jet valve engine (release circa September 1986 to August 1990)
Engines with Jet valves have additional adjusting screws on the intake rocker arms to adjust the Jet valves. The jet valve is an additional, third valve for 8-valve engines and works from the rocker arms of the intake valves.
Adjust the jet valve clearance before adjusting the intake valve clearance.
When adjusting the jet valve clearance, loosen the intake valve adjusting screw.
If the cylinder head was removed, the cylinder head bolts must be tightened before adjustment.
The clearance of the Jet valve is adjusted in the same way as the clearances of conventional valves.
Attention: Adjustment is somewhat difficult due to the weaker spring. Be careful not to turn the adjusting screw in too much, otherwise the jet valve may be pressed into the cylinder head.
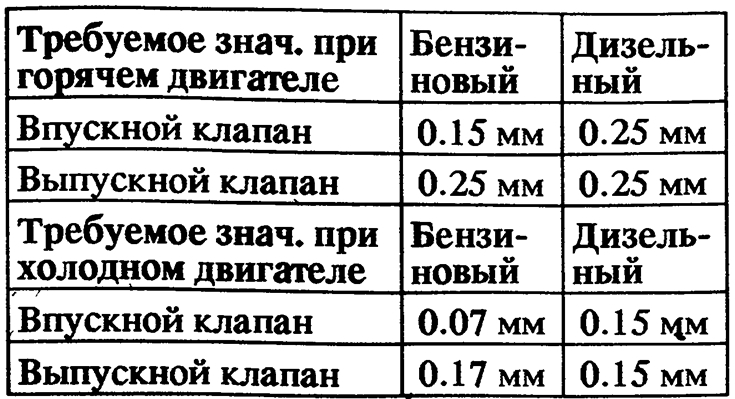
- Required Jet Valve Gap: 0.25mm (hot engine)
- Required Jet Valve Gap: 0.17mm (cold engine)
