The cylinder block is made of gray cast iron. In case of severe wear or scuffing of the cylinder mirror, the cylinders must be honed, that is, ground, in a special workshop. After that, oversized pistons must be installed. At the bottom of the block is the crankshaft in the main bearings. Connecting rods are connected to the crankshaft through plain bearings, which communicate with the pistons. At the bottom of the engine is the oil pan, which collects the engine oil needed to lubricate and cool the engine. On top of the engine, a cylinder head made of aluminum alloy is installed, since this material has better thermal conductivity and less weight compared to cast iron.
The cylinder head of a gasoline engine is designed according to the so-called cross-flow principle. This means that fresh air/fuel mixture enters from one side of the cylinder head and exhaust gases are expelled from the opposite side. The cross-flow design ensures faster gas exchange and therefore more power output. The camshaft is located at the top of the cylinder head. It is driven by the crankshaft through a toothed belt drive and acts through the rocker arms on the V-shaped valves.
Engines 124 and 136 liters. c have two camshafts, one each for the intake and exhaust valves. There are 4 valves for each cylinder, 2 inlet and 2 outlet V-shaped valves open via rocker arms. Since the valve clearance is compensated here by hydraulic tappets, valve clearance adjustment on these engines is not required, the valve mechanism does not require maintenance.
In a diesel engine, the intake and exhaust manifolds tilt to one side of the cylinder head to save space. The camshaft located at the top acts on the vertically located valves through rocker arms, which have roller bearings to reduce noise at the point of contact with the camshaft.
Engine lubrication is provided by an oil pump mounted in front of the engine block in one housing together with the crankshaft oil seal. In this case, we are talking about a sickle-shaped pump, the inner rotor of which is connected to the crankshaft and is driven from it. Oil is pumped from the oil sump and through the holes and channels gets to the bearings of the crankshaft and camshaft, as well as to the working surfaces of the cylinders.
The water pump is built into the engine block and is driven through the alternator V-belt. Attention should be paid to the fact that the engine cooling circuit is filled with antifreeze and anti-corrosion compounds, as well as lime-free water throughout the year
To prepare the air-fuel mixture ready for ignition, COLT / LANCER II models are equipped with a register carburetor with an automatic engine start device, or the fuel injection device for 1.6l COLT / LANCER III engines is equipped with an electronic carburetor (1.3 l) or an electronic fuel injection device, which usually do not require maintenance.
The ignition spark is generated by an electronic ignition device that sets the ignition timing. The ignition distributor for engines with a volume of 1.3 and 1.5 liters is located on the left side of the rear side of the cylinder head. It is driven by a camshaft through a helical gear. From September 1990, the ignition distributor is located on the right side of the front side of the cylinder head and is driven from the camshaft via a driver. 16 valve engines (1.6 and 1 8 l) do not have an ignition distributor. Ignition is carried out by a fully electronic ignition system with 2 ignition coils located in the intake manifold branch. Warning: The radiator fan can come on even when the engine is not running and the ignition is off.
Due to the formation of stagnant thermal zones, this can happen repeatedly. Therefore, when working in the engine compartment and with a hot engine, you can always expect a sudden activation of the radiator fan. To prevent this from happening, you should remove the electrical connector from the fan motor.
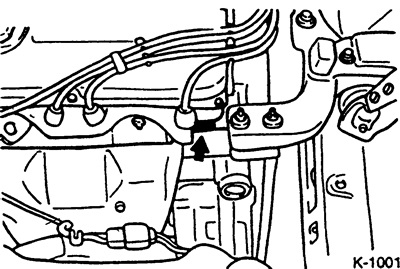
The engine number consists of the engine code and serial number. For gasoline engines, the number is stamped on the top side of the engine block. For diesel engines, the engine number is located on the right side of the block.
The engine code has 4 digits, for example, for a 1.3 l engine - 4G 13. The serial number starts from AA0001 to AA9999, followed by AB0001, etc. to AY9999 and finally to YY9999.
The engine code is also stamped on an identification plate riveted to the front inside the engine compartment.
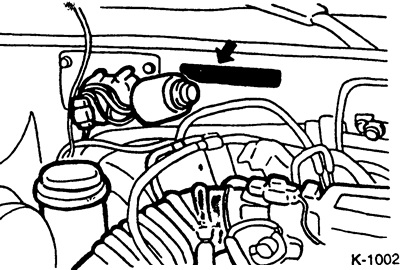
The car body number is stamped on the rear transverse bulkhead of the engine compartment.
Body number coding:
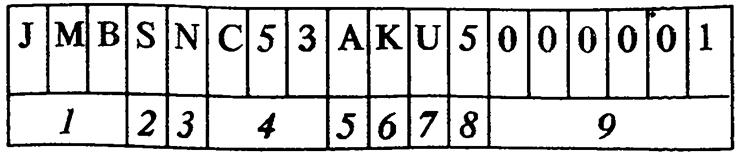
1 - World mark of the manufacturer Mitsubishi (Europe, left hand drive)
2 - Body type
L = 5-door hatchback, M = 3-door hatchback, S in a limousine
3 - Gearbox type
F = 4-speed gearbox, N = 5-speed gearbox, K = 3-speed automatic, R = 4-speed automatic.
4 - Short model designation
C10 = COLT II / LANCER II, C50 = COLT III, C60 - LANCER III, C70 = LANCER III with all-wheel drive.
5 - Vehicle type
A = passenger car, V = combi.
6 - Model Year Information
E = 1984, F-1985... K = 1989, L = 1990, etc.
7 - Place of production
U = Mizushima Motor Vehicle Works
8 - Engine version
9 - current number
Each model in each year starts with 000001.
