Examination
Check tire pressure, correct if necessary.
Make a test drive, as accurately as possible determine the boundaries of the defect, speed range, road surface condition, turns or driving in a straight line.
lift the car, see par. 29.
Check wheel alignment. In this case, the hub or brake drum must protrude from the hole in the disc or be at least flush with it. Otherwise, replace the rim.
Check wheel suspension. To do this, check the condition of silent blocks, hinges, shock absorbers and wheel disks.
Remove and clean wheels In doing so, remove stones, etc. from the tire profile.
Make sure that there are no bald spots on the tires from braking. These are places with a shallower profile depth that occur when braking with a complete wheel lock.
Check the profile depth of the individual tires and compare them with each other. If the front and/or rear tires are abnormally worn, check and, if necessary, adjust the alignment angles of the front and rear wheels. In this case, the toe-in should be set at the upper tolerance limit.
Attention: To check the wheel alignment, a special measuring stand is required, which, as a rule, is only available at service stations.
Do a test drive and check if the defect is still present.
Checking the lateral and radial runout of the wheels
With the vehicle raised, attach the appropriate dial indicator first to the working surface of the tire, and then to its side surface. Turn the wheel slowly by hand, take the reading of the dial indicator and mark with chalk the place of the maximum reading of the indicator.
Required values:
- Maximum radial runout of 2.0 mm;
- maximum lateral runout = 2.0 mm.
If these values are not maintained, balance the wheels on a stationary balancing machine. In this case, the wheels must be centered on the machine in the same way as on the car. Tapered jigs centering the wheel in the middle hole are not allowed. The permissible residual imbalance in both balancing planes is 5 grams.
Elimination of radial runout
Deflate the tire and press the tire beads into the rim bed.
Rotate the tire 120°.
Inflate the tire and recheck the radial runout.
If the maximum value has increased, turn the tire on the rim another 120°and check the radial runout.
If the maximum value has not decreased, balance the wheel.
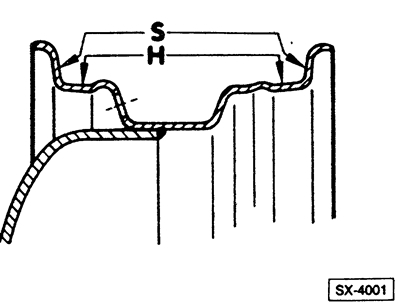
Checking radial and lateral runout
Install the rim without tire on the wheel balancer or on the vehicle. Attach a pointer indicator.
Measure the radial runout -H- and the lateral runout -S- at the positions indicated in the illustration. In this case, point emissions of indicator readings due to elevations or depressions in the disk material are not taken into account.
Required values:
- H - 2.0 mm;
- S - 2.0 mm.
If the tolerance limits are exceeded, replace the rim.
Installing wheels on a car
With the vehicle raised, position the wheels so that the point of maximum radial play is at the top. In this position, tighten the wheel nuts crosswise. Torque see 19.4.
Attention: If the difference in wear of the individual tires is small, put on the front axle the wheels with the smallest radial runout and the smallest balance weights.
Make a test drive. If there is an imbalance in the front of the car or vibration of the steering wheel, this is a residual imbalance and the need to rebalance the wheels on the car.
Balancing and re-balancing of wheels on a car
When balancing the drive wheels, be sure to install both tires of the same axle on the rollers.
The wheels must be driven by the vehicle's engine to ensure they rotate in sync. Vehicles with all-wheel drive must be fully raised. First, balance the wheels on one axle, and then on the other.
Make a test drive.
If the defect continues to appear, then this means that the radial or "lame" movement of one or more wheels. They cannot be measured by means of a service station. In this case, it remains only to replace the front and / or rear tires. In this case, the tires must be replaced in pairs.
