- Long vibrations of the body with uneven road surfaces.
- The buildup of the body with uneven road surfaces, following one after another.
- Bullying of the front of the car during acceleration.
- Wheel bouncing even on flat road surfaces.
- Pulling the car to the side when braking (may have other reasons).
- Uncertain cornering due to lack of traction. Car drifts.
- Knocks while driving.
The shock absorber can be checked by hand. However, a reliable check of shock absorbers is carried out using a shock tester (with damper removed) or on a special machine for checking shock absorbers.
Manual check
Remove shock absorber.
Hold the shock absorber in the working position, stretch the shock absorber and compress it.
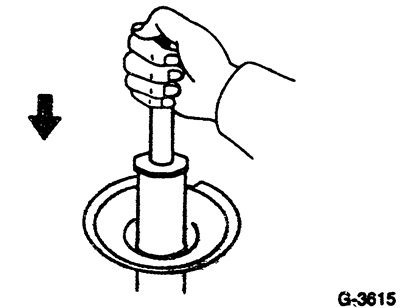
At the same time, the shock absorber rod must move with the same resistance force and without jerks throughout the entire working stroke.
Fully push in the piston rod and then release. The piston rod must then move forward again at a uniform speed.
With perfect functioning, traces of liquid are not grounds for replacing the shock absorber.
If there is a large fluid leak, replace the shock absorber.
Caution: The shock absorber must be degassed before disposal.
Install shock absorber.
Disposal of the shock absorber.
Fully extend the shock absorber rod and keep the shock absorber horizontal.
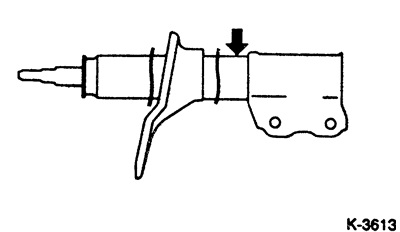
Before disposing of the shock absorber, drill a hole with a diameter of about 3 mm in the place shown in the figure to release the gas.
Note: The escaping gas is colorless, odorless and non-toxic. When drilling, sawdust can fly off, so wear safety goggles.
