Only vehicles with 16 valve engines
For screwing (reverse installation) pistons require a special tool. If a special tool is not available, you can make it yourself with some skill, otherwise contact a service station.
Removing
Mark the position of the rim on the knee hub with paint. This ensures that the balanced wheel is reinstalled in its original place.
Raise the back of the car see par. 29.
Remove wheel.
Attention: Swapping pads from the outside to the inside and vice versa, as well as from the right to the left wheel and vice versa is not allowed. Swapping pads can cause uneven braking. Be sure to replace all pads on the same axle at the same time. If it is necessary to reinstall the pads, mark the pads before removing them.
Release the handbrake.
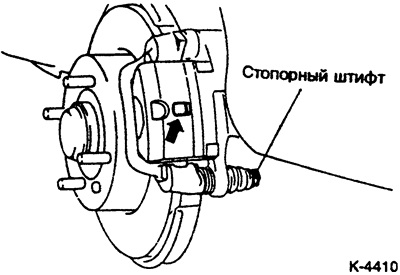
Unscrew locking pin, tilt brake caliper up and secure with wire to vehicle. Make sure that the brake hose is not stretched.
Caution: The locking pin is coated with special grease. Never remove grease. Make sure no dirt gets in.
Pull the piston housing up and attach with wire to the body.
Attention: Do not remove the brake hose, otherwise you will have to remove air from the brake system.
Pull out the brake pads with spacer springs, spacers and anti-squeak pads.
Installation
Attention: When the brake pads are removed, do not press the brake pedal, otherwise the piston will be squeezed out of the housing. If the piston came out due to an oversight, contact a MITSUBISHI service station to install the piston.
Clean the guide surfaces and pad seats with a soft metal brush or clean with a cloth soaked in alcohol. Do not use any solvents containing mineral oils or sharp-edged tools.
Before installing the pads, check with your fingers that there are no grooves on the brake disc. If there are grooves or scratches, replace the brake disc.
Measure the thickness of the brake disc, see point 18.3.
Make sure that there are no ruptures and cracks on the anther and cuffs in the caliper. Replace a damaged boot immediately, as penetrating dirt quickly leads to depressurization of the brake caliper. To do this, the caliper must be removed and disassembled (workshop work).
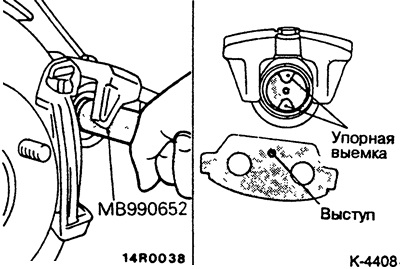
Slowly screw the brake piston in a clockwise direction until it stops into the brake caliper using the special tool MB-990652. The caliper does not need to be removed for this.
Caution: The brake piston must be screwed on. If it is simply pressed in, the automatic handbrake setting device will be damaged.
To rotate the piston, a special tool is inserted into the stop recesses. If a special device is not available, you can make it yourself with some skill, otherwise contact a service station.
Caution: When the piston is screwed in, brake fluid is squeezed out into the reservoir. Observe the level of brake fluid in the reservoir, it is possible to suck the brake fluid with an aspirator.
When suctioning, use a plastic bottle, which should only be used for brake fluid. Do not use drink bottles! Brake fluid is poisonous and must never be sucked out by mouth through a hose. Apply suction. After replacing the pads, the level of brake fluid in the reservoir should not exceed the MAX mark, as the fluid expands when heated. Leaking brake fluid flows onto the brake master cylinder, destroying paint and causing corrosion.
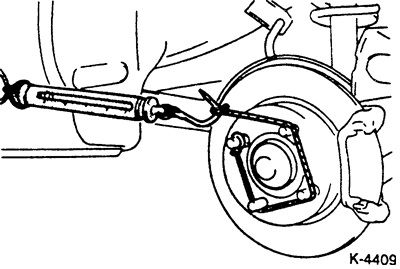
Measure the starting torque of the wheel hub as shown in the illustration and record the measured value. To do this, screw on the wheel nuts to secure the brake disc to the wheel hub.
To prevent squeaking of disc brakes, coat the reverse sides of the brake pads, as well as the anti-squeal linings, with a thin layer of lubricant (e.g. Plastilube, Tunap VC 582/S, Chevron SRJ/2, Liqui Moly LM-36 or LM-508-ASC, brake paste SAE J310 NLGI Nr. 1). Lubricant must never get on the working surface of the brake pad and on the brake disc. In case of contact, wipe off the grease immediately and clean the surface with alcohol. Apply the paste in such a thin layer that in the installed state, when the brake pad is pressed during braking, it does not protrude beyond the edge.
Note: Paste is available in some repair kits.
Slide both brake pads with new anti-squeak pads into the retaining springs in the caliper bracket.
Swing the piston housing down and insert and secure the locking pin.
Start the engine depress and hold the brake pedal down for about 5 seconds. In this case, the brake pads will take up their working position. Stop the engine and rotate the wheel hub 10 revolutions forward. After that, measure the moment of starting off the wheel hub, see fig. K-4405. Compare the measured value with the starting torque measured with the old brake pads. If the difference exceeds the required value, it is necessary to disassemble and repair the brake caliper (workshop work). Required value: 70 N (7.0 kg) or less.
Remove wheel nuts.
Put the wheels in accordance with the marking, screw the wheel nuts. Lower the vehicle and tighten the nuts crosswise. Torque see 19.4.
Start the engine and press the brake pedal hard 6-7 times until strong resistance appears. Then check the travel of the handbrake lever and adjust if necessary.
Check the fluid level in the reservoir and, if necessary, top up to the MAX mark.
Adjust the handbrake see 18.15.
Carefully break in new brake pads, for which several times with a small effort on the brake pedal, brake the car from a speed of 80 km / h to 40 km / h. Allow brakes to cool between braking.
Attention: For the first 200 km, do not allow full braking.
