The engine management system is designed to perform a number of basic and additional functions.
The main functions of the system include injecting the right amount of fuel at the right time into the engine cylinders.
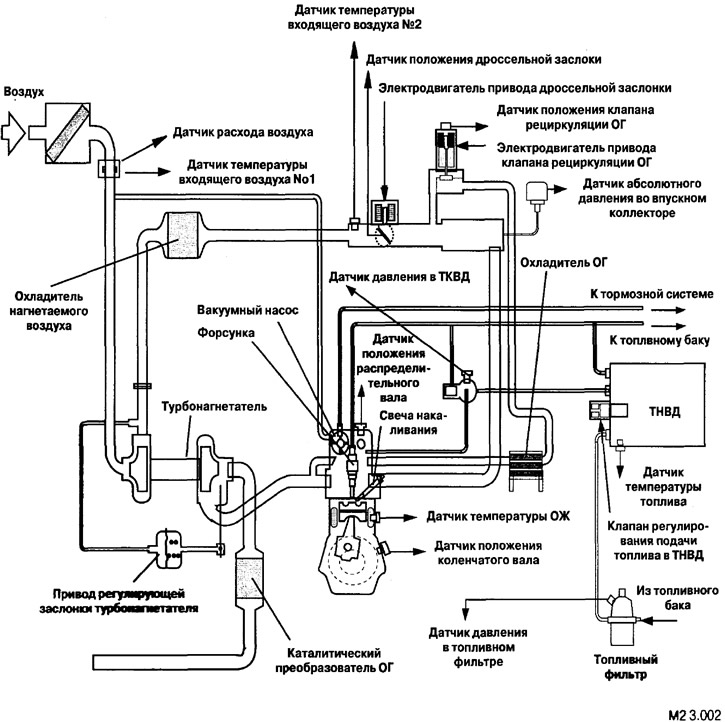
Additional functions include control of devices for limiting harmful emissions into the atmosphere, control of the condition of elements of the fuel and air supply system, as well as their control (turbocharger), diagnostic functions.
In addition, the engine management system interacts with the transmission control system, the exchange rate stability system.
The engine management system consists of three main groups of components:
- sensors;
- electronic control unit (ECM);
- executive devices.
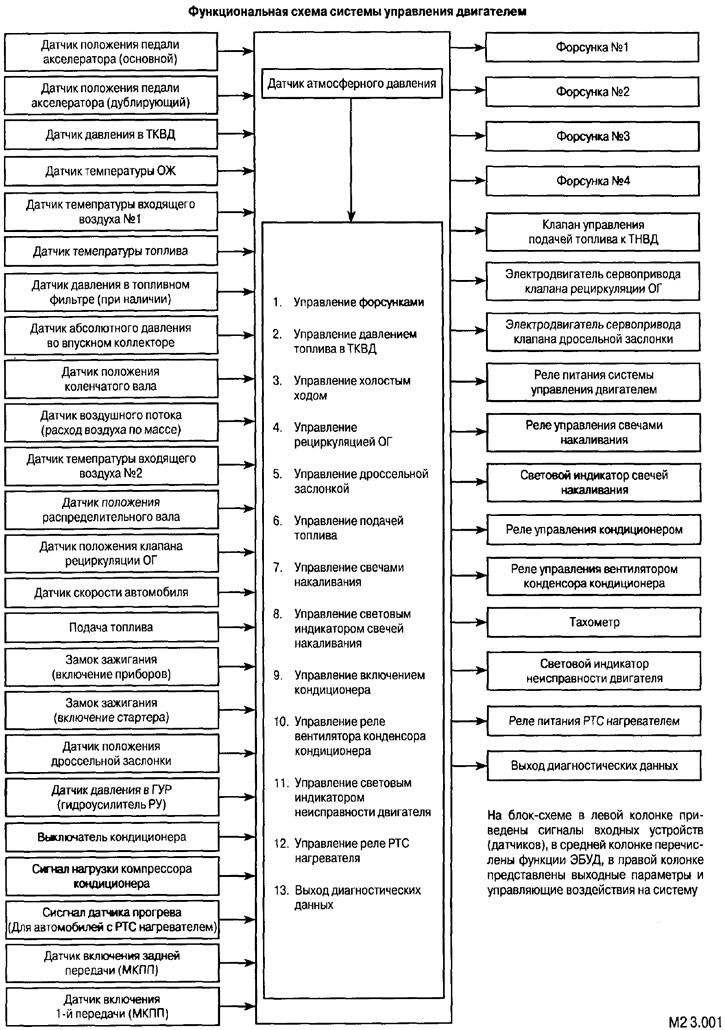
The sensors supply the control unit with a set of signals reflecting the state of the mechanisms, environmental conditions, driver control actions, signals about the behavior of the car on the road (and so on.).
The control unit, based on the program embedded in it, finds the optimal combination of output parameters for each of the possible combinations of input parameters. In this case, the change of parameter values occurs at a high frequency, which makes it possible to smoothly control the process. The transmission and processing of data is carried out in digital form. A multiplex data bus is used to transfer data in digital form (CAN).
Actuators are a group of system elements that directly affect the change in process parameters (control valves, fuel injectors, throttle and bypass dampers, servo drives, glow plugs, etc.).
More specifically, the composition, functions and arrangement of the system elements are described below.