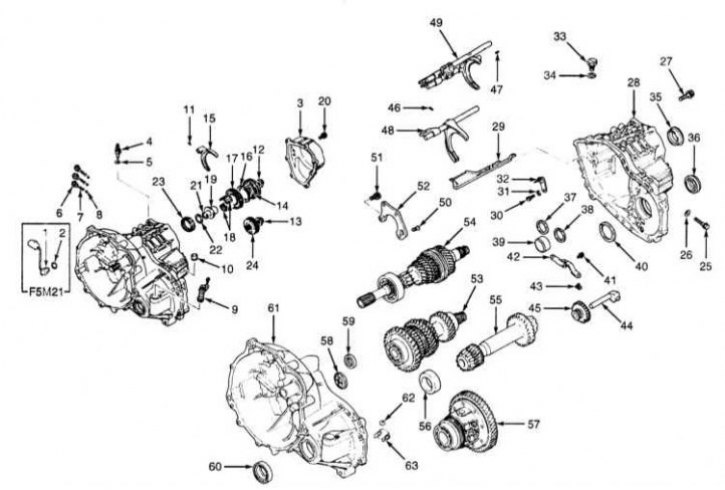
The design of the manual transmission F5M21 and F5M22
1 - Sensor-switch transmission; 2 - Sealing gasket; 3 - Back cover; 4 - Sensor-switch of reversing lights; 5 - Sealing gasket; 6 - Stopper of the latch; 7 - Lock spring; 8 - Locking ball; 9 - Assembling the speedometer drive; 10 - Manual transmission crankcase ventilation breather; 11 - Spring-loaded pin; 12 - Locknut; 13 - Locknut; 14 - Assembling the synchronizer of the 5th gear; 15 - 5th gear engagement fork; 16 - Synchronizer blocking ring; 17 - Gear 5th gear; 18 - Needle bearing; 19 - Bearing sleeve; 20 - End cap bolt; 21 - Retaining ring (is selected); 22 - Distance ring (is selected); 23 - Roller bearing; 24 - Intermediate gear 5th gear; 25 - Bolt of an axis of an intermediate gear wheel of a reverse gear; 26 - Sealing gasket; 27 - Bolt; 28 - Transmission housing; 29 - Oil flow chute; 30 - Bolt; 31 - Spring washer (puck Grover); 32 - Thrust bar; 33 - Assembling the ball stop; 34 - Sealing gasket; 35 - Outer ring; 36 - Oil seal; 37 - Distance ring (is selected); 38 - Distance ring (is selected); 39 - Outer race of the bearing; 40 - Distance ring (is selected); 41 - Bolt; 42 - Lever assembly of the drive for engaging the reverse gear; 43 - Shoe assembly drive reverse gear; 44 - Axis of the intermediate gear of the reverse gear; 45 - Intermediate reverse gear; 46 - Spring-loaded pin; 47 - Spring-loaded pin; 48 - Assembly of the switching rod; 49 - Assembly of the switching rod; 50 - Bolt; 51 - Bolt; 52 - Bearing holder; 53 - Assembly of the intermediate gear; 54 - Assembly of the input shaft; 55 - Assembling output (secondary) shaft; 56 - Outer race of the bearing; 57 - Assembling the differential; 58 - Oil supply guide; 59 - Oil seal; 60 - Oil seal; 61 - Clutch dome; 62 - Magnet; 63 - Magnet holder
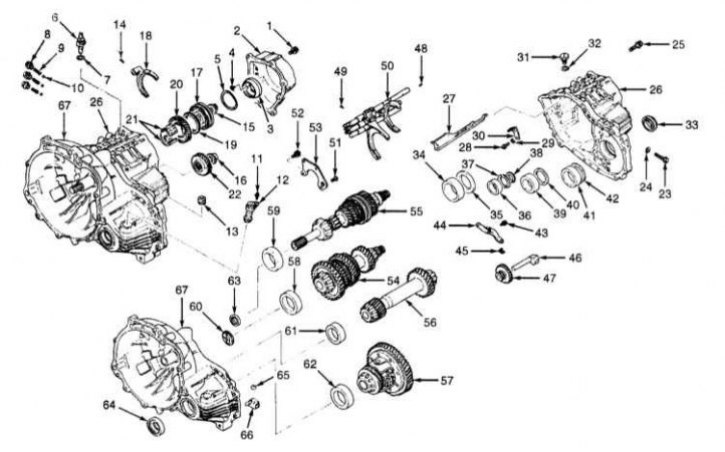
The design of the manual transmission F5M31 / F5M33
1 - Bolt; 2 - Back cover; 3 - Reversible brake cone; 4 - Wavy spring; 5 - Self-tapping screw; 6 - Sensor-switch of reversing lights; 7 - Sealing gasket; 8 - Stopper of the latch; 9 - Lock spring; 10 - Lock ball; 11 - Bolt; 12 - Assembling the speedometer drive; 13 - Crankcase ventilation breather; 14 - Spring-loaded pin; 15 - Locknut; 16 - Locknut; 17 - Assembling the synchronizer of the 5th gear; 18 - 5th gear engagement fork; 19 - Synchronizer blocking ring; 20 - Gear 5th gear; 21 - Needle bearing; 22 - Intermediate gear 5th gear; 23 - Bolt of the axis of the intermediate gear of the reverse gear; 24 - Sealing gasket; 25 - Bolt; 26 - Carter manual transmission; 27 - Oil flow chute; 28 - Bolt; 29 - Spring washer (puck Grover); 30 - Thrust bar; 31 - Assembling the ball stop; 32 - Sealing gasket; 33 - Oil seal; 34 - Outer race of the bearing; 35 - Distance ring (is selected); 36 - Outer race of the bearing; 37 - Distance ring (is selected); 38 - Filter (only F5M33); 39 - Outer race of the bearing (only F5M33); 40 - Distance ring (is selected) (only F5M33); 41 - Outer race of the bearing; 42 - Distance ring (is selected); 43 - Bolt; 44 - Lever assembly of the drive for engaging the reverse gear; 45 - Shoe assembly drive reverse gear; 46 - Axis of the intermediate gear of the reverse gear; 47 - Intermediate reverse gear; 48 - Spring-loaded pin; 49 - Spring-loaded pin; 50 - Assembly of the switching rod; 51 - Bolt; 52 - Bolt; 53 - Bearing holder; 54 - Assembly of the intermediate gear; 55 - Assembly of the input shaft; 56 - Assembly output (secondary) shaft; 57 - Assembling the differential; 58 - Outer race of the bearing; 59 - Outer race of the bearing; 60 - Oil supply guide; 61 - Outer race of the bearing; 62 - Outer race of the bearing; 63 - Oil seal; 64 - Oil seal; 65 - Magnet; 66 - Magnet holder; 67 - Clutch dome
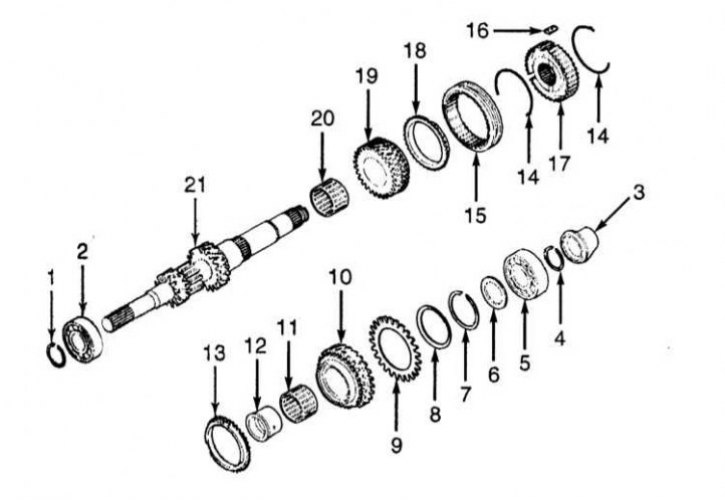
The design of the input shaft of the manual transmission
1 - Retaining ring; 2 - Ball or cone bearing; 3 - Bearing sleeve; 4 - Retaining ring (is selected); 5 - Ball or cone bearing; 6 - Distance ring (is selected); 7 - Retaining ring (is selected); 8 - Cone spring; 9 - Spring-loaded toothed ring; 10 - Gear 4th gear; 11 - Needle bearing; 12 - Bearing sleeve; 13 - Synchronizer blocking ring; 14 - Synchronizer spring; 15 - Sliding clutch synchronizer 3/4 gears; 16 - Sliding key synchronizer; 17 - Synchronizer hub 3/4 gear; 18 - Synchronizer blocking ring; 19 - Gear 3rd gear; 20 - Needle bearing; 21 - Primary shaft
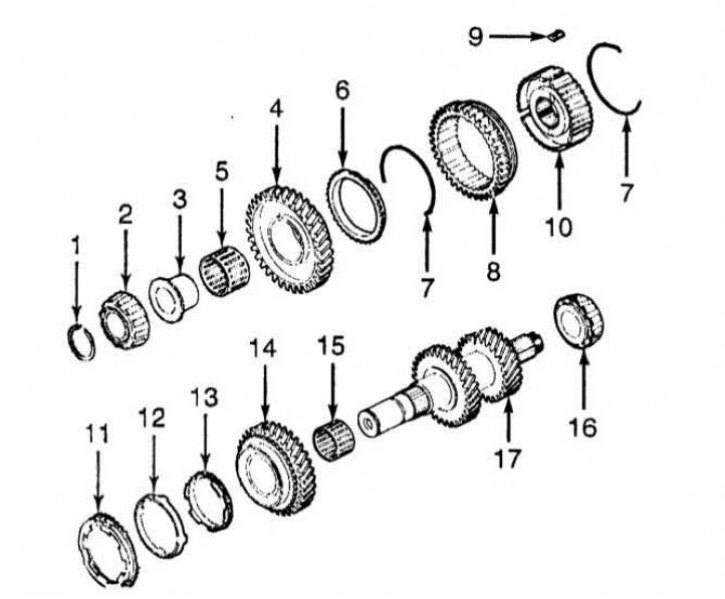
Components of the assembly of the intermediate shaft of the manual transmission
1 - Retaining ring (is selected); 2 - Ball or cone bearing; 3 - Bearing sleeve; 4 - Gear 1st gear; 5 - Needle bearing; 6 - Synchronizer blocking ring; 7 - Synchronizer spring; 8 - Sliding clutch of the synchronizer 1/2 gears; 9 - Sliding key synchronizer; 10 - Synchronizer hub 1/2 gears; 11 - External blocking ring of the synchronizer (only F5M33); 12 - Synchronizer cone (only F5M33); 13 - Internal blocking ring of the synchronizer; 14 - Gear 2nd gear; 15 - Needle bearing; 16 - Ball or cone bearing; 17 - Intermediate gear
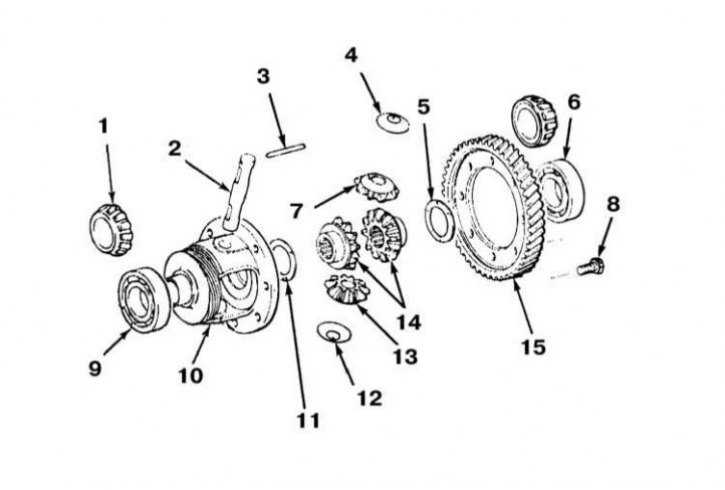
The design of the main gear differential of the manual transmission
1 - Tapered roller bearing (F5M22, F5M31/F5M33); 2 - Axis of satellites; 3 - Locking pin; 4 - Washer; 5 - Distance ring (is selected); 6 - Ball bearing (F5M21/F5M210); 7 - Satellite; 8 - Bolt; 9 - Ball bearing (F5M21/F5M210); 10 - Differential box; 11 - Distance ring (is selected); 12 - Washer; 13 - Satellite; 14 - Side gears; 15 - Driven gear of the final drive
General information
The compilers of this Guide do not recommend car owners to undertake the overhaul of manual transmissions on their own. During the disassembly and assembly procedures, the gearbox has to be removed and then replaced with many small components. It is necessary to make a lot of accurate measurements and, by selecting shims, rings and spacers, clearly set a lot of gaps. In view of the foregoing, it would be wiser to entrust the overhaul of the manual transmission to the car service specialists. Note that in many cases it is possible to purchase a refurbished unit on an exchange basis, which is often cheaper than a complex repair.
Despite the foregoing, the independent repair of the manual transmission by an amateur mechanic is not at all an absolutely impossible undertaking. Indispensable conditions are only the availability of the necessary special tools and accuracy in the approach to the implementation of all procedures.
Tools needed to rebuild manual transmissions include needle nose pliers for removing inner and outer circlips, a bearing puller, a slide hammer, a set of punches and punches, a DTI dial gauge, and possibly a hydraulic press. In addition, of course, you will need a durable, vise-equipped workbench, or a special assembly stand.
During the manual transmission disassembly procedures, try to remember, or rather write down, the installation order of each of the removed parts.
Before proceeding with the disassembly of the gearbox, it would be wise to try to analyze the symptoms of its failures in order to approximately determine their causes. Many failures are uniquely related to the failure of well-defined components. See also the Manual Transmission Troubleshooting Section at the beginning of the Manual.
Let us consider in more detail three of the gearboxes used on the vehicles considered in this Guide: F5M31 (Galant), F5M21 (Mirage 1.5 l) and F5M22 (Mirage 1.8 l).
Disassembly of manual transmission
1. The design of the manual transmission is shown in the illustrations.
2. On F5M21 models, remove the transmission switch with gasket. On all other models, remove the back cover. Remove the reversing light switch with its gasket. Remove the wave spring, give the bolts and remove the reversible brake cone. Turn out stoppers and take fixing springs and balls.
3. Remove the speedometer drive assembly and crankcase ventilation breather from the clutch dome. Remove the spring loaded pin from the 5th shift fork. Loosen the lock nuts of the input and intermediate shafts.
4. Use the control and select levers to shift the transmission into reverse gear. Throw a split socket wrench with a collar on the pin of the input shaft. Screw a 10 mm bolt into the clutch dome and rest the key collar in it, thereby blocking the input shaft from turning. Give lock nut (locknut).
5. Remove the synchronizer assembly and the 5th gear fork. Remove the synchronizer ring and 5th gear. On F5M21 models, remove the needle bearing, spacer, bearing sleeve, circlip and roller bearing.
6. On all models, remove the 5th idle gear. Turn out a bolt of an axis of an intermediate gear wheel of a reverse gear, remove a sealing lining. Remove the manual transmission housing and oil supply guide. Turn out a bolt of a persistent lath and remove a spring washer. Remove the ball detent assembly with gasket.
7. On F5M21 models, remove the outer ring. On all models, remove the seal. On F5M21 models, remove three spacers and one bearing outer race. On all other models, remove the three spacers and the outer races of the three bearings.
8. Remove the lever assembly of the reverse gear drive, the shoe of the lever assembly, remove the axle with the reverse intermediate gear.
9. Remove the 1/2 and 3/4 shift fork spring pins. Move the corresponding shift fork to the 2nd gear positions, the second fork to the 4th gear position.
10. On models F5M21 and F5M22, turn the shift rod assemblies until the shift tongues disengage from the control pin and retainer plate. By pulling the rods up, release the ends from the clutch dome. Remove shift rods and forks.
11. On F5M31/F5M33 models, remove the shift fork stem assembly. On all models, remove the bearing retainer. Raise the input shaft and remove the intermediate gear assembly.
12. Remove assemblies of primary and secondary shafts. Remove the differential assembly. Remove the outer races of the bearings from the primary and secondary shafts. If equipped, remove the bearing races from the differential housings in the clutch dome. Remove the oil guide and seals from the clutch dome. Remove the magnet with its holder.
Synchronizer 5th gear
Disassembly
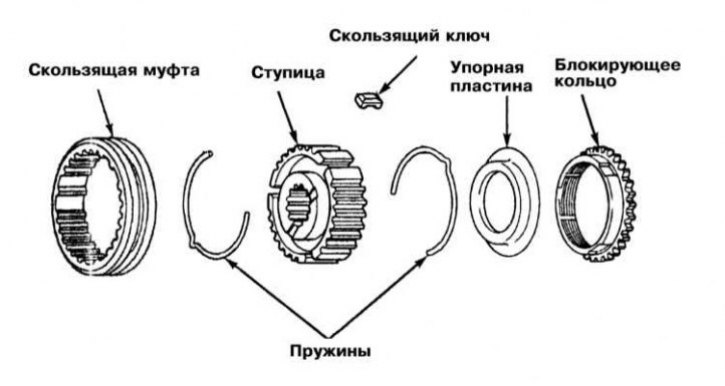
Remove the blocking ring, thrust plate, springs, sliding sleeve, sliding keys and synchronizer hub.
Examination
1. Insert the synchronizer hub into the clutch and manually check for free rotation of the components. Check the clutch for signs of wear or damage to the front and rear inner edges. Check up a condition of a surface of a nave interfaced with a gear wheel of the fifth transfer. Assess the wear on the top lugs of the sliding keys. Check the springs for signs of weakening, deformation, cracks and other mechanical damage.
2. Replace defective components.
Note. The replacement of the sliding clutch is assembled with the hub.
Assembly
1. Insert the hub with the sliding keys installed into the synchronizer sleeve - make sure that the components are correctly engaged.
2. Install the springs so that the sliding keys rest against their ledges. Make sure that the springs are turned by the locks in different directions.
3. Finally install the thrust plate and locking ring.
Primary shaft manual transmission F5M21
Disassembly
1. The design of the input shaft assembly is shown in the illustration.
2. Remove the circlip and remove the front bearing from the shaft journal.
3. Remove inner ring (rear bearing), distance ring and 4th gear.
4. Remove the 3rd gear, 3/4 synchro assembly, and bearing sleeve.
Examination
1. Assess the degree of wear of the bearing surfaces and shaft splines. Install a needle bearing on the shaft and check its tightness and freedom of rotation. Make sure there is no deformation of the bearing housing.
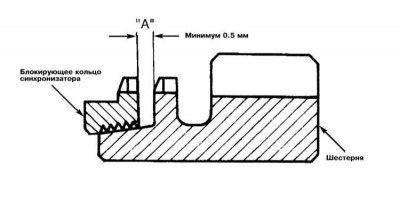
2. Check up integrity of teeths of a blocking ring of the synchronizer. Make sure that there are no signs of damage and the integrity of the threads of the inner surface. Press the synchronizer ring towards the gear and measure the gap between the components. If the measurement result is greater than 0.5 mm, replace the blocking ring.
3. Thread the synchronizer hub into the clutch and check the freedom of movement of the components relative to each other. Check the condition of the front and rear edges of the coupling, evaluate the degree of wear of the hub surface mating with the gear and the working protrusions of the sliding keys. Check the condition of the synchronizer springs.
4. Replace defective components.
Note. The replacement of the sliding clutch is assembled with the hub.
5. Check up smoothness of a surface of a cone of the synchronizer. Assess the condition of the front and rear mating surfaces. Make sure the teeth of all gears are intact.
Assembly
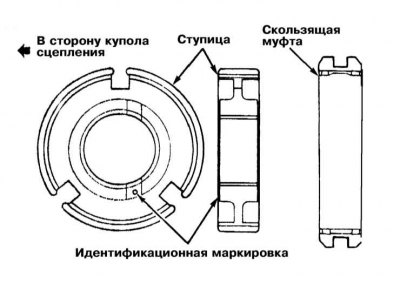
1. Assembly is carried out in the reverse order to the dismantling of components. Fit the synchronizer hub (forward marking) in a sliding sleeve. Follow the correct articulation of the components - the central tooth of the hub must fall between the two missing teeth of the coupling and engage with the sliding key.
2. Install the synchronizer springs so that the sliding keys rest against their protruding sections. Make sure that the springs are deployed with locks in different directions.
3. Place the 3/4 gear synchronizer assembly on the shaft.
Note. Make sure that the sliding keys fall into the grooves in the blocking ring, check the freedom of rotation of the 3rd gear.
4. Fit the bearing sleeve onto the shaft using the special tool. Install distance ring (identification mark "1" towards the 4th gear).
Note. In the absence of marking, the ring can be planted arbitrarily. Place the inner ring on the shaft (rear bearing).
5. Using the special tool, fit the front bearing onto the shaft and fit a new circlip into the groove.
Note. Retaining rings are available in various thicknesses - choose the maximum that fits into the groove.
Take care not to damage the surface of the shaft journal in contact with the gland.
Primary shaft manual transmission F5M22 and F5M31 / F5M33
Disassembly
1. Remove the circlip and remove the front bearing from the shaft journal. Remove the rear bearing, spacer and 4th gear with bearing.
2. Remove the bearing sleeve, 3/4 synchro assembly and 3rd gear.
3. Remove the needle bearing.
Examination
1. Assess the degree of wear of the bearing surfaces and shaft splines. Install a needle bearing on the shaft and check its tightness and freedom of rotation. Check for deformation or damage to the bearing housing.
2. Check up integrity of teeths of a blocking ring of the synchronizer. Make sure that there are no signs of damage and the internal surface of the integrity of the threads applied to it. Press the synchronizer ring towards the gear and measure the gap between the components. If the measurement result is greater than 0.5 mm, replace the blocking ring.
3. Thread the synchronizer hub into the sliding sleeve and check the freedom of movement of the components relative to each other. Check the condition of the front and rear edges of the coupling, evaluate the degree of wear of the hub surface mating with the gear and the working protrusions of the sliding keys. Check the condition of the synchronizer springs.
4. Replace defective components.
Note. The replacement of the sliding clutch is assembled with the hub.
5. Check up smoothness of a surface of a cone of the synchronizer. Assess the condition of the front and rear mating surfaces. Make sure the teeth of all gears are intact.
Assembly
1. Fit the synchronizer hub (forward marking) in a sliding sleeve. Follow the correct articulation of the components - the central tooth of the hub must fall between the two missing teeth of the coupling and engage with the sliding key.
2. Install the synchronizer springs so that the sliding keys rest against their protruding sections. Make sure that the springs are deployed with locks in different directions.
3. Place the 3/4 gear synchronizer assembly on the shaft.
Note. Make sure that the sliding keys fall into the grooves in the blocking ring, check the freedom of rotation of the 3rd gear.
4. Fit the bearing sleeve onto the shaft using the special tool. Install distance ring (identification label "1" towards the 4th gear).
Note. In the absence of marking, the ring can be planted arbitrarily. Fit the rear bearing with the clutch.
5. Using a special tool, seat the front bearing on the shaft, fill the groove with a new circlip.
Note. Retaining rings are available in various thicknesses - choose the maximum that fits into the groove. Take care not to damage the surface of the shaft journal in contact with the gland.
Intermediate shaft
Disassembly
1. The design of the intermediate shaft assembly is shown in the illustration.
2. Remove the circlip and dismantle the bearing with the coupling from the shaft.
3. Remove the needle bearing and 1st gear.
Note. The bearing must be replaced without fail.
4. Remove the 1/2 synchro assembly, 2nd gear, and needle bearing from the shaft.
5. Remove the rear bearing assembly.
Examination
1. Assess the degree of wear of the bearing surfaces of the assembly. Install a needle bearing on the shaft and check its tightness and freedom of rotation. Check for deformation or damage to the bearing housing.
2. Check up integrity of teeths of a blocking ring of the synchronizer. Make sure that there are no signs of damage and the internal surface of the integrity of the threads applied to it. Press the synchronizer ring towards the gear and measure the gap between the components. If the measurement result is greater than 0.5 mm, replace the blocking ring.
3. Thread the synchronizer hub into the sliding sleeve and check the freedom of movement of the components relative to each other. Check the condition of the front and rear edges of the coupling, evaluate the degree of wear of the hub surface mating with the gear and the working protrusions of the sliding keys. Check the condition of the synchronizer springs.
4. Replace defective components.
Note. The replacement of the sliding clutch is assembled with the hub.
5. Check up smoothness of a surface of a cone of the synchronizer. Assess the condition of the front and rear mating surfaces. Make sure the teeth of all gears are intact.
Assembly
1. Assembly is carried out in the reverse order to the dismantling of components. Using a special tool, place the bearing on the shaft - make sure that the mandrel of the tool rests only on the end surface of the inner race of the bearing.
2. Fit the 1/2 gear synchro hub (forward marking) in a sliding sleeve. Follow the correct articulation of the components - the central tooth of the hub must fall between the two missing teeth of the coupling and engage with the sliding key.
3. Install the synchronizer springs so that the sliding keys rest against their protruding sections. Make sure that the springs are deployed with locks in different directions.
4. Place the 1/2 gear synchronizer assembly on the shaft.
5. Fit the bearing sleeve onto the shaft using the special tool. Install the 1st gear with the bearing sleeve, finally place the bearing on the shaft.
High school graduation (secondary) shaft
1. The design of the output shaft assembly is shown in the illustrations.
2. Remove the bearings from the shaft - during assembly they must be replaced without fail, the replacement of the inner and outer races is carried out as a set. Assess the condition of the shaft and the degree of wear of its working components. Install new bearings on the shaft. Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
Shift forks
1. Remove the shift fork 1.2 gears. Remove the shift rod assembly.
2. Remove the 3/4 shift fork assembly and 5th/reverse shift rod. Remove the 3/4 shift fork stem. Remove the reverse gear shift pawl.
3. Assembly is carried out in the reverse order. Make sure that the plunger of the locking latch engages with the reverse shift pawl in the groove of the 3/4 gear rod.
Final drive differential
Disassembly and checking the condition of components
1. The design of the differential is shown in the illustration.
2. Turn out fixing bolts and remove a conducted gear wheel of a back transfer. Squeeze the bearings out of the differential box - during assembly, the bearings must be replaced without fail.
3. From the side of the driven gear seat flange, remove the lock pin. Release the axle and pinion gears from the box, remove the washers and remove the side gears.
4. Carefully inspect all components for signs of excessive wear and mechanical damage. Replace defective elements.
Assembly
1. Place the spacers on the back of the side gears and install the latter into the differential case. Fill both satellites into the differential box. Establish an axis of satellites.
2. Measure the backlash of the gearing of the pinion gears with the side gears. If the measurement result is out of range (0.025÷0.150 mm), disassemble the differential and select spacer rings of the required thickness.
Note. When installing new side gears, they should be equipped with the same distance rings of medium thickness (0.93÷1.00 mm).
3. Lock the satellite shaft with a new locking pin.
Note. The pin must not protrude more than 3 mm above the surface of the differential box.
4. Press new bearings into the differential box.
Attention! The tool arbor must only rest against the inner race of the bearing!
5. Before driving in used idler gear bolts, run through the threads with an appropriately sized tap to remove any corrosion/old sealant and repair damaged threads, then lubricate the bolts with fresh fixative sealant. Tightening bolts to the required torque (130÷140 Nm) do it diagonally.
Manual transmission assembly
Note. Distance rings used when setting the preload, as well as retaining rings, are subject to selection.
1. Assembly is carried out in the reverse order to the dismantling of components.
2. Establish epiploons of driving and primary shafts. At the same time, fill the intermediate and input shaft assemblies into the transmission case.
3. Lubricate the input shaft bearing bolt closest to the differential with 3M STUD Locating Sealant (4170), - try not to let the sealant get on the bolt head. Screw in the bolts and tighten them to the required torque (16÷22 Nm).
4. Fit the 1/2 shift clutch into the 2nd gear, the 3/4 shift clutch into the 4th gear, respectively. Insert the forks of the shift assemblies into engagement with the grooves in the couplings. Insert the fork stems into the appropriate holes in the clutch dome and rotate them to engage the pawls with the control pin and lock plate.
5. Using a suitable drift, seat the new spring pins (cut along the stem axis). Install the intermediate gear axle (threaded hole in the head towards the differential).
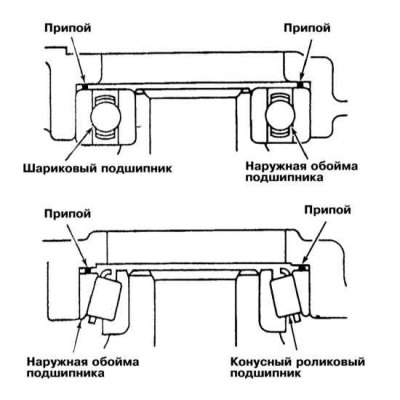
6. Place two pieces of solder 10 mm long and 1.6 mm in diameter in place of the spacer rings.
7. Install the transmission housing and tighten the bolts of its fastening with the required force. Remove the bolts again, remove the crankcase, dismantle the outer bearing races and remove the flattened solder. Measure the thickness of the solder with a micrometer and select the appropriate distance rings, this procedure will allow you to correctly select the axial play of the components (see specs).
8. Fit the oil guide into the transmission case. Slide spacer rings of the correct thickness onto the intermediate gear assembly, then seat the differential bearing outer race. Install distance rings of the appropriate thickness between the outer race of the bearing and the manual transmission housing. Make sure that the shaft of the reverse intermediate gear is turned with the threaded hole in the head in the correct direction, then you can proceed with the installation of the gearbox housing.
9. Evenly apply a pad of sealant with a thickness of 1.0÷2.0 mm to the surface of the crankcase mating with the clutch dome (use Mitsubishi sealant MD997740 or Three Bond 1216). Press the crankcase against the dome.
10. With a punch (Phillips screwdriver) 8.0 mm diameter, align the threaded hole in the reverse idler gear shaft with the corresponding bolt hole in the transmission case. Screw in the bolt and tighten it to the required torque (43÷55 Nm). Torque tighten the other transmission case mounting bolts.
11. With the appropriate configuration, select the retaining ring of the thickness corresponding to the size of the mounting groove, - the retaining ring must be replaced in a mandatory order. Place the circlip on the input shaft stub. Check the tightness of the coupling flange against the bearing.
12. Install the 5th shift fork (complete with synchronizer). Block the shaft from turning with a slotted socket wrench and a 10mm bolt in the clutch dome.
13. Using the control and select levers, shift the manual transmission into reverse gear. Screw on new locknuts, tighten them to the required torque (140÷160 Nm) and check.
14. Install a new 5th gear shift fork (cut along the stem axis).
15. Lubricate with 3M Super Weatherstrip (8001) onto the air breather mounting surface and install the clutch dome. Install the rear clutch dome cover after applying an even pad of sealant to its mating surface (type Mitsubishi MD997740 or Tree Bound 1216) 1÷2 mm thick.
16. Install the manual transmission assembly on the engine (see Section Removal and installation of a transmission).
