Note. To avoid voiding your warranty on emission control system components, have the catalytic converter inspected and serviced at an auto repair shop.
General information
The catalytic converter is a component of exhaust gas toxicity reduction systems, is included in the exhaust system and serves to reduce the emission of toxic components into the atmosphere. There are two types of catalytic converters. A conventional oxidizing converter can reduce the content of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide in the exhaust gases. Tri-functional catalytic converter further reduces nitrogen oxide emissions (NOx). All models covered in this manual use three-function catalytic converters.
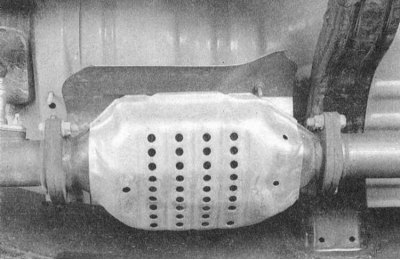
The catalytic converter is part of the exhaust system and looks like an additional muffler.
Examination
1. Diagnostic equipment for checking the health of the catalytic converter is expensive and extremely difficult to operate. If you suspect a converter failure, drive the vehicle to a workshop for inspection.
2. Whenever the vehicle is lifted off the ground for any reason, inspect the transducer for signs of mechanical damage, signs of leakage, and corrosion. Check the condition of the welds and the tightness of the flange bolts securing the device to the sections of the exhaust system. A defective catalytic converter must be replaced.
3. Make sure that the heat shield is securely fastened and that there is always a sufficient gap between the converter and the chassis / bodywork (see chapter Settings and ongoing maintenance).
Replacement
The description of procedures for replacing the components of the exhaust gas system is given in Chapter Power and exhaust systems.
