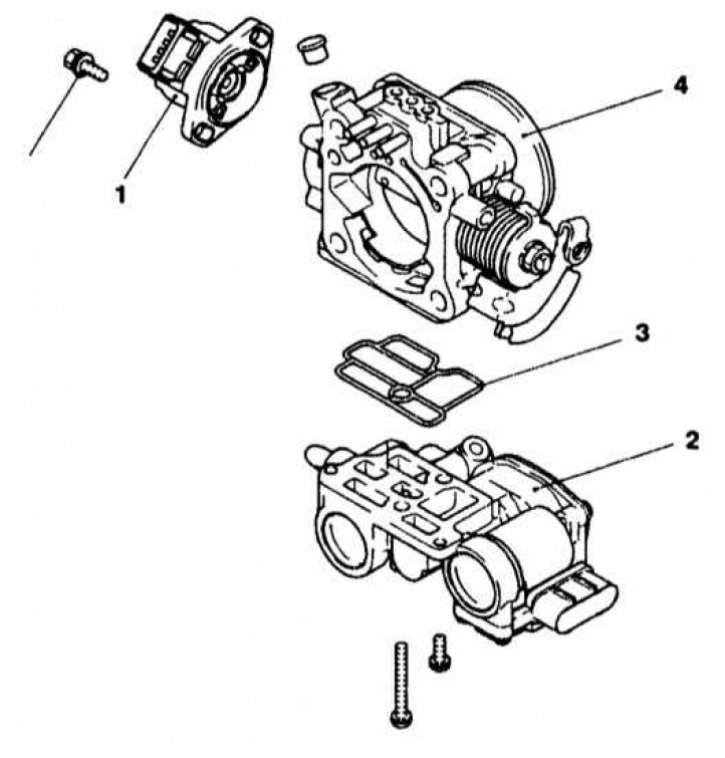
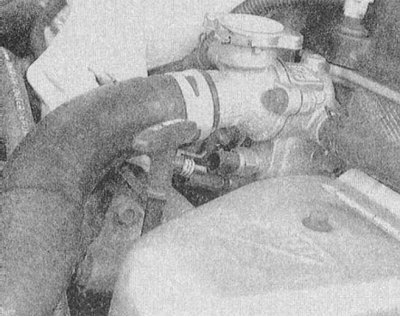
IAC Servo Motor Installation Details
1 - TPS (with sensor-switch closed throttle position); 2 - IAC servomotor; 3 - Sealing gasket; 4 - Throttle body
Attention! To avoid damage to the ECM, use only a high voltage digital voltmeter when performing the following checks (over 10 MΩ) impedance!
Note. A car equipped with an OBD-II system should be driven to a service station for reading fault codes using a special scanner. There are only a few checks (related to identifying the causes of failures when starting the engine), which the owner of the vehicle can perform on his own, in all other cases the car should be driven to a car service.
Oxygen sensors
O2 sensors, or l-probes, monitor the percentage of oxygen in the engine's exhaust gases. The O2 molecules present in the exhaust system, reacting with the sensitive element of the sensor, cause the latter to generate a signal voltage. The amplitude of the signal, depending on the oxygen concentration, can be from 0 to 1 V, and a signal below 0.4 V indicates a high content of O2, - a lean air-fuel mixture, more than 0.6 V, - a low (rich mixture). The ECM continuously monitors the signal from the oxygen sensor and, based on the incoming data, makes the appropriate adjustments to the air-fuel composition, trying to maintain it at an optimal level (14.7 parts of air to 1 part of fuel, - stoichiometric number), which corresponds to the reading of the oxygen sensor 0.4÷0.6 V. The composition of the mixture is adjusted by controlling the duration of the opening time of the injection injectors. The oxygen sensor does not start generating signal voltage until it has warmed up to its normal operating temperature of approximately 320°C. With that said, the ECM operates in open loop during the engine warm-up process.
On OBD-II equipped models, there are usually two oxygen sensors, one mounted in front of the catalytic converter and one behind, which allows the control module to maintain the efficiency of the catalyst at its maximum level. To speed up the output of the sensors in the operating mode, they can be equipped with electric heating elements.
Examination
Attention! Connecting the scanner by piercing the wire insulation is fraught with damage to the electrical wiring - insert the meter probes into the terminals on the reverse side of the connector!

1. Do not forget to check the condition of all oxygen sensors included in the system.
Note. Access to oxygen sensors is usually difficult. Be careful - remember that exhaust system components can remain hot for a long time after the engine has stopped and pressing wire harnesses against their surface can lead to destruction of their insulation. Try, if possible, to check the components of the system using a special scanner that allows you to detect changes in signal voltage within thousandths of a volt.
2. Disconnect the wiring from the sensor.
3. Measure the resistance between the PWR and GRD terminals of the sensor. If the measurement result differs from the nominal value stipulated by the regulatory requirements (6 ohm at 20°C), therefore, the sensor heating element is defective and the assembly must be replaced.
4. Restore the original wiring connection and start the engine. Connect a digital voltmeter between the HO2S and SIG RTN terminals (GND) sensor connector, - if the fluctuations of the meter readings do not occur quickly enough, or go beyond the range of the nominal range (0.01÷1.0 V), replace the sensor.
Removal and installation
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!
2. Jack up the car and put it on stands.
3. Mark the wires and disconnect the oxygen sensor from the main engine wiring harness.
4. Using a special key, turn out the sensor and remove it from the car.
 |  |
 |
5. Estimate a condition of deposits covering a working element of the oxygen sensor.
6. Before installation, the sensor should be lubricated with penetrating oil.
7. Screw the sensor into its regular place and tighten it with the required force (37÷45 Nm).
8. Restore the original wiring connection.
9. Lower the vehicle to the ground and connect the negative cable to the battery.
Idle stabilization servomotor (IAC)
The servo drive of the IAC system is based on a DC-powered stepper motor. A sensor built into the servomotor assembly continuously monitors the position of the actuator and provides relevant information to the PCM, which performs general control of the operation of the idle speed stabilization system.
Examination
1. Press a stethoscope or large screwdriver against the IAC servo assembly. Have an assistant turn the ignition on without starting the engine - the drive motor should make a few distinct clicks, confirming the condition of the circuit in the area between the PCM and the system servo. Next, proceed to check the condition of the electric motor itself.
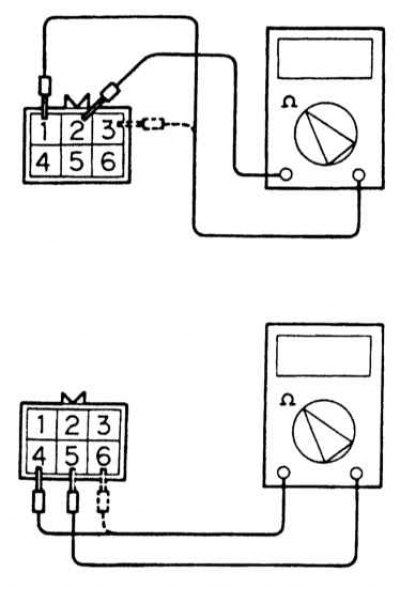
2. Disconnect the electrical wiring from the servomotor assembly and use an ohmmeter to probe in pairs the terminals 1-2 and 2-3 of the pin connector on the drive side (don't bite!). If the measurement result is out of range (28÷33 Ohm), replace the IAC motor. If the first test is positive, probe terminals 5-4 and 5-6, the result should lie within the same range. If the test fails, replace the servomotor.
Removal and installation
1. The installation details of the IAC servo motor are shown in the illustration.
2. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!
3. Remove the air cleaner intake sleeve.
4. Disconnect the hoses connected to the IAC servo.
5. Remove the mounting bolts and remove the IAC servo assembly from the throttle body.
6. Installation is carried out in the reverse order - do not forget to replace the sealing gasket.
Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECT)
As its name suggests, the ECT sensor measures the engine coolant temperature. By design, the sensor is a thermistor, the resistance of which changes inversely with temperature. The sensor provides readable information to the PCM, which uses the received data when adjusting the ignition timing, EGR flow rate, air-fuel ratio, etc. Two wires are connected to the sensor, through which a reference voltage of 5 V is applied to it. Sensor output signal parameters are determined by a change in the temperature-dependent resistance of the working element.
Examination
1. Drain the engine coolant below the level of the ECT sensor installed in the intake manifold.

2. Disconnect from the gauge electroconducting and remove it from the engine.
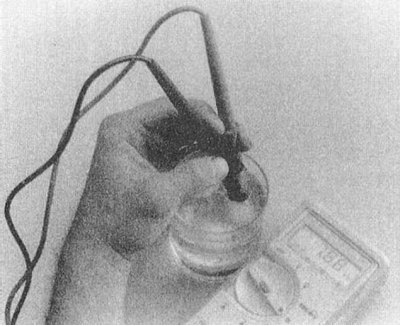
3. Lower the working element of the sensor into a vessel with a heated liquid, where the thermometer must also be lowered.
4. Connect an ohmmeter to the sensor and start heating the water, monitoring the nature of the change in the meter readings in accordance with the thermometer readings. Compare the measurement results with the requirements of the Specifications (5.1÷6.5 kOhm at 0°С; 2.1÷2.7 kΩ at 20°С and 0.26÷0.36 kΩ at 80°С. A defective sensor must be replaced.
Note. Alternatively, the ECT sensor check can be done using a diagnostic scanner.
 |  |
Removal and installation
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!
2. Drain the engine coolant below the level of the ECT sensor installed in the intake manifold.
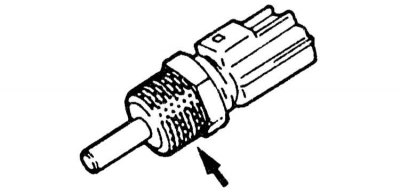
3. Disconnect the wiring from the sensor.
4. Turn out the gauge and remove it from the engine.
 |  |
 |
5. Before installation, the threaded part of the sensor should be lubricated with a suitable sealant.
6. Screw the sensor into its original place and tighten it with the required force (30 Nm).
7. Fill the cooling system with the required amount of mixture of the required grade (see chapter Settings and ongoing maintenance).
8. Connect the wiring to the ECT sensor (make sure the connector is secure).
9. Connect the negative cable to the battery.
Intake air temperature sensor (IAT)
The IAT sensor is part of the air mass sensor (MAF) and serves to control the temperature of the air sucked into the engine. The sensor, like the ECT sensor discussed above, is an NTC thermistor. The information from the IAT sensor is used by the PCM to make adjustments to ignition timing and air/fuel ratio settings. In addition, this information, in combination with data from the pressure sensor, is used when the control module calculates the mass of air supplied to the engine cylinders. The operating signal is generated by the sensor by converting the 5-volt reference voltage in accordance with the change in the resistance of the thermal sensor assembly.
Examination

1. The IAT sensor is part of the air mass sensor assembly (MAF).
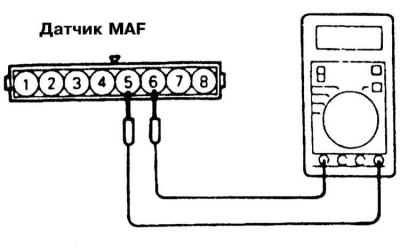
2. Disconnect the wiring from the MAF sensor.
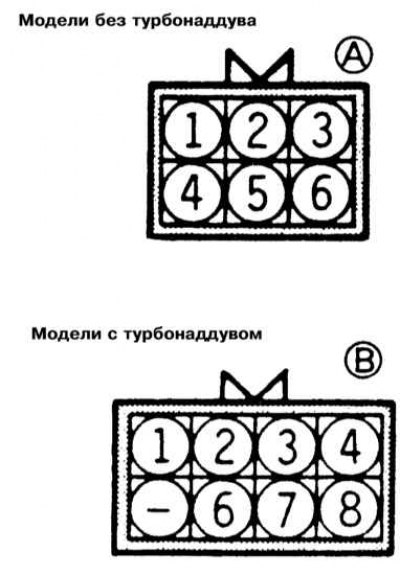
3. Measure the resistance between terminals 4 and 6 (all models except 2.0L DOHC) /6 and 8 (2.0L DOHC models) sensor connector.
Note. Alternatively, the IAT sensor check can be done using a diagnostic scanner.
 |  |
 |  |
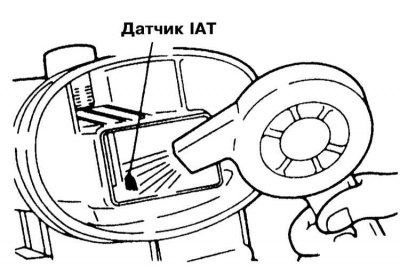 |
4. Compare the measurement results with the requirements of the Specifications (5.3÷6.7 kΩ at 0°C; 2.3÷3.0 kΩ at 20°С and 0.30÷0.42 kΩ at 80°С).
Note. The sensor can be heated using a household hair dryer.
5. A defective sensor must be replaced.
Removal and installation
The IAT sensor is a part of the MAF sensor, the description of which removal and installation procedures is given below in this Section.
Air mass sensor (MAF)
The MAF sensor is used to measure the mass of air flow sucked into the engine. The information provided by the sensor is used by the PCM to determine how long the injectors should open. As a work item ("hot wire") The MAF sensor uses a thin platinum wire wrapped around a ceramic ingot and filled with glass. The thread is heated to a value exceeding the ambient temperature by 200°C, and the working element is blown by the air flow sucked into the engine. The operating signal, which determines the temperature of the intake air, is taken from "cold" MAF sensor element (IAT sensor).
Reference voltage is supplied to the MAF sensor with PCM, grounding is also organized through the control module. The sensor returns to the module a signal whose amplitude is proportional to the strength of the current flowing through "hot wire" working element and ensuring the maintenance of the temperature of the latter at a given level. Increased blowing of the working element leads to a decrease in resistive resistance "hot wire" and to keep the temperature at the same level, a large current is required. The amplitude of the information pulses of the signal is directly proportional to the strength of the wire flowing through the working element and, if the sensor is functioning properly, should increase with an increase in the flow rate of air drawn into the engine.
Examination
1. Connecting a multimeter to the reverse side of the terminals of the connector, measure the voltage of the MAF sensor.
2. With the ignition on (do not start the engine) the voltage between the BATT and GND terminals must be at least 10.5 V. If this condition is not met, check the condition of the wiring of the power supply and ground circuits of the sensor.
3. Now start the engine and measure the voltage between the GND and SIG terminals. If the measurement is less than 4.5 V, check the condition of the power and ground circuit wiring.
4. Without stopping the engine, measure the signal voltage between the GND and SIG RTN terminals, - if the measurement result is outside the range of 0.34÷1.96 V, replace the sensor.
Removal and installation
Attention! Try not to expose the removed MAF sensor to shock, temperature and chemical influences!
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!

2. Release the air cleaner cover fasteners.
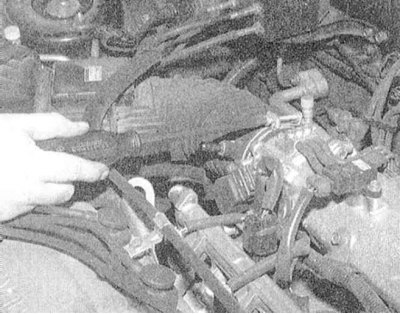
3. Loosen the outlet duct clamp on the throttle body.
4. Remove a branch pipe of a breather and disconnect electroconducting from the gauge MAF.
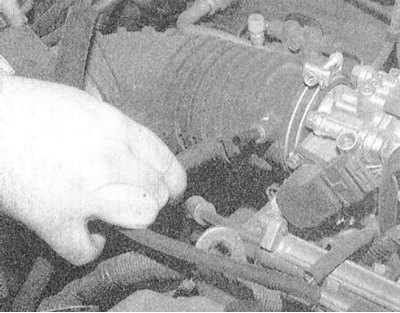 |  |
 |
5. Remove the outlet duct, then disconnect it from the air cleaner cover.
 |  |
6. Give four fixing nuts and remove assembly of the gauge MAF from an air cleaner cover.
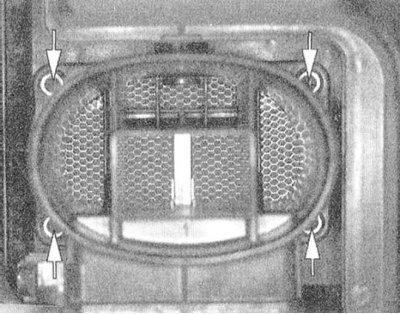 |  |
7. Installation is carried out in the reverse order.
Absolute pressure sensor in the intake manifold (MAP)
The information provided by the MAP sensor is fundamental to the air/fuel ratio control process. Using temperature and relative pressure data (atmospheric pressure data comes from the BARO sensor) in the intake manifold, the PCM calculates the current intake air flow into the engine and, based on the analysis of the received information, determines the required amount of fuel injected into the combustion chambers.
Examination
1. Using a multimeter, check the voltage at the MAP sensor connector (sensor probes are inserted into the contact terminals on the reverse side of the connector).
2. Turn on the ignition (do not start the engine) and make sure that the voltage between the SIG and GND terminals is at least 48 V, otherwise check the condition of the wiring of the power supply and ground circuits, make the necessary remedial repairs.
3. Start the engine and measure the voltage between the GND and SIG RTN connector terminals. If the measurement result is out of range (0.8÷2.4 V), replace the sensor.
4. If the results of the last check are positive, repeat the measurement, while sharply depressing the gas pedal, the reading should rise to 2.4 V and stabilize at this level. A defective sensor must be replaced.
Removal and installation
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!

2. Disconnect the electrical wiring from the MAP sensor.
3. Turn out bolts of fastening of the gauge and remove it from the inlet pipeline.
 | 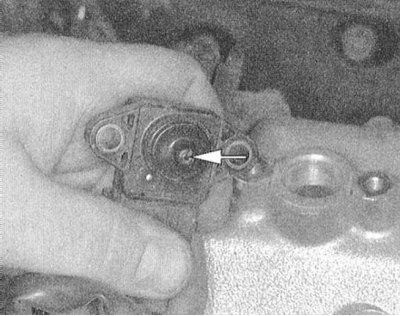 |
4. Installation is carried out in the reverse order.
Throttle position sensor (TPS)
The basis of the design of the throttle position sensor (TPS) potentiometer is set, i.e. a resistor whose resistance changes as a result of mechanical movement of moving components. The sensor is mechanically connected to the throttle valve shaft and generates a signal voltage proportional to the current value of the potentiometer resistance, determined by the position of the valve in the throttle body. The signal from the sensor is sent to the PCM, which, based on the analysis of the incoming data, determines the position and direction of movement of the damper and, accordingly, corrects the composition of the air-fuel mixture, the setting of the ignition timing and the intensity of the mixing of exhaust gases (EGR).
control module (PCM) organizes the supply of a reference voltage to the TPS (5 V) and grounding. The amplitude of the working signal of the sensor is determined by the position of the slider of the potentiometer associated with the axis of the throttle valve and at idle should be about 0.9 V.
Examination
Note. Adjustment of the TPS is not possible, in the event of a malfunction, the sensor must be replaced.

1. Start up and use a digital voltmeter to measure the voltage between the SIG RTN and GND terminals on the rear side of the sensor connector - at idle, the readings should lie within the range of 0.2 ÷ 1.4 V.

2. Slowly move the throttle to the fully open position - the voltage should also slowly increase to 4.8 V.
3. If there is no signal, check the correctness of the reference voltage supply to the sensor (5.0 V) and ground potential (less than 0.3 V), rewiring/replace PCM as required. If the power and ground are OK, replace the sensor.
Note. Alternatively, the TPS check can be done using a scanner-type diagnostic reader.
 |  |
Removal and installation
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!

2. Disconnect the wiring from the throttle position sensor.
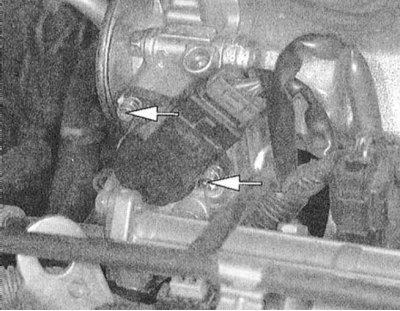
3. Remove the two mounting screws and remove the TPS from the throttle shaft.
4. Installation is carried out in the reverse order - make sure that the sensor is correctly engaged with the damper axis.
Camshaft position sensor (CMP)
Based on the analysis of the information coming from the CMP sensor, the PCM determines the position of the piston of the first cylinder of the engine and uses the obtained data when calculating the valve timing. When the CMP signals are missed, the control module injects fuel into the cylinders in accordance with the results of the last successful calculation, which eliminates the possibility of spontaneous engine shutdowns in the event of a CMP sensor failure (the recoil efficiency of the power unit can be significantly reduced in this case).
Examination
The sensor generates an AC signal whose frequency is proportional to the engine camshaft speed. Checking the sensor can only be done using expensive diagnostic equipment, which is why it would be wise to entrust it to Mitsubishi car service specialists. The performance of the CMP sensor can be monitored using a scanner-type diagnostic reader - follow the instrument manufacturers' instructions.
Removal and installation
1.6L, 2.0L DOHC and 1.8L models since 1997
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!
2. Disconnect the wiring from the sensor and remove the wiring harness mounting bracket from the throttle body.
3. Turn out fixing screws and remove the gauge from the engine.
4. Installation is carried out in the reverse order - make sure that the electrical wiring is laid correctly and that the fasteners are tightened securely.
Models 1.5 l, 2.4 l, 3.0 l SOHC, 3.5 l and 1.8 l 1993÷1996 issue
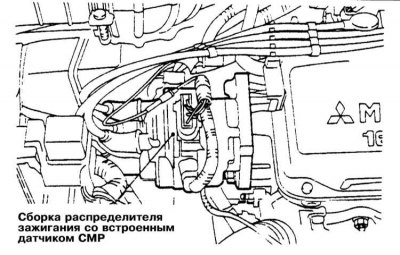
On these models, the CMP sensor is built into the ignition distributor. The description of procedures of removal and installation of the distributor see in the Chapter Engine electrical equipment this guide.
3.0L DOHC Models
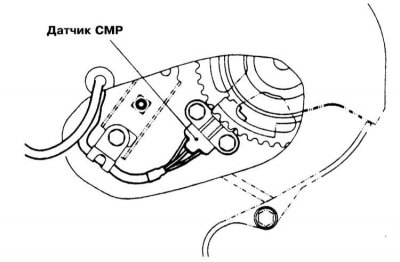
1. CMP sensor installation details on 3.0L DOHC models are shown in the illustration.
2. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!
3. Remove the timing belt (see chapter Engine). Disconnect wiring from CMP sensor.
4. Loosen the mounting bolts and remove the CMP sensor from the vehicle.
5. Installation is carried out in the reverse order.
Crankshaft Position/Angle Sensor (CKP)
The PCM uses pulse signals from the CKP sensor to determine the exact piston position of each of the engine's cylinders. Based on the results of the analysis of the information received, the control module determines the optimal moments of injection and ignition of the fuel.
Examination
As in the case of the CMP, the CKP sensor check should be entrusted to a car service specialist. Alternatively, you can use a diagnostic scanner.
Removal and installation
Models 2.0 l SOHC and 1.5 l 1990÷1996 issue
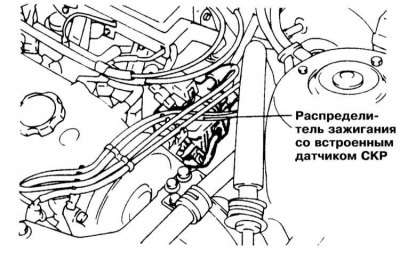
On these models, the CKP is built into the ignition distributor assembly, a description of the removal and installation procedures of which is presented in Chapter Engine electrical equipment.
1.6L and 2.0L DOHC Models
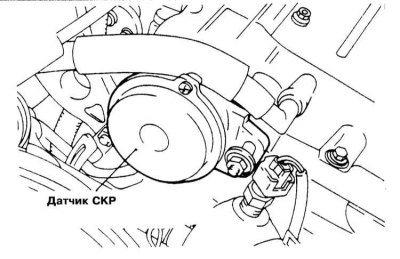
1. Details of installing the CKP sensor on these models are shown in the accompanying illustration.
2. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!
3. Disconnect the wiring from the CKP sensor and remove the wiring harness mounting bracket from the throttle body.
4. Turn out fixing screws and remove the gauge from the engine.
5. Installation is carried out in the reverse order - make sure that the electrical wiring is laid correctly and the fasteners are tightened securely.
Models 1.8 l, 2.4 l, 3.0 l and 3.5 l since 1997
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention! If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!
2. Remove the timing belt (see chapter Engine).
3. Disconnect wiring from CKP sensor.
4. Turn out fixing bots and remove the CKP sensor from the car.
 |  |
5. Installation is carried out in the reverse order.
