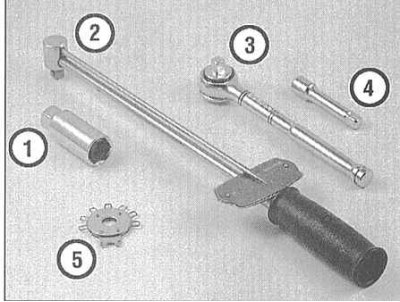
Tools needed when changing spark plugs
1 - Candle head - Equipped with a special elastic insert, which excludes the possibility of accidental damage to the porcelain insulator when the candle is turned out.
2 - Torque wrench - Not a mandatory tool, provides a reliable guarantee of the correct tightening torque of the spark plugs.
3 - Ratchet drive - Used in conjunction with a candle head and a torque wrench.
4 - Extension - Depending on the model and its accessories, access to spark plugs can be limited to varying degrees, so the use of extensions of the appropriate shape and design will greatly facilitate the procedure.
5 - A device for measuring and correcting spark plug gaps - Several types of this kind of tools are available - make sure that the tool is equipped with a feeler gauge that matches the size of the spark plug gaps in your car.
If the original spark plugs are re-installed on the engine after checking the condition, they must be screwed strictly into the previous cylinders - make the appropriate marking.
General information
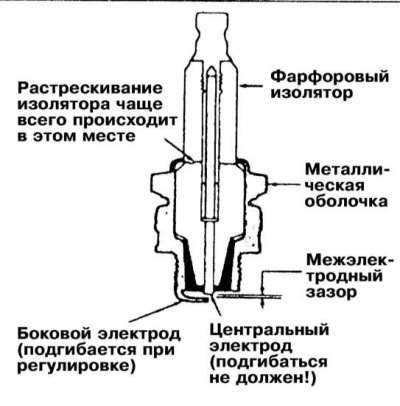
The spark plug is a metal sheath that surrounds a ceramic (porcelain) insulator. In the axial part of the insulator, a vertical channel is provided inside which the pin of the central electrode is inserted. The upper part of the pin is connected to the threaded tip screwed into the upper part of the insulator, the lower part protrudes from below, forming the working part of the electrode. The side electrode is welded directly to the metal of the shell of the candle assembly and, bending at 90°, goes to the central part of the lower end surface of the candle, located directly above the end of the working part of the central electrode. The air gap formed between the two electrodes is called the interelectrode gap and is one of the main operating parameters of the candle. The gap must be set strictly in accordance with the regulatory requirements determined by the types of candles and engine. When applying voltage to the spark plug (20÷50 kV) A spark forms from the ignition coil between the electrodes, which ignites the air-fuel mixture in the engine's combustion chamber. The intensity of sparking is actually determined by the size of the interelectrode gap.
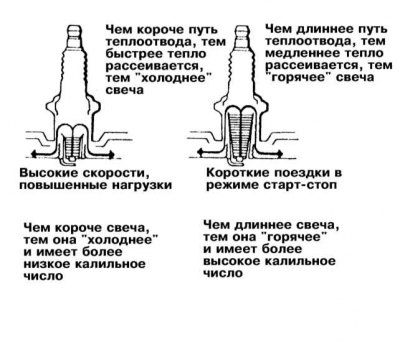
Another of the fundamental parameters of any candle is its glow number. The glow number determines the ability of a candle to dissipate heat. The longer the lower threaded part of the candle shell (the deeper the electrodes go into the combustion chamber), the hotter its operating temperature will be. Installation on the engine is excessive "cold" spark plugs leads to the rapid formation of oil and carbon deposits on their electrodes, eventually leading to misfiring. Use too "hot" spark plugs can lead to problems related to ignition timing (too early ignition), in addition, a diesel effect may occur when the engine continues to run for some time after the ignition is turned off. Generally the following rule applies: when driving long distances at high speeds, colder plugs should be used; "hot" candles. The best compromise is always achieved using original spark plugs recommended by the vehicle manufacturer (see Specifications).
Check and adjustment
During normal operation of the vehicle, the electrode gap of the spark plugs increases by an average of 0.025 mm for every 4000 km of run, which leads to a gradual decrease in the intensity of sparking. Carries out adjustment/replacement of spark plugs in strict accordance with the Vehicle Maintenance Schedule (see Section Mitsubishi Galant/Mirage/Diamante Routine Maintenance Schedule).
1. Most spark plug replacements require a special spark plug head (with elastic lining inside) complete with a ratchet drive, as well as a set of wrench drive extensions and a device for checking and adjusting the interelectrode gaps. A special tool is also available for safely disconnecting the BB wire tips from the spark plug shanks, although its use is not strictly required. Using a torque wrench will allow you to achieve the correct tightening torque for the candles.
2. It is best to keep a set of replacement spark plugs with a correctly adjusted electrode gap in the car at all times. When buying new spark plugs, make sure that they meet the requirements of your car engine in terms of their parameters. The necessary information is given in Specifications to this Chapter, as well as on the VECI label attached under the hood (in case of discrepancies, preference should be given to information from VECI).
3. Proceed to turning out the candles only after the engine has completely cooled down. In order not to waste time in vain, use the pause to check the status of the replacement kit. Carefully inspect the new candles - if the slightest cracks are found in the insulator, the corresponding candle should be rejected. Measure the electrode gaps of the new set (see below).
4. The gap between the electrodes of the spark plug is checked by inserting the appropriate meter probe into it and must comply with the requirements given in the specifications / on the VECI label. The required thickness of the probe should slip with slight resistance between the side and center electrodes of the spark plug. The gap can be adjusted using a special tool, usually included in the meter - bend the side electrode of the spark plug accordingly.
 | 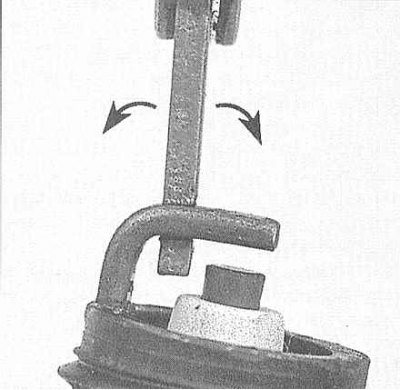 |
5. If the side electrode is not positioned exactly above the center electrode, adjust its position accordingly. Check for cracks or other damage in the porcelain insulator of the spark plug. The presence of any kind of defects in the insulator is unacceptable.
Removal and installation
1. In order to avoid violation of the ignition order when connecting the electrical wiring, each of the candles should be serviced individually.
2. Wait for the engine to cool completely. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
If the stereo system installed in the car is equipped with a security code, before disconnecting the battery, make sure that you have the correct combination to activate the audio system!
3. If equipped, remove the center cover. On 3.0L models (SOHC and DOHC engines) and 3.5 l in order to provide access to the spark plugs of the rear row of cylinders, it is necessary to remove the upper section of the intake manifold (see chapter Engine).
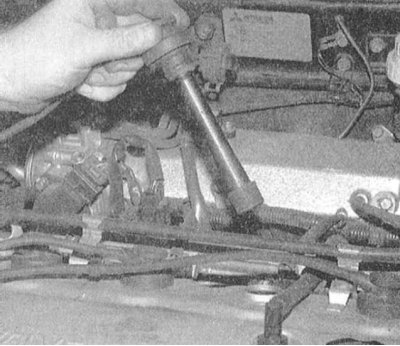
4. Disconnect the BB wire from the spark plug of the first cylinder - pull only by the tip, and in no case by the wire! It would be wise to use a special tool.
5. If you have a source of compressed air at hand, use it to remove debris from the spark plug niches of the engine (For this purpose, a conventional bicycle pump is no worse).
Remember to wear protective goggles when using compressed air!
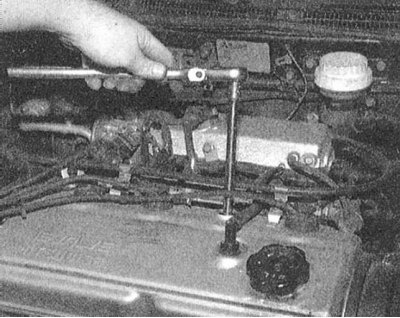
6. Unscrew the spark plug using a socket wrench with a special rubber-lined spark plug head (if necessary, pre-drop a little penetrating oil into the candle niche).
7. Compare the removed spark plug to the identification card on the photographic insert to give a good idea of the overall condition of the engine. Also evaluate the condition of the BB wire lugs, replace the defective components.
8. Before screwing in new spark plugs, lightly lubricate their threaded part with anti-seize sealant. Thread one of the new spark plugs into the appropriate hole in the engine by hand. After making sure that the candle is not skewed in the thread, tighten it with the required force (with a torque wrench handy). To facilitate the process of baiting a candle, pull a piece of flexible fuel hose onto its shank. This eliminates the possibility of thread breakage, since at the slightest biting, the hose will simply begin to turn.
9. Rotate the tip of the BB wire onto the shank of the spark plug.
Before connecting wires to BB candles, evaluate their condition.
10. Repeat the procedure for the remaining spark plugs, performing each step in turn to avoid misfiring.
11. Replace all components removed for access.
Coal deposits

Symptoms: The presence of soot indicates an over-rich air-fuel mixture or a weak spark intensity. Causes misfiring, difficult starting and engine instability.
Recommendations: Check if the air cleaner is clogged, if the fuel level in the float chamber is too high, if the air damper is stuck, and if the contacts are too worn. Try using plugs with a longer insulator, which increases fouling resistance.
The normal state of the candle

Symptoms: Gray-brown color and slight wear of the electrodes. The number of glow plugs corresponds to the type of engine and its general condition.
Recommendations: When replacing spark plugs, use spark plugs of the same type.
Oiling

Symptoms: Lubrication of the candle is caused by wear of the valve stem seals. Oil enters the combustion chamber through worn valve guides or piston rings. Causes misfiring, difficult starting and engine instability.
Recommendations: Carry out mechanical repairs and replace spark plugs.
Ash formation
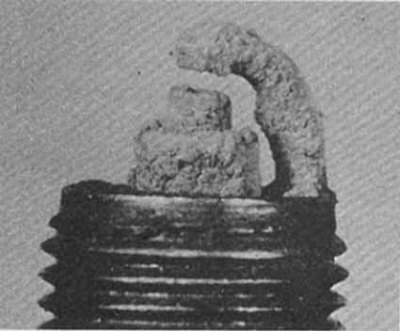
Symptoms: Soft brownish deposits on one or both spark plug electrodes. The source of their formation is the additives used in oil and/or fuel. Excessive buildup can insulate the electrodes and cause misfiring and engine instability when accelerating.
Recommendations: If deposits build up quickly, replace the oil seals to prevent oil from entering the combustion chambers. Try changing the brand of fuel.
Overheat
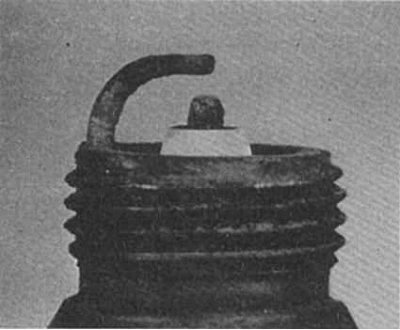
Symptoms: Porous, white insulator, electrode erosion and lack of any deposits. This will shorten the life of the spark plug.
Recommendations: Check if the glow rating of the installed plugs meets the requirements of the Specifications, if the ignition timing is set correctly, if the air-fuel mixture is supplied too lean, if there are vacuum leaks in the intake pipeline and if the valves are stuck. Also check the coolant level and check if the radiator is clogged.
Wear

Symptoms: Rounding of electrodes with a slight accumulation of deposits at the working end. The color is normal. Causes engine start difficulty in cold, wet weather and increased fuel consumption.
Recommendations: Replace spark plugs with new ones of the same type.
Too early ignition
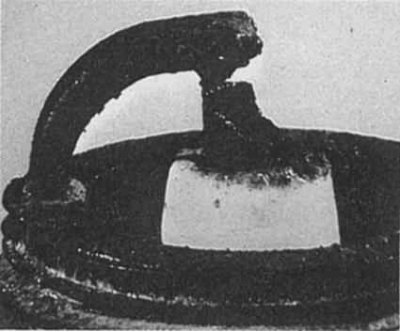
Symptoms: The electrodes are melted. The insulator is white, but may be dirty due to misfiring or foreign particles entering the combustion chambers. May lead to engine failure.
Recommendations: Check the glow number of the installed candles, the ignition timing, the quality of the mixture (isn't it too poor), whether the cooling system is clogged and the lubrication system is functioning properly.
Detonation
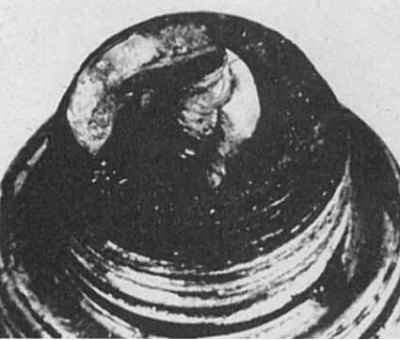
Symptoms: Insulators may be chipped or cracked. Insulator damage can also result from inaccurate spark plug gap adjustment. May damage pistons.
Electrically conductive gloss

Symptoms: The insulator has a yellowish color and a polished appearance. It speaks of a sudden increase in temperature in the combustion chambers during sharp acceleration. At the same time, ordinary deposits are melted, acquiring the appearance of a varnish coating. Causes misfiring at high speeds.
Recommendations: Change spark plugs (colder, while maintaining driving style).
Splashing
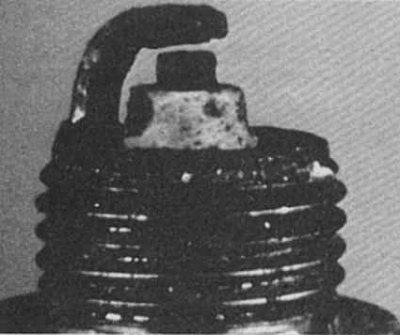
Symptoms: After misfiring for a long period of time, deposits can loosen while maintaining the operating temperature in the combustion chamber. At high speeds, deposits flake off the piston and adhere to the hot insulator, causing misfiring.
Recommendations: Replace spark plugs or clean and reinstall old ones.
Closing the electrodes
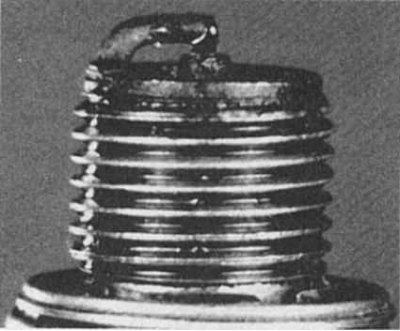
Symptoms: Waste products of combustion fall into the interelectrode space. Solid deposits accumulate, forming a jumper between the electrodes. Leads to ignition failure in the cylinder.
Recommendations: Remove deposits from the interelectrode space.
Mechanical damage
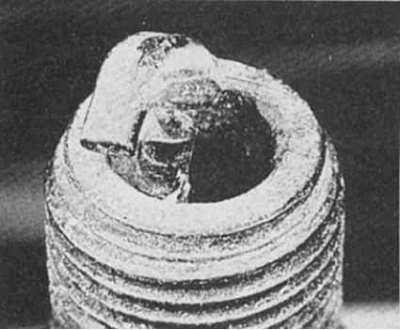
Symptoms: May be caused by foreign material entering the combustion chamber or caused by a piston hitting a spark plug that is too long. Lead to cylinder failure and piston damage.
Recommendations: Remove foreign particles from the engine and/or replace.
