- a) Two front airbags. The driver's airbag module is housed in the steering wheel hub. The front passenger airbag is placed in a special cavity on the right side of the car's instrument panel. The locations of both cushions are marked with warning labels "SRS AIRBAG";
- b) Sensors of directional overloads, triggered by a strong frontal impact;
- c) An electronic self-diagnostic system that, with the ignition on, provides continuous testing of overload sensors, the control unit, airbag gas generators and the connecting wiring of the corresponding circuit;
- d) Automatic emergency tensioners for front seat belts (see above);
- e) The control lamp of refusals of SRS which is built in in the panel of devices (see below);
- f) A spare autonomous power source designed to back up the main power supply system in the event of its failure in a car collision.
The principle of operation of the front airbags
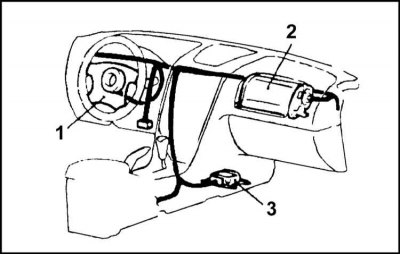
SRS Front Airbag Layout Diagram
1 - Driver's airbag module
2 - Passenger airbag module
3 - Control unit with directional overload sensor
1. Directional g-force sensors respond to exceeding a certain limit value that may occur during a severe frontal collision. At the signal of the sensors, the control unit turns on the gas generators of the airbags, causing them to instantly fill.
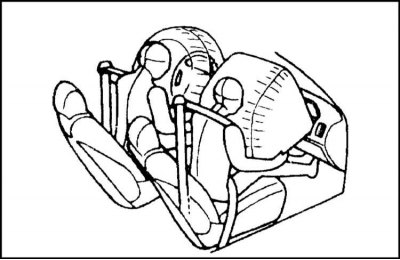
2. During a collision, the seat belt keeps the occupant's lower torso from moving. Front airbags help prevent injury to the driver and front passenger from head and chest impacts on the steering wheel/dashboard.
3. Because both airbags are triggered by the same sensors, both airbags will deploy at the same time. However, the probability of initiation of only one of the pillows is not ruled out. This becomes possible when the magnitude of the directional overloads that occurred during the collision was on the verge of the range of operation of the gas generators. In this case, the seat belts provide sufficient protection for the driver and front passenger, while the effect of the airbag deployment will be minimal.
4. Immediately after the airbags are activated and perform their functions, gas is released from them, which allows the driver to maintain visibility and freely manipulate all vehicle controls.
5. The full duration of the process from the moment the signal is given by the overload sensors to the release of gas from the pillows takes a fraction of a second. The airbags deploy so quickly that the human ear is simply unable to perceive the sound of gas generators when the airbags are filled.
6. After a traffic accident in which the airbags were deployed, the interior of the car looks slightly smoky. In fact, this is a suspension of finely dispersed powder, which is usually sprinkled with pillow shells in the folded state. People with a respiratory disease may experience some discomfort from the airborne gaseous products emitted by airbag generators.
Order of functioning of a control lamp of failures SRS
1. The SRS indicator lamp is built into the vehicle's instrument panel and is designed to warn the driver about failures detected by the self-diagnosis system in the additional security system. On some modifications of the car, the operation of the warning lamp indicates possible malfunctions in the side airbag units or automatic emergency seat belt tensioners.
2. When the ignition is turned on (ignition key turned to position "ON" [II]) the control lamp lights up for a short time, then immediately goes out, which confirms that all system components are functioning correctly.
3. If the warning light comes on randomly at any other time, the vehicle owner should seek help from a Mitsubishi dealer as soon as possible. Such situations include the following:
- a) The control lamp does not turn on when the ignition key is turned to the ON position (II);
- b) The control lamp continues to burn after implementation of start of the engine;
- c) The control lamp has turned on and is lit in a constant or flashing mode while the vehicle is moving.
4. In the presence of the above symptoms of a malfunction, the additional security system may fail in a vehicle accident.
Attention! Neglecting the SRS warning light signals can lead to the most serious consequences if the airbags fail during an accident.
Side airbags
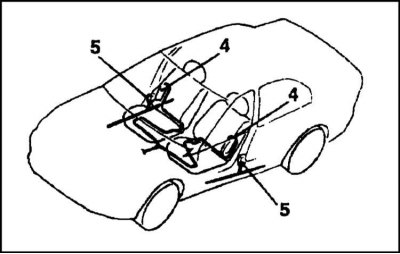
SRS Side Airbag Layout Diagram
4 - Side airbags
5 - Sensors of directional overloads
1. On some models, side airbags for the driver and front passenger can be installed as an option. Cushion modules are built into the outer ends of the front seat backs. The locations of both side airbags are labeled "SIDE AIRBAG". The SRS warning lamp on the vehicle's instrument panel also comes on when there is a malfunction in the side airbag initiation circuits.
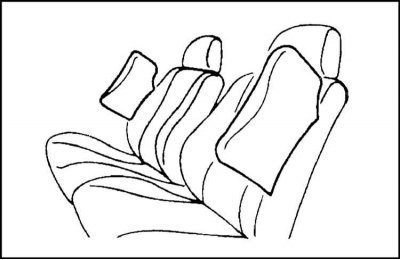
2. In case of a strong side impact, the sensors of directional overloads detect the excess of the emerging loads of a certain threshold value and issue an information signal to the control unit, which generates a command to deploy the gas generator of the corresponding side airbag. In this case, if the impact came from the side of the passenger seat, the passenger side airbag will work even if there is no passenger in the front seat.
3. For the most effective protection provided by the airbags, the driver and front seat passenger should sit upright and wear their seat belts.
Seat belts with automatic emergency retractors
1. On some models, the front seat belts may be equipped with automatic emergency retractors. The tensioners are activated in case of severe frontal overloads that occur in a frontal collision and provide instant removal of the slack in the belts, as a result of which the belts of the latter tightly cover the body of the seated person, significantly increasing the degree of protection for the driver and front passenger.
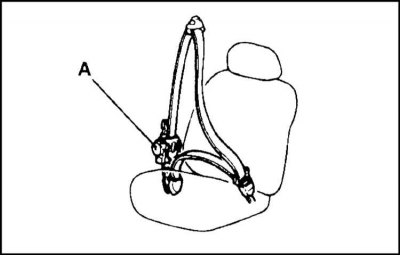
A - Tensioner
2. Tensioner (A) built into the belt return mechanism assembly. The procedure for using such seat belts is similar to the procedure for using conventional belts equipped with inertial return devices. The tensioner actuation mechanism is absolutely transparent to the user and does not require any additional skills and knowledge from the latter.
3. Activation of the tensioners occurs only with significant frontal overloads. The operation of the modules is accompanied by a loud bang and a small amount of smoke.
Note. The smoke emitted during the operation of the tensioners is safe for human health, however, if inhaled directly, it can cause irritation of the mucous membranes.
4. It should be noted that failures in the operation of tensioners during a frontal collision in most cases are not due to a malfunction of the system, but to the fact that the overloads that occur during an impact do not reach the threshold value at which the modules are activated.
5. As in the case of airbags, emergency tensioner modules are designed for a single operation and after that they must be replaced as an assembly with belts - contact Mitsubishi authorized service stations. All complaints about failures of SRS components are also accepted there.
Maintenance of SRS elements
1. Airbags and automatic emergency retensioners require little or no regular inspection and maintenance. However, the owner of a properly equipped vehicle should keep in mind the following points:
- a) After the airbags have deployed, they must be replaced together with the system control unit. Do not attempt to dismantle used airbags yourself. These operations should be performed only in the conditions of a car service workshop;
- b) If the activation of the SRS warning light indicates a system failure, contact the nearest Mitsubishi workshop without delay, where a complete diagnosis and necessary system repair will be carried out. Otherwise, the airbags may not deploy in an accident and fail to perform their protective function;
- c) Only specially trained personnel are allowed to work with the nodes of the additional security system. It is forbidden to dismantle the airbags and emergency seat belt pretensioners from the vehicle. In the event of SRS failure or after an emergency deployment of airbags and seat belt tensioners, you must contact a Mitsubishi workshop for repair or replacement of system components;
- d) Do not open the modules and do not change the wiring of the airbag systems and automatic emergency tensioner of seat belts - such intervention can lead to involuntary operation of the airbags and tensioners and cause injury to the performer or people nearby;
- e) Do not replace the front seats without first consulting a Mitsubishi Dealership. Careless or incorrect replacement or removal of the covers may cause the side airbags to fail to deploy in the event of an accident.
2. When transferring the car to another person, it is mandatory to inform the latter about all installed SRS elements, indicating the relevant paragraphs of the instructions for the rules for using the car.
3. On all models equipped with SRS, special warning signs are installed at the locations of the active elements of the system.

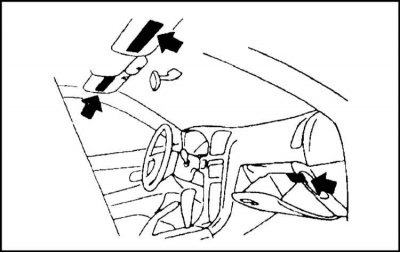
4. In addition, information labels are attached to the places indicated in the accompanying illustration, warning of a possible danger. Carefully read the text of the warnings - neglecting this information is fraught with the most serious consequences.
