Circuit breakers
Each individual fuse is used to protect a specific electrical circuit or several circuits at once. The identification card for the placement of fuses in the mounting block is usually printed on the cover of the latter, from its outer side.
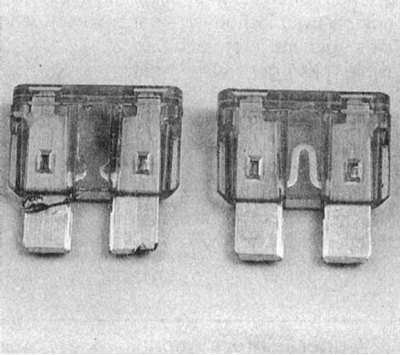
The mounting blocks contain fuses of a compact design, equipped with bayonet contact terminals, and, if necessary, easily removed with fingers from their sockets in the block. In case of failure of any of the consumers of electricity, first of all, you should always check the condition of the corresponding fuse. Turn the key in the ignition switch to the ON position and, using a test lamp, probe the open terminals of each of the fuses. If the lamp lights up when connected to each of the terminals, then the fuse is good. If there is voltage only on the power supply side, then the fuse is blown. We also note that usually the fuse case is made of transparent plastic, through which it is easy to determine the state of the working jumper.
When replacing a blown fuse, make sure that the replacement fuse being installed matches the type of the fuse that came out of the element. Fuses designed for different rated currents may not physically differ from each other in any way, while not being interchangeable. Each of the electrical circuits has different operating parameters and needs a different degree of protection, therefore, replacing a fuse designed for a certain current strength with one that does not correspond to it in terms of parameters is fraught with the most serious consequences (until the fire). Fuse operating parameters (rated current) usually marked on its plastic case.
If the new fuse also fails immediately after installation, it makes no sense to replace it further - first, the cause of the overload in the circuit should be identified and eliminated. In most cases, this is a short circuit of the connecting wiring, caused by damage to its insulation.
Replacement
1. The diagrams of the location of the fuses in the mounting blocks are presented in Specifications to this chapter.
2. In the engine compartment, the mounting block is located in close proximity to the battery, in the cabin - on the left under the instrument panel.
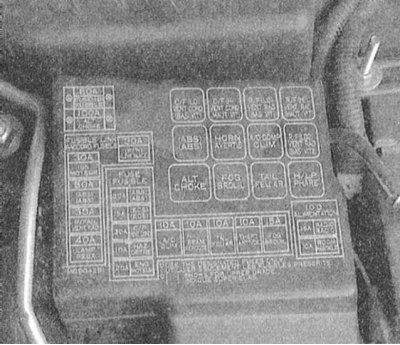 |  |
3. Remove the cover of the appropriate mounting block.
 |  |
4. By visual inspection, identify the failed fuse and, using a special clip, remove it from its seat.
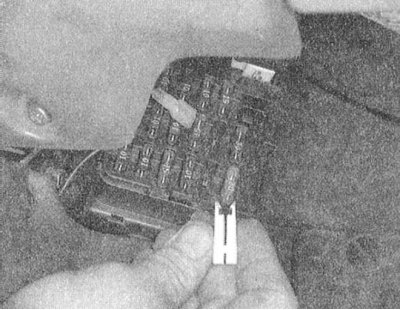 | 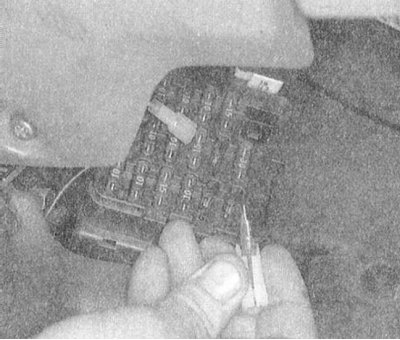 |
5. Examine the condition of the contact terminals in the receiving socket of the mounting block, remove traces of oxidation, replace the defective terminals.
6. Replace the failed fuse with a replacement fuse that matches the original one in terms of parameters.
Note. A set of spare fuses is usually stored in the cabin mounting block.
Fusible links
1. Fused links are used to protect circuits in which conventional fuses cannot be used for any reason, such as the ignition circuit, as well as for power circuits in which high current circulates.
2. The main set of fusible links is mounted in the engine compartment near the battery. The second group is housed in a nearby fuse/relay box.
3. When a fusible link fails, it is extremely important to find out the cause of the overload in the corresponding electrical circuit.
4. Failed fuse-links of the usual type are not subject to refurbishment. Make sure that the replacement element is fully consistent with its nominal characteristics of the failed one.
Circuit breakers
Circuit breakers are used to protect vehicle electrical system components such as headlights and power window motors, door lock actuators, etc.
On some models, after operation, the breakers return to their original state automatically. If the overload that caused the tripping of the breaker was not episodic, the condition of the corresponding circuit should be checked without delay. After the fault has been cleared, the circuit breaker will return to normal operation. Sometimes the interrupter must be reset manually after the cause of the overload has been eliminated.
