General information
When the vehicle is equipped with a conventional brake system, depressing the foot brake pedal suddenly causes the wheels to lock. In this case, the grip of the tread with the road surface is disturbed, and the car can go skidding, losing controllability. Anti-lock brake system (ABS) prevents premature blocking of the wheels by continuously controlling the speed of their rotation during braking by modulating the pressure of the hydraulic fluid in each of the brake mechanisms.
Electronic control unit (ECU) ABS monitors the speed of rotation of each of the wheels of the car, focusing on signals from wheel sensors. When, during emergency braking, any of the wheels begins to lock up prematurely, the ECU issues a command to activate the solenoid valve placed inside the hydraulic modulator, which, when activated, opens the corresponding section of the brake circuit, releasing some of the hydraulic fluid from it into the reservoir and, accordingly, reducing the working pressure. As soon as the wheel speeds equalize, the valve closes again and the pressure continues to rise. The cycle lasts a fraction of a second on each of the wheels and repeats until the braking is completed. The design of the system allows you to adjust the pressure in the hydraulic circuits of each of the four wheels. In reality, the ABS operation is much more complicated than it might seem, so the compilers of this manual do not recommend car owners to attempt to repair the system on their own. In the event of a problem, it would be wiser to contact a car service specialist.
Fault Diagnostics and Fault Codes
If the ABS warning light built into the vehicle's instrument panel comes on and stays on while driving, first make sure that the parking brake is fully released and that the brake system is functioning properly. If everything is normal, then the ABS has failed. Do not forget that the operation of the ABS warning lamp may be caused by a decrease in the level of brake fluid in the GTZ reservoir - the brake system warning lamp will also work at the same time. Constant, not related to the wear of the friction linings of the pads, the consumption of brake fluid indicates the presence of leaks in the hydraulic path:
- a) Check the condition of the brake calipers and wheel cylinders;
- b) Check the components of the hydraulic path for signs of leak development;
- c) Check up a condition and reliability of fastening of contact sockets of electroconducting ECU and wheel gauges (see chapter Onboard electrical equipment);
- d) Check the relevant fuses (see chapter Onboard electrical equipment).
control module (ECU) ABS monitors any malfunction of the system components. If a failure is detected on the instrument panel, the corresponding control lamp lights up, the anti-lock brake system is disabled. In this case, a failure code is written to the memory of the control module.
Note. When the ignition is switched on, the ABS warning lamp illuminates two (FWD models) or four (AWD models) flashes for 1 second, then it should turn off.
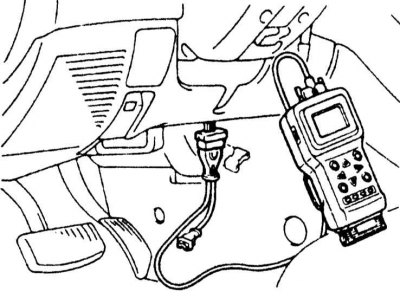
If no irregularities can be found during self-checks, drive the vehicle to a workshop. Full ABS diagnostics require the use of a special reader type DRB-II or MUT-III, connected to the DLC diagnostic connector located on the left under the instrument panel.
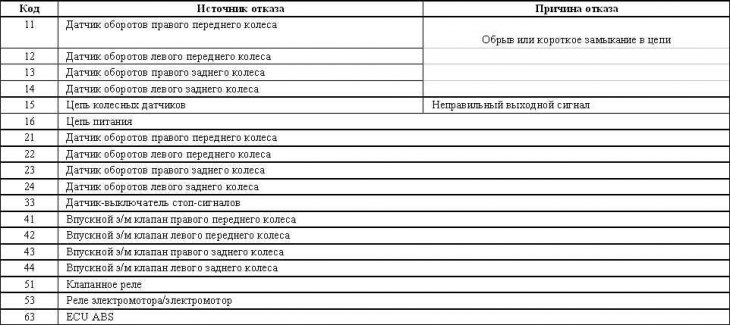
List of ABS fault codes
Diamante models 1992÷1996 issue
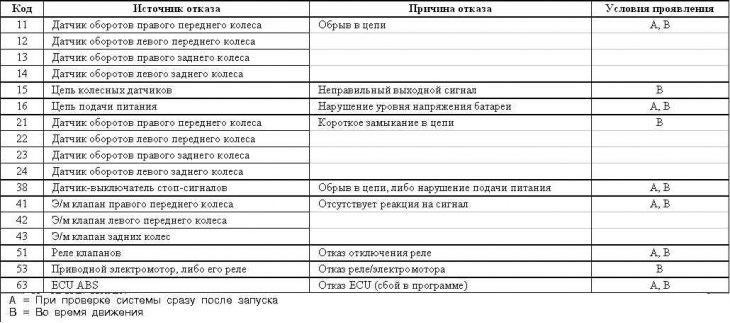
Diamante models since 1997 issue
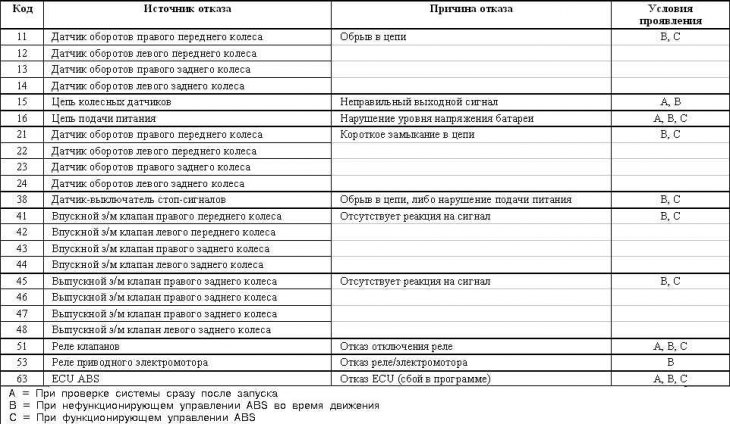
Galant models through 1993 no.
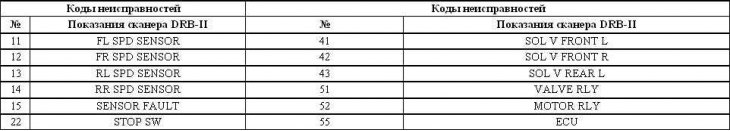
Galant models 1994÷1998 issue
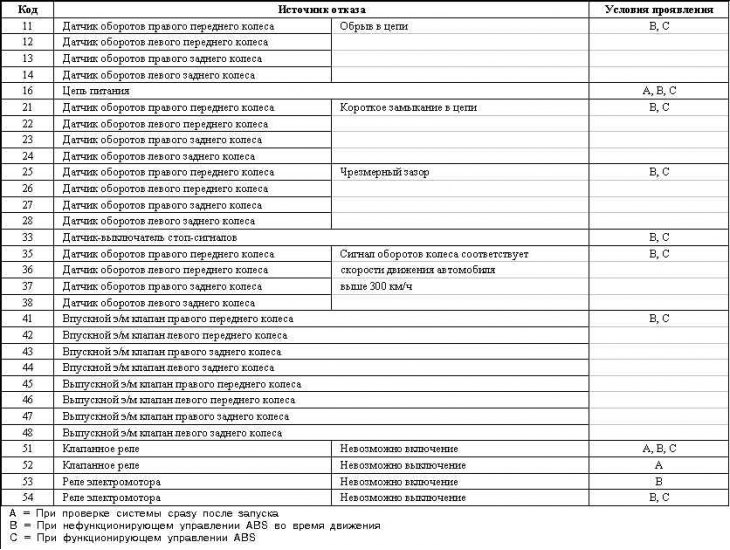
Galant models since 1999
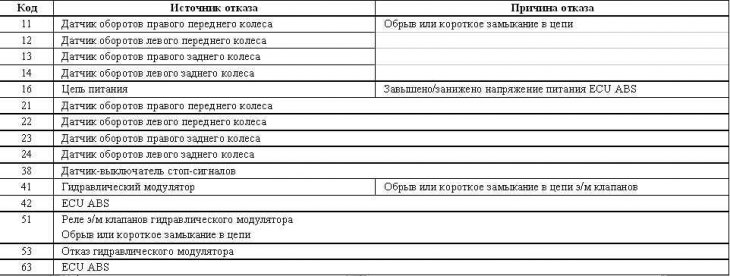
Mirage models 1993÷1996 issue
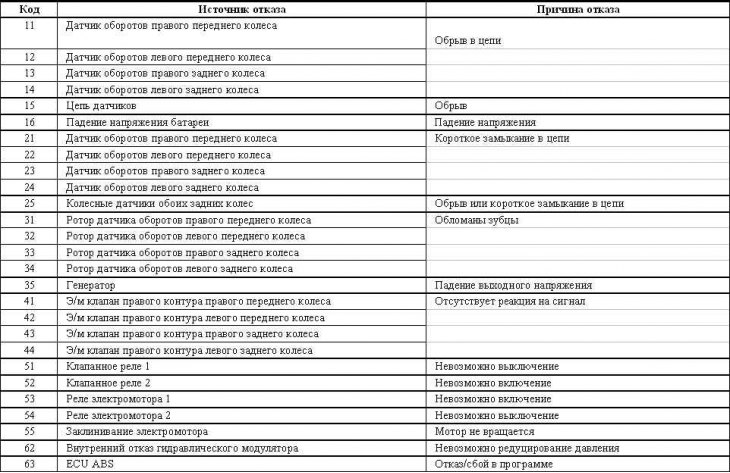
Mirage models since 1997