Share with friends:
4G1 engines since 1995 car Mitsubishi Colt 5 (CJ)
Engine specifications and data
Technical characteristics of engines are given in tables 3.1 a-c, technical data - in table 3.2. Table 3.1a. Specifications for 4G13 12V motors Table 3.1b....
Technical characteristics of engines are given in tables 3.1 a-c, technical data - in table 3.2. Table 3.1a. Specifications for 4G13 12V motors Table 3.1b....
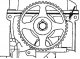
Toothed timing belt — design description
The timing belt for SOHC engines is shown in fig. 3.4, DOHC - in fig. 3.5. Pic. 3.4. Timing belt for SOHC engines: 1 - Upper protective cover of the timing belt; 2 -...
The timing belt for SOHC engines is shown in fig. 3.4, DOHC - in fig. 3.5. Pic. 3.4. Timing belt for SOHC engines: 1 - Upper protective cover of the timing belt; 2 -...
Toothed timing belt — check
1. Replace the toothed belt if the following defects are found: hardened rubber on the outside of the belt. If the outer side of the belt is shiny, inelastic, and so...
1. Replace the toothed belt if the following defects are found: hardened rubber on the outside of the belt. If the outer side of the belt is shiny, inelastic, and so...
Toothed Timing Belt — Installation
SOHC engines 1. Align the TDC mark on the camshaft with the mark on the cylinder head (pic. 3.7). Pic. 3.7. Align the TDC mark on the camshaft with the mark on the...
SOHC engines 1. Align the TDC mark on the camshaft with the mark on the cylinder head (pic. 3.7). Pic. 3.7. Align the TDC mark on the camshaft with the mark on the...
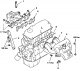
Intake and exhaust manifolds
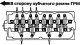
The intake and exhaust manifolds of SOHC engines with a carburetor are shown in fig. 3.23, SOHC engines with MPI injection - in fig. 3.24, 16V SOHC engines with MPI...
The intake and exhaust manifolds of SOHC engines with a carburetor are shown in fig. 3.23, SOHC engines with MPI injection - in fig. 3.24, 16V SOHC engines with MPI...
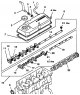
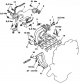
Rocker arms, rocker shafts and camshaft
Rocker arms, rocker axles and camshaft of SOHC 12V engines are shown in fig. 3.28, SOHC 16V motors (up to 2000 onwards) - in fig. 3.29 SOHC 16V motors (since 2000) - in...
Rocker arms, rocker axles and camshaft of SOHC 12V engines are shown in fig. 3.28, SOHC 16V motors (up to 2000 onwards) - in fig. 3.29 SOHC 16V motors (since 2000) - in...
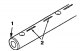
Camshaft — check and installation
1. Measure the cam height and replace the camshaft if the measured value exceeds the limit (pic. 3.32). The heights of the camshaft cams are shown in Table 3.3. Pic....
1. Measure the cam height and replace the camshaft if the measured value exceeds the limit (pic. 3.32). The heights of the camshaft cams are shown in Table 3.3. Pic....
Camshaft bearing caps — installation
1. Position the camshaft adjusting pins as shown in Figure 3.34a. With this position of the adjusting pins of the camshafts, the grooves for tightening the bolts for...
1. Position the camshaft adjusting pins as shown in Figure 3.34a. With this position of the adjusting pins of the camshafts, the grooves for tightening the bolts for...
Rocker arms and rocker axles — installation
Installing the rocker axle 1. On SOHC 12V engines: the rocker shaft with the larger chamfer on the end is placed in the direction of the flywheel. On SOHC 16V engines:...
Installing the rocker axle 1. On SOHC 12V engines: the rocker shaft with the larger chamfer on the end is placed in the direction of the flywheel. On SOHC 16V engines:...
Valve clearance adjustment
1. Set the piston of the first cylinder to TDC on the compression stroke. 2. Adjust the valves shown in fig. 3.39a,b. To do this, loosen the locknut of the adjusting...
1. Set the piston of the first cylinder to TDC on the compression stroke. 2. Adjust the valves shown in fig. 3.39a,b. To do this, loosen the locknut of the adjusting...
Cylinder head and valves
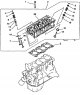
The cylinder head and valves for SOHC 12V engines are shown in fig. 3.42, SOHC 16V engines - in fig. 3.43, DOHC engines - in fig. 3 44. Pic. 3.42. Cylinder head and...
The cylinder head and valves for SOHC 12V engines are shown in fig. 3.42, SOHC 16V engines - in fig. 3.43, DOHC engines - in fig. 3 44. Pic. 3.42. Cylinder head and...
Cylinder head — check
1. Using a fine ruler and feeler gauge, check the deformation of the cylinder head sealing surface (pic. 3.45). If the deformation exceeds the maximum allowable value,...
1. Using a fine ruler and feeler gauge, check the deformation of the cylinder head sealing surface (pic. 3.45). If the deformation exceeds the maximum allowable value,...
Valves — check
1. Check the valve disc for tightness. Correct it if necessary. The working surface of the valve seat must be in the middle of the valve disc and evenly distributed...
1. Check the valve disc for tightness. Correct it if necessary. The working surface of the valve seat must be in the middle of the valve disc and evenly distributed...
Valve spring — check
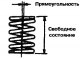
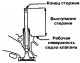
1. Measure the free length of the valve spring (pic. 3.47). If the value obtained is less than the maximum allowable value, the spring must be replaced. Pic. 3.47....
1. Measure the free length of the valve spring (pic. 3.47). If the value obtained is less than the maximum allowable value, the spring must be replaced. Pic. 3.47....
Valve stem guide — check
1. Measure clearance between valve guide and valve stem (pic. 3.48). If the value is out of range, replace the valve or valve guide (or both parts). The clearance values...
1. Measure clearance between valve guide and valve stem (pic. 3.48). If the value is out of range, replace the valve or valve guide (or both parts). The clearance values...
Valve seat — inspection, processing and replacement
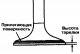
Examination 1. Install the valve. Press the valve stem against the seat and measure the distance from the end of the stem to the working surface of the valve spring seat...
Examination 1. Install the valve. Press the valve stem against the seat and measure the distance from the end of the stem to the working surface of the valve spring seat...
Valve Stem Guide Replacement
1. Press out the valve stem guide bushing from the cylinder block side. 2. Drill in a head of the block of cylinders a hole for the directing plug of a core of the valve...
1. Press out the valve stem guide bushing from the cylinder block side. 2. Drill in a head of the block of cylinders a hole for the directing plug of a core of the valve...
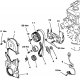
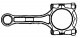
Connecting rod and piston — design description
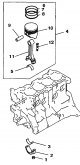
The connecting rod and piston group is shown in fig. 3.53. Pic. 3.53, Connecting rod and piston group: 1 - Nut of the bottom cover of the connecting rod; 2 - The bottom...
The connecting rod and piston group is shown in fig. 3.53. Pic. 3.53, Connecting rod and piston group: 1 - Nut of the bottom cover of the connecting rod; 2 - The bottom...
Piston rings — check
1. Check the piston rings for excessive wear, damage or breaks and replace with new ones if defective. If the piston was replaced, it was necessary to replace the piston...
1. Check the piston rings for excessive wear, damage or breaks and replace with new ones if defective. If the piston was replaced, it was necessary to replace the piston...
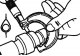
Connecting rod bearings — check
1. Bearings are selected according to the identification marks or color markings of the crankshaft and connecting rod (pic. 3.56a,b and table 3.7). Pic. 3.56a....
1. Bearings are selected according to the identification marks or color markings of the crankshaft and connecting rod (pic. 3.56a,b and table 3.7). Pic. 3.56a....
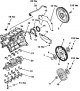
Crankshaft and cylinder block
The crankshaft and the block of cylinders are shown on fig. 3.57. Pic. 3.57. Crankshaft and cylinder block: 1, 3, 8, 17 - Bolts; 2, 5 - Flywheels; 4, 6, 9 - Intermediate...
The crankshaft and the block of cylinders are shown on fig. 3.57. Pic. 3.57. Crankshaft and cylinder block: 1, 3, 8, 17 - Bolts; 2, 5 - Flywheels; 4, 6, 9 - Intermediate...
Cylinder block — check
1. Visually inspect for cracks and corrosion; To do this, carry out a powder test. If possible, repair defects or replace the cylinder block. 2. Check that the top is...
1. Visually inspect for cracks and corrosion; To do this, carry out a powder test. If possible, repair defects or replace the cylinder block. 2. Check that the top is...
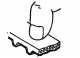
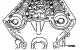
Main bearing shells — installation
1. Liners are selected in accordance with the identification marks or color marking of the crankshaft, for which table 3.8 is used. If the bearings cannot be identified,...
1. Liners are selected in accordance with the identification marks or color marking of the crankshaft, for which table 3.8 is used. If the bearings cannot be identified,...
Main bearing caps — installation
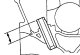
1. The underside of each cap is marked with the main bearing cap number and has an arrow showing the direction towards the front of the engine (pic. 3.60). Starting with...
1. The underside of each cap is marked with the main bearing cap number and has an arrow showing the direction towards the front of the engine (pic. 3.60). Starting with...
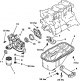
Oil pump and sump — design description
The oil pump and engine sump are shown in fig. 3.62. Pic. 3.62. Oil pump and engine sump: 1 - Oil filter; 2 - Threaded drain plug; 3 - Oil seal; 4.Support gearbox; 5 -...
The oil pump and engine sump are shown in fig. 3.62. Pic. 3.62. Oil pump and engine sump: 1 - Oil filter; 2 - Threaded drain plug; 3 - Oil seal; 4.Support gearbox; 5 -...
Oil pump and sump — check
1. Install the rotor in the front crankcase cover. 2. Measure the radial clearance with a feeler gauge (pic. 3.63). Rated value: 0.06-0.18mm. Pic. 3.63. Radial clearance...
1. Install the rotor in the front crankcase cover. 2. Measure the radial clearance with a feeler gauge (pic. 3.63). Rated value: 0.06-0.18mm. Pic. 3.63. Radial clearance...
Tightening torques for elements and parts of 4G1 engines
Engine mounting elements Tightening torque, Nm coolant pump pulley bolt 9 Generator rack (from the generator side) 22 Generator rack (tightened with coolant pump) 23...
Engine mounting elements Tightening torque, Nm coolant pump pulley bolt 9 Generator rack (from the generator side) 22 Generator rack (tightened with coolant pump) 23...
Changes in the design of 4G1 engines since 2001
Technical data of the 4G1 engine after 2001 are given in table 17.1. Table 17.1. Technical data of the 4G1 engine after 2001 Options Rated value Intake air temperature...
Technical data of the 4G1 engine after 2001 are given in table 17.1. Table 17.1. Technical data of the 4G1 engine after 2001 Options Rated value Intake air temperature...
Changes in the design of the intake and exhaust manifold since 2001
The following technical data refer to the addition of a steel tube intake manifold for 4G1 engines and an exhaust manifold with catalytic converter (pic. 17.8, 17.9a,b)....
The following technical data refer to the addition of a steel tube intake manifold for 4G1 engines and an exhaust manifold with catalytic converter (pic. 17.8, 17.9a,b)....
This section is available on: russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Similar materials for other Mitsubishi models
➤ Power unit: Petrol engines 4G1 Mitsubishi Space Star (1998-2005)
Link in different formats to this section
TEXTHTMLBB Code
- General information
- User manual
- Specifications
- Gasoline engines
- 4G1 engines until 1995
- 4G1 engines since 1995
- Repair of 4G9 engines
- Cooling system
- Reduced exhaust gas toxicity
- Engine electrical equipment
- Injection system MPI
- Carburetors
- Transmission
- Clutch and drive shafts
- Manual gearbox F4M21/F5M21
- Manual gearbox F4M41
- Automatic gearbox F4A21
- Automatic gearbox F4A41
- Chassis and running gear
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine in a car
- Engine repair (gasoline)
- Engine repair (diesel)
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Carburetor
- Fuel injection MPI
- Fuel injection GDI
- Emission reduction
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Ignition system
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Manual gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis and running gear
- Chassis malfunctions
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Wheels and tires
- Brake system
- Body and interior
- Body elements
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices
- Heating and air conditioning
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Daily care
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine in a car
- Engine overhaul
- Cooling system
- Heater and air conditioner
- Power and exhaust system
- Engine electrical equipment
- Emission reduction
- Transmission
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Clutch and axles
- Chassis and running gear
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body and interior
- Body and elements repair
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
MitsubishiMan.ru © 2018–2024 • Mobile version • Articles about Mitsubishi • Contacts • Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU • Site search • Bookmark
Colt 2 and 3 (1983-1993) · Colt 4 and 5 (1991-2003) · Colt 5 (1995-2003) · Lancer 3 and 5 (1984-1992) · Lancer 9 (2000-2007) · Galant 6 and 7 (1987-1998) · L200 4 (2005-2014) · Outlander 1 (2003-2008) · Pajero 1 and 2 (1982-1999) · Carisma (1995-2004) · Space Star (1998-2005) ·
Colt 2 and 3 (1983-1993) · Colt 4 and 5 (1991-2003) · Colt 5 (1995-2003) · Lancer 3 and 5 (1984-1992) · Lancer 9 (2000-2007) · Galant 6 and 7 (1987-1998) · L200 4 (2005-2014) · Outlander 1 (2003-2008) · Pajero 1 and 2 (1982-1999) · Carisma (1995-2004) · Space Star (1998-2005) ·