Purge control valve
Check the condition of all hoses and connections. Many problems often arise from loose connections in the system or limited hose capacity.
Check valve (1), by removing the valve from the vehicle and connecting a hand vacuum pump to the valve's vacuum port. The valve must maintain vacuum.
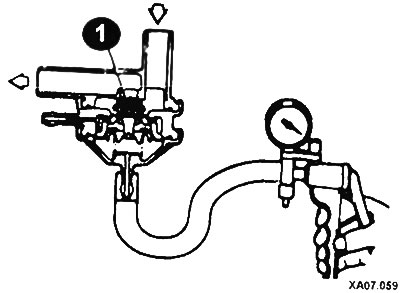
Lower the vacuum and apply a stream of air at low pressure to the hose fitting located on the side of the filter.
In the absence of vacuum, air should not pass through the valve. Lower the vacuum to 150 mmHg. Art. Re-inject air into the nozzle. Air must pass through the valve.
The charcoal filter is controlled by the purge control solenoid valve. With the engine off, disconnect the two vacuum hoses leading to the valve.
Disconnect the electrical supply wire from the valve. Connect the hand vacuum pump to the connection to which the hose was connected. Create some vacuum with the pump; it must be preserved.
Connect the battery to the solenoid valve terminals.
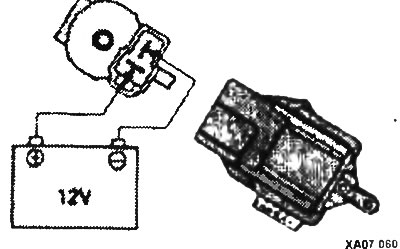
The polarity must be absolutely correct. Connect the positive terminal to the terminal forming «upper part» letters «T». After energizing the solenoid valve, the vacuum should decrease as the hand pump is operated.
Disconnect the battery and check the resistance at the solenoid valve terminals. The resistance value should be 36-44 ohms at a temperature of 20°.
WARNING: Remember that the resistance value varies with temperature.
Thermal valve
Thermal valves are mounted on the intake manifold or cylinder head so that their bottom is immersed in coolant (On later engine models, the purge system is controlled by the fuel injection computer). The thermal valve provides a delay or vacuum to the purge control valve depending on the temperature of the coolant. Check on a cold engine.
Disconnect the two vacuum hoses at the thermal valve. With the engine off, connect a hand vacuum pump to the top port on the two port valves or to the single port.
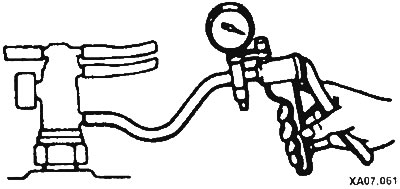
Apply vacuum and check that the valve passes or does not retain vacuum.
Start and warm up the engine. After the coolant has reached operating temperature, disconnect the appropriate hose and recheck. The valve must maintain vacuum.
Replace the thermal valve only on a cold engine.
Overflow limiter (two-way valve)
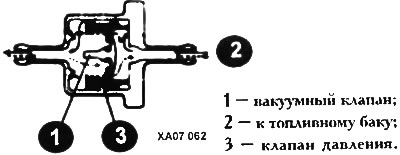
Elements of a two-way valve
This device, sometimes mistaken for a fuel filter, is installed on the steam line leading from the tank to the carbon filter. Located on or near the tank, this valve is sensitive to both compression and vacuum. It is designed to compensate for pressure drops that occur in the tank.
When the tank is pressurized, for example at high air temperature or after a long distance run, the valve releases pressure and vapors into the carbon filter, thereby venting the tank and preventing the evaporation level from rising. Conversely, when a vacuum is formed in the tank, the valve will bleed some air from the filter into the tank.
WARNING: If you hear a sound coming from the rear of your vehicle (even with the engine off), then this is the sound of the operation of this valve when it releases pressure. To eliminate this sound, unscrew the fuel filler cap and screw it back on.
By replacing the valve, you can only change the tone of the sound, while the sound itself is preserved in most cases.
To check, do the following:
- Remove the valve from the steam line.
- Lightly blow the valve on each side. If the air passes with some resistance, the valve is operational.
- Connect the valve to the line in the appropriate direction and secure the clamps. Before installing the clamps, make sure that the lines are securely installed on the nozzles.
Gravity valve
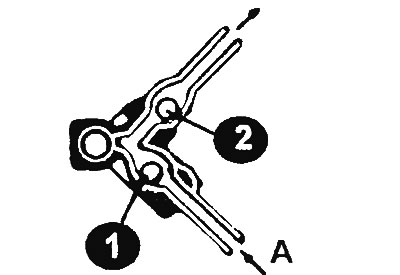
This valve is located in the steam line leading from the tank to the carbon filter. The valve prevents gasoline from leaking from the fuel tank into the system if the vehicle rolls over in the event of an accident. Under normal conditions, vapors are supplied through this line, which are easily absorbed and retained by the carbon mass of the filter.
When the vehicle rolls over, the line fills with liquid gasoline. Therefore, the gravity valve shuts off the fuel line and keeps the fuel in the tank.
To check it is necessary to remove the valve and disconnect the hoses from it. If it clicks when you shake it, it is working.
Carbon filter
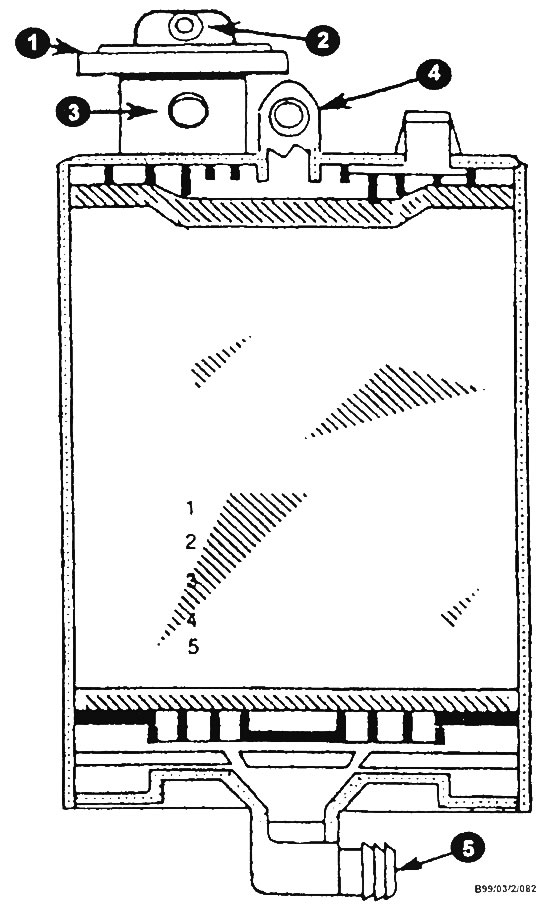
Typical carbon filter elements (tank for collecting fuel vapors)
1 - tank purge valve; 2 - branch pipe of the valve control cavity for connecting a vacuum hose; 3 - branch pipe of the purge line; 4 - branch pipe for connecting the hose for removing gasoline vapors from the tank; 5 - air inlet.
The carbon filter should be checked periodically for blockage cracks and hose connections. On many models, the carbon filter is replaced after a certain period of time or after a certain number of kilometers have been driven.
