ATTENTION: Some car models have a different optimal temperature regime for the cooling system. Temperature values are usually printed on the thermostat housing.
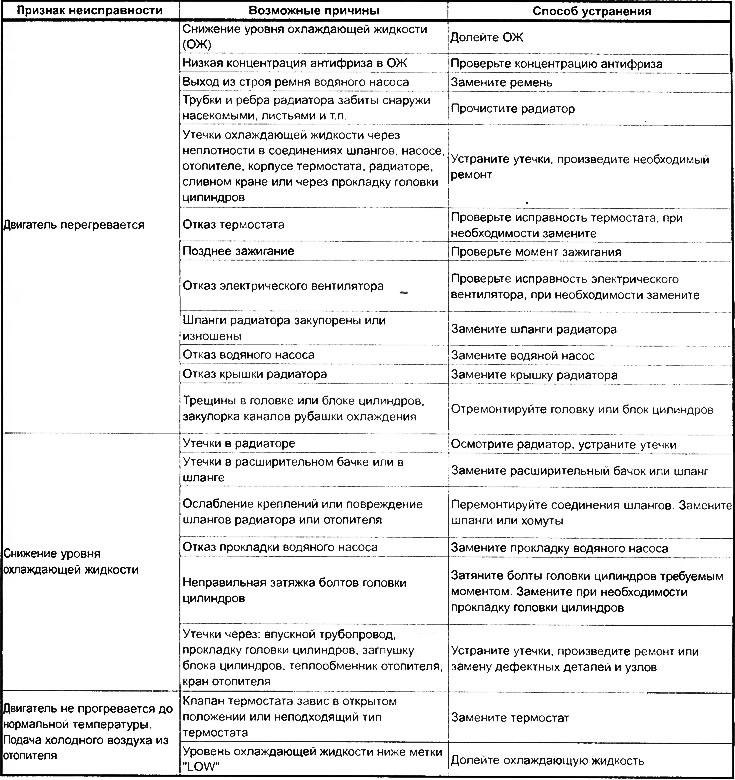
Typical malfunctions of the cooling system are leaks and insufficient engine cooling efficiency. The first is due to damage to the hoses and their connections, the liquid pump seal, damage to the gaskets, cracks, and the second is due to a malfunction of the fan, breakdowns of the water pump, malfunction of the thermostat, internal and external contamination of the radiator as a result of scale formation.
Signs of a malfunction in the cooling system are engine overheating and boiling of coolant in the radiator, if they are not the result of a long and heavy engine load or improper adjustment of the ignition or power system.
Thermostat Troubleshooting Algorithm
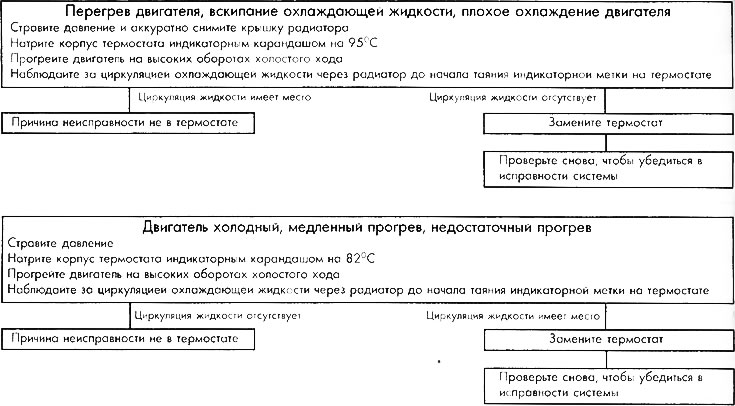
WARNING: An indicator stick is similar to a regular stick and contains a material with certain chemical additives that provide the desired melting point. By applying pencil marks at 82°C and 95°C to the thermostat housing, you can check the temperature at which the thermostat operates. These marks should melt when the coolant reaches 82°C and 95°C, respectively. These temperatures determine the operating range of the thermostat. Therefore, if the circulation does not occur as shown in the diagram, this means that the thermostat may be faulty.