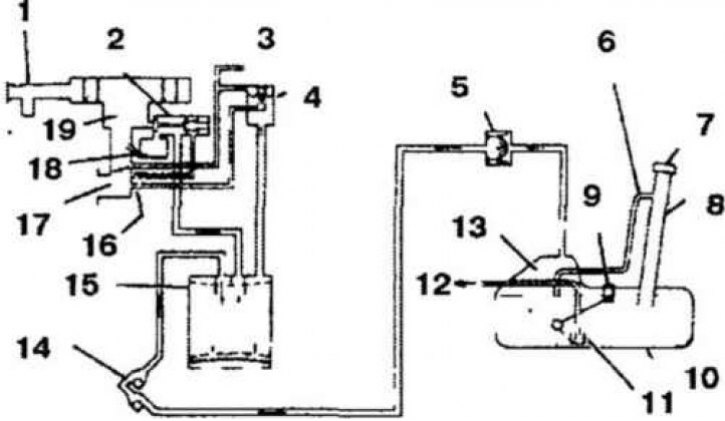
3.1a Elements of the fuel vapor collection system for models with a carburetor engine
1. Air filter; 2. Ventilation valve of the float chamber; 3. To the temperature valve; 4. Purge valve; 5. Safety valves; 6. Tube safety system; 7. Filler cap; 8. Tube of the gulf of fuel; 9. Fuel level sensor; 10. Fuel tank; 11. Filter; 12. Fuel (to the carburetor); 13. Additional volume for the expansion of fuel vapor when heated; 14. Control fuel valve; 15. Charcoal filter; 16. Hole; 17. Intake manifold; 18. Carburetor float chamber; 19. Carburetor
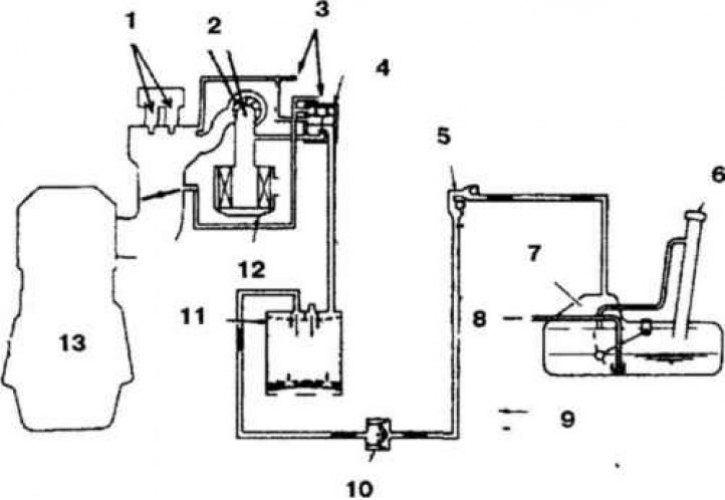
3.1b Elements of the fuel vapor collection system for models with two-point fuel injection (TBI)
1. Injector; 2. Air intake hose; 3. To the temperature valve; 4. Purge valve; 5. Control fuel valve; 6. Fuel filler cap; 7. Additional volume for the expansion of fuel vapors when heated; 8. To the carburetor; 9. Fuel vapor Air; 10. Safety valves; 11. Charcoal filter; 12. Air filter; 13. Engine
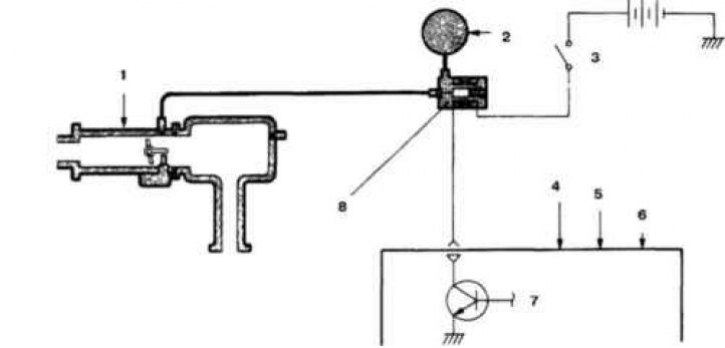
3.1c Elements of the fuel vapor collection system for models with multipoint fuel injection and an engine capacity of 1.5 liters
1. Throttle body; 2. Charcoal filter; 3. Control relay; 4. Inlet air temperature sensor; 5. Coolant temperature sensor; 6. Air flow sensor; 7. Electronic engine control unit; 8. Purge solenoid valve
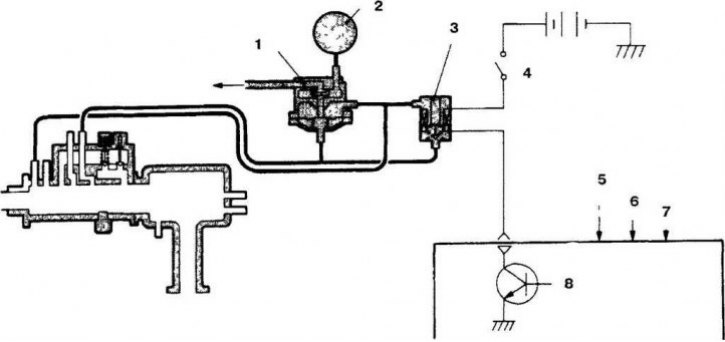
3.1g Elements of the fuel vapor collection system for models with multipoint fuel injection and an engine capacity of 1.5 liters
1. Purge valve; 2. Charcoal filter; 3. Purge solenoid; 4. Control relay; 5. Inlet air temperature sensor; 6. Coolant temperature sensor; 7. Air flow sensor; 8. Electronic engine control unit
1. The system serves to prevent fuel vapors from entering the atmosphere and consists of a carbon filter, a float chamber vent valve, a purge system, a safety system, a temperature valve, a fuel control valve and a special fuel tank filler cap (3.1a, 3.1b, 3.1c and 3.1d).
Carbon filter
2. When the engine is not running, fuel vapors from the fuel tank and carburetor float chamber are collected in the carbon filter. When the engine is running, they are released into the intake manifold.
Float chamber vent valve (models with carburetor engine)
3. The vent valve controls the flow of fuel vapor into the carbon filter. When the engine is running, the valve is closed, and when the engine is off, the valve is open and fuel vapors are collected in the carbon filter.
Purge system
4. The purge system is closed when the engine is idling to prevent fuel vapor from entering the intake manifold. When the engine speed increases, the purge valve opens.
Temperature valve
5. The temperature valve monitors the temperature of the coolant and controls the operation of the purge system, which reduces the level of CO and HC in the exhaust gases when the engine warms up.
Fuel filler cap
6. A vacuum valve is installed in the cover, which prevents the release of fuel vapors into the atmosphere.
Safety system
7. The system consists of two valves:
- A) A pressure valve that opens when the internal pressure in the fuel tank exceeds normal pressure.
- b) A vacuum valve that opens when the internal pressure in the fuel tank is below normal levels.
Fuel control valve
8. The valve prevents fuel leakage in the event of a vehicle overturn. The valve has two balls. When the car rolls over, one of the balls closes the fuel passage, preventing fuel from leaking.
